Un evento breve resuelto inexplicable se define como un evento reportado, repentino y breve (< 1 minuto) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un niño < 1 año de edad, que se resuelve en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el momento de la presentación. La definición incluye ≥ 1 hallazgo de cambio de color (cianosis o palidez), patrón respiratorio (ausente, disminuido o irregular), tono muscular (hipertonía o hipotonía) o nivel de conciencia. Los LOS Neisseria resultados se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el informe de un padre o cuidador. Adoptado por la American Academy of Pediatrics en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2016, el nuevo término va VA Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing a sustituir a los LOS Neisseria anteriormente utilizados “evento aparentemente mortal” y “síndrome de muerte casi súbita del lactante”. El cambio de terminología tiene como objetivo definir mejor un evento inexplicable después de una evaluación exhaustiva, estratificar los LOS Neisseria grupos de alto y bajo riesgo, identificar a los LOS Neisseria que necesitan una evaluación adicional y evitar pruebas e ingresos innecesarios. Es importante destacar que el evento breve resuelto inexplicable solo puede diagnosticarse si no hay ninguna otra explicación para el episodio tras una toma de antecedentes clínicos y una exploración física cuidadosa.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
Un evento breve resuelto inexplicable se define como un cambio repentino e inexplicable en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la respiración, la apariencia o el comportamiento de un bebé que fue breve (< 1 minuto, con una media de 20–30 segundos) y que se resuelve por completo.
Un “evento aparentemente mortal” ya no es actual, pero se definía como:
El evento breve resuelto inexplicable especifica que “no hay otra explicación en una toma de antecedentes y una exploración física completas” y elimina “el atragantamiento o las arcadas”.
Por definición, no existe una explicación o causa para el evento breve resuelto inexplicable, pero es necesario identificar las causas comunes e importantes de no evento breve resuelto inexplicable.
Condiciones comunes que conducen a un evento y excluyen un evento breve resuelto inexplicable:
Condiciones menos comunes que conducen a un evento y excluyen un evento breve resuelto inexplicable:
El evento breve resuelto inexplicable es “inexplicable”, por lo que se desconoce el mecanismo que produce el evento. Sin embargo, los LOS Neisseria hallazgos bien definidos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria lactantes ayudan a determinar si un evento tiene una patología subyacente.
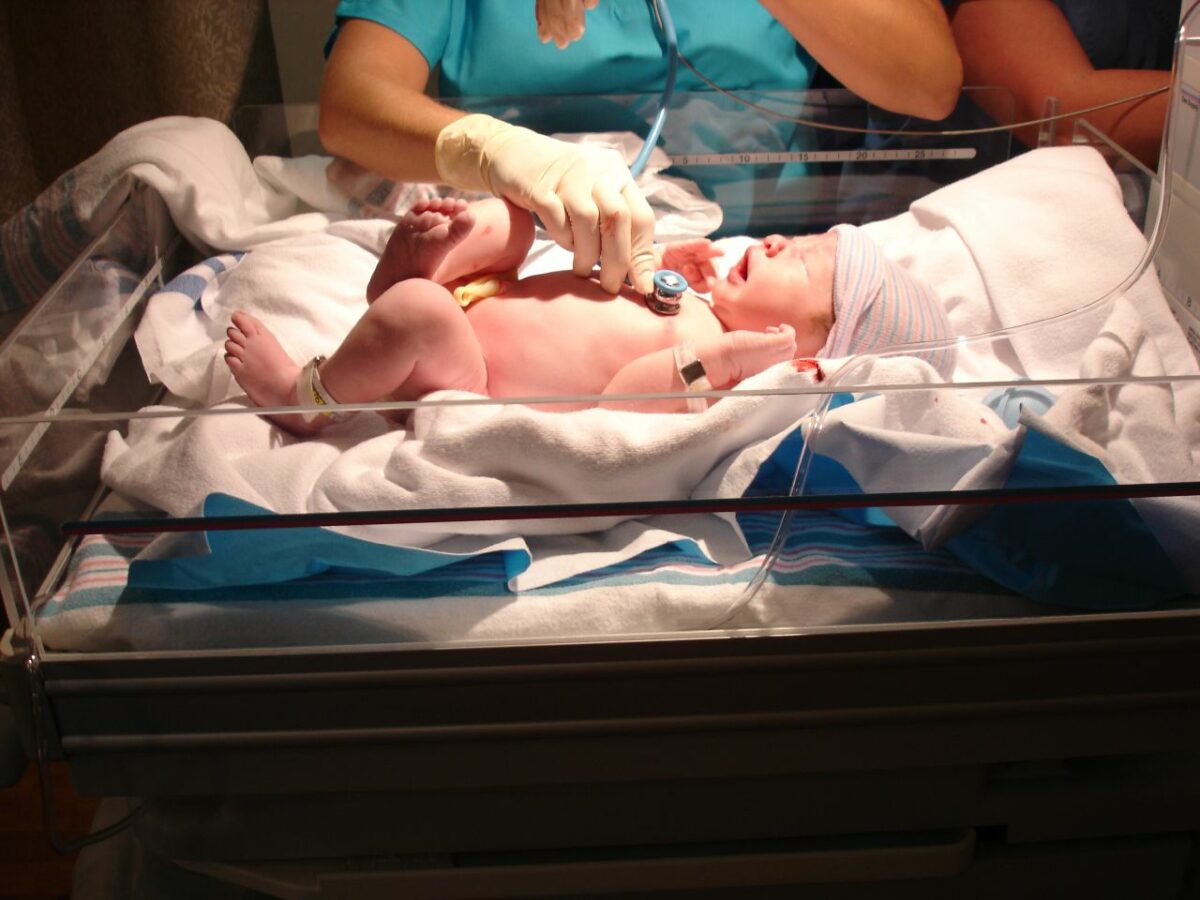
Bebé normal en la exploración:
La frecuencia respiratoria es de 30–60/min; se observan patrones respiratorios periódicos en los bebés a término y en los prematuros tardíos. La piel es normalmente rosada (lo que indica una oxigenación adecuada), las extremidades superiores e inferiores tienen un tono flexor y el bebé se despierta al ser estimulado.
Respiración normal de un bebé a término:
La apnea (pausa de > 20 segundos) puede ser el resultado de:
Tono infantil normal:
Hipotonía (disminución del tono muscular):
Hipertonía (aumento del tono muscular):
Comprobar la respuesta normal a las maniobras de excitación (estimulación táctil) y a los LOS Neisseria estímulos nocivos (roce del esternón).
Las descripciones de los LOS Neisseria hechos y de la historia apuntan a otras explicaciones del suceso:
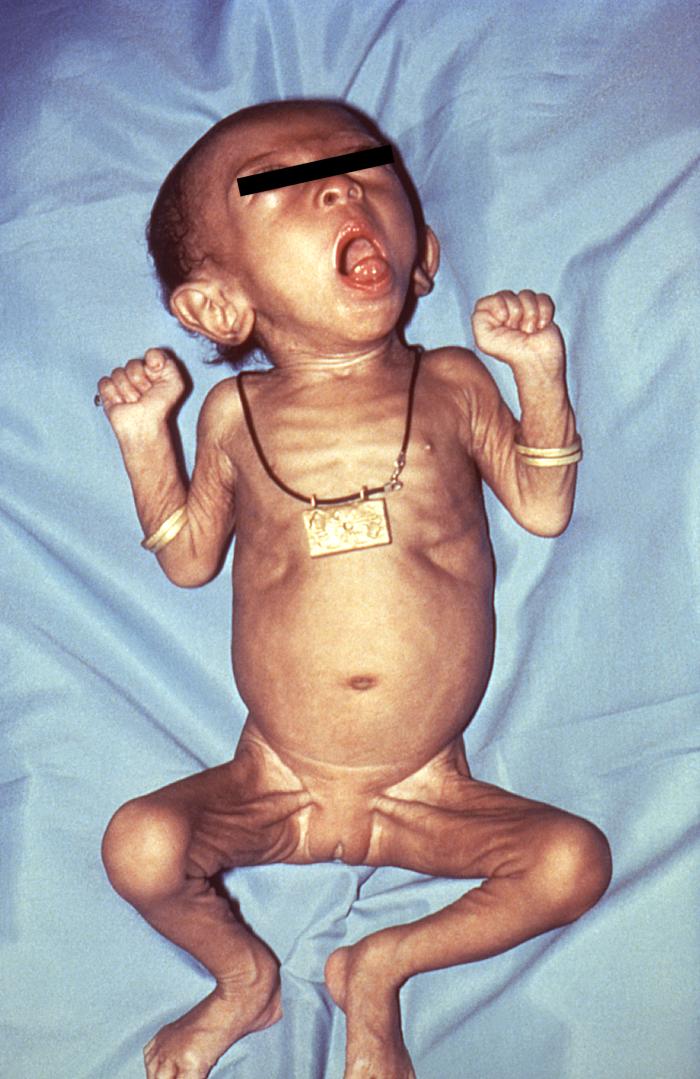
Un lactante con tosferina:
La presentación de la infección es atípica y puede incluir abultamiento de los ojos, cianosis, retracciones subcostales/intercostales, náuseas y apnea.
El evento breve resuelto inexplicable se diagnostica cuando no hay otra explicación para el evento. Por lo tanto, un antecedente clínico y un examen físico exhaustivo son fundamentales.
Los LOS Neisseria bebés se estratifican como de bajo riesgo (necesitan poca evaluación) o de alto riesgo (pueden necesitar más evaluación, seguimiento y observación).
Criterios:
Tratamiento conservador
Lactantes de alto riesgo (no cumplen los LOS Neisseria criterios de bajo riesgo):