La esferocitosis hereditaria es el tipo más común de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica hereditaria. La afección está causada por una deficiencia proteica del citoesqueleto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos. Esto da lugar a la pérdida de estabilidad de la membrana y a la deformabilidad de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos, dando a la célula su forma esférica (esferocito). Estas células son susceptibles de degradación esplénica, lo que conduce a la hemólisis. El examen físico puede mostrar ictericia y esplenomegalia, mientras que las pruebas de laboratorio son consistentes con anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica y aumento de la concentración de hemoglobina. Entre las múltiples pruebas de confirmación de la esferocitosis hereditaria, se prefiere la prueba de unión a eosina-5'-maleimida. El único tratamiento definitivo de la esferocitosis hereditaria es la esplenectomía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la esferocitosis hereditaria, las mutaciones genéticas conducen a la deficiencia de las proteínas del citoesqueleto:
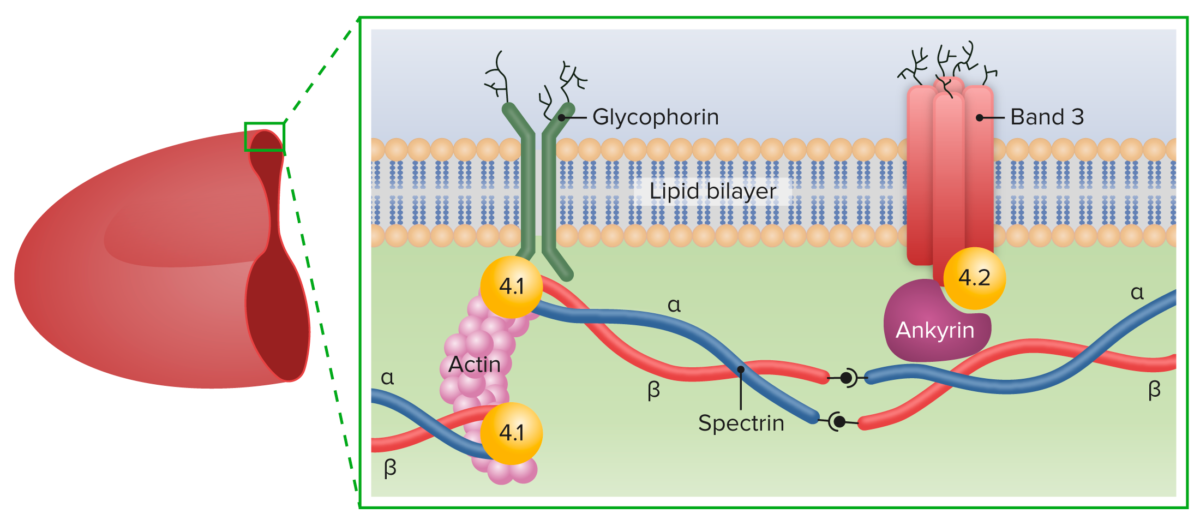
Principales proteínas de la membrana de los eritrocitos
Imagen por Lecturio.Se han establecido cuatro categorías clínicas basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hemoglobina ( Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange), el recuento de reticulocitos y el nivel de bilirrubina.
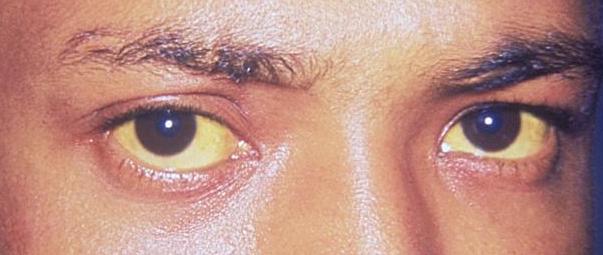
Ictericia escleral: El 1er signo clínico de depósito de bilirrubina en el organismo
Imagen: “Jaundice eye new” por CDC/Dr. Thomas F. Sellers/Emory University. Licencia: Dominio Público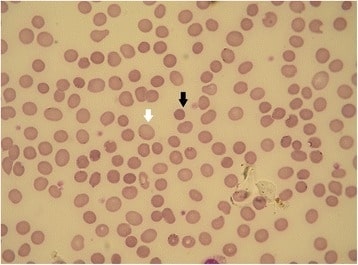
Esferocitosis hereditaria: frotis de sangre periférica
La flecha negra muestra un esferocito. La flecha blanca muestra un eritrocito normal (la falta de palidez central es un artefacto). Las formas de esferocitosis hereditaria que tienen diferentes defectos de membrana pueden mostrar diferentes morfologías de los eritrocitos.
El diagnóstico diferencial incluye otras causas de hemólisis, la mayoría de las cuales mostrarán al AL Amyloidosis menos algunos esferocitos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre periférica.