La esclerosis tuberosa o complejo de esclerosis tuberosa es un trastorno autosómico dominante con síntomas principalmente neurocutáneos. La mutación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure del complejo de esclerosis tuberosa provoca crecimientos excesivos similares a tumores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cerebro, ojos, corazón, riñones y pulmones. Las manifestaciones cutáneas incluyen hipopigmentación (i.e., manchas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hojas de fresno, lesiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum confeti) o crecimiento excesivo (i.e., angiofibroma Angiofibroma A benign neoplasm of fibrous tissue in which there are numerous small and large, frequently dilated, vascular channels. Tuberous Sclerosis, parche de Shagreen). El diagnóstico se realiza ante la sospecha clínica y se confirma mediante pruebas genéticas. El tratamiento implica un enfoque multidisciplinario que se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la monitorización y tratamiento de las diversas manifestaciones del trastorno. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del mTOR mTOR Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome, como sirolimus Sirolimus A macrolide compound obtained from streptomyces hygroscopicus that acts by selectively blocking the transcriptional activation of cytokines thereby inhibiting cytokine production. It is bioactive only when bound to immunophilins. Sirolimus is a potent immunosuppressant and possesses both antifungal and antineoplastic properties. Immunosuppressants y everolimus Everolimus A derivative of sirolimus and an inhibitor of tor serine-threonine kinases. It is used to prevent graft rejection in heart and kidney transplant patients by blocking cell proliferation signals. It is also an antineoplastic agent. Immunosuppressants, se utilizan para tratar las manifestaciones graves.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
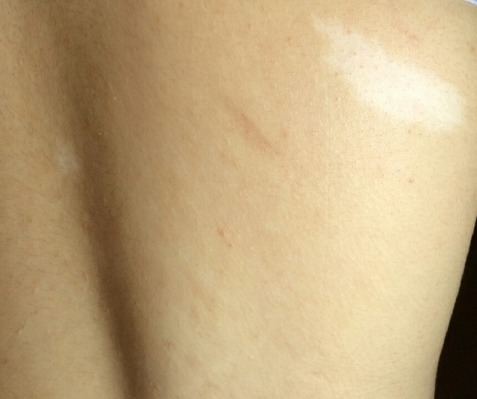
Mácula hipopigmentada (mancha en hoja de fresno)
Imagen: “Hypomelanotic lesions (ash leaf spot) on skin” por Falsafi P, Taghavi-Zenouz A, Khorshidi-Khiyavi R, Nezami N, Estiar MA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0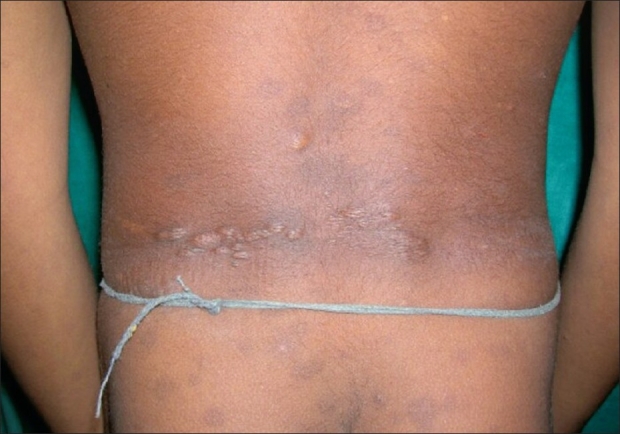
Parche de Shagreen observado en la parte inferior de la espalda
Imagen: “Shagreen patches on the back in a child” por Ghosh SK, Bandyopadhyay D, Chatterjee G, Ghosh A, Sarkar S, Sarkar S. Licencia: CC BY 2.0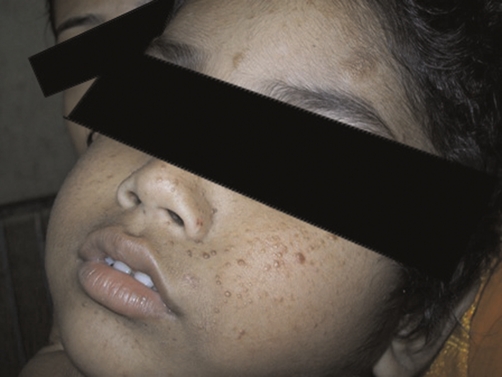
Angiofibroma
Imagen: “Shows the characteristics skin lesions on the face” por Datta AK, Mandal S, Bhattacharya S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0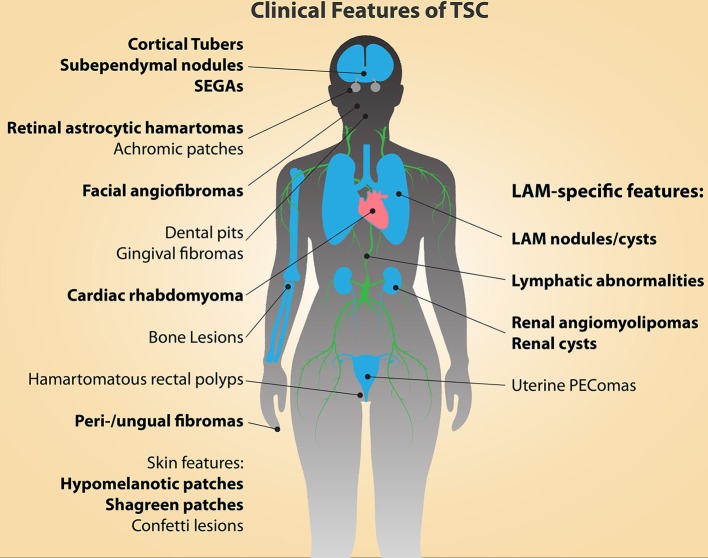
Principales características diagnósticas del complejo de esclerosis tuberosa (TSC; indicadas en negritas)
LAM: linfangioleiomiomatosis
PEComa: tumor que muestra diferenciación de células epitelioides perivasculares
SEGA: astrocitoma subependimario de células gigantes
Ninguna presentación clínica única del complejo de esclerosis tuberosa se considera diagnóstica.
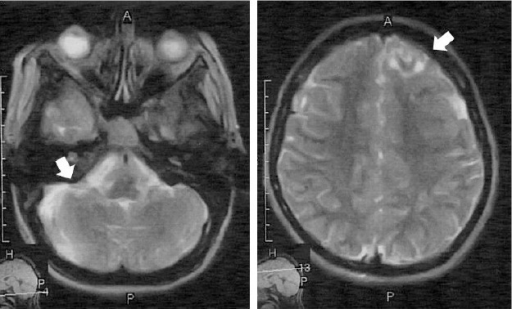
La resonancia magnética muestra los tubérculos corticales y subcorticales
Image: “F5” by Parisa Falsafi et al. License: CC BY 3.0