La enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante es un proceso inflamatorio intestinal que puede provocar lesiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mucosa y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage. La enfermedad es multifactorial, con factores de riesgo subyacentes que incluyen la prematuridad y la alimentación con fórmula. La presentación clínica varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gravedad desde la intolerancia a la alimentación, los LOS Neisseria hallazgos agudos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen abdominal y los LOS Neisseria síntomas sistémicos. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una sospecha clínica, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum radiografías abdominales anormales y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum resultados de laboratorio anormales. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuidados médicos de soporte para los LOS Neisseria estadios más leves y reposo intestinal e intervención quirúrgica para los LOS Neisseria estadios más avanzados. La enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante y sus complicaciones conllevan un alto riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante es una enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal asociada a la ulceración y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage focal o difusa que afecta principalmente al AL Amyloidosis íleon terminal y al AL Amyloidosis colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy.
El diagnóstico de la enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante se realiza principalmente por medio de imagenología.
La radiografía abdominal es el método de elección para establecer el diagnóstico de enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante.
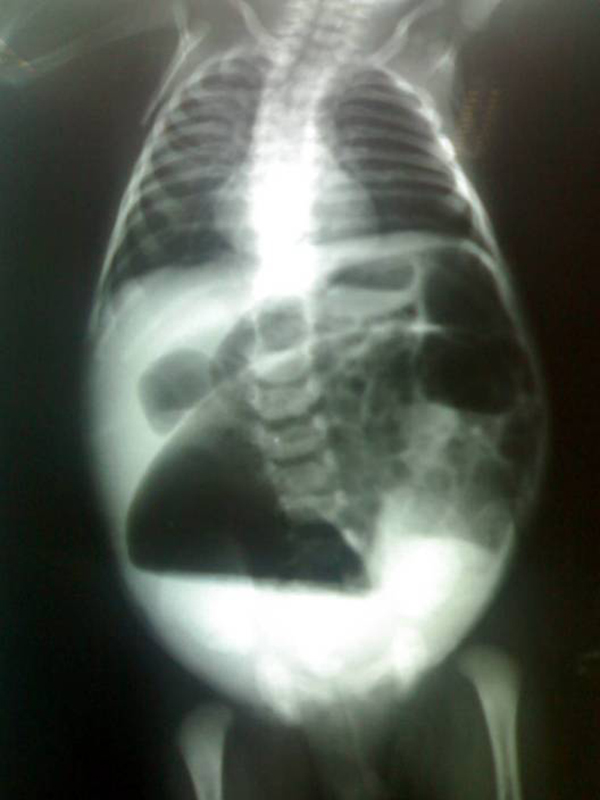
Asas intestinales dilatadas en una radiografía abdominal en un paciente con enterocolitis necrosante
Imagen: “A report of a rare congenital malformation in a Nepalese child with congenital pouch colon: a case report” por Shakya VC, Agrawal CS, Koirala R, Khaniya S, Poudel P, Adhikary S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0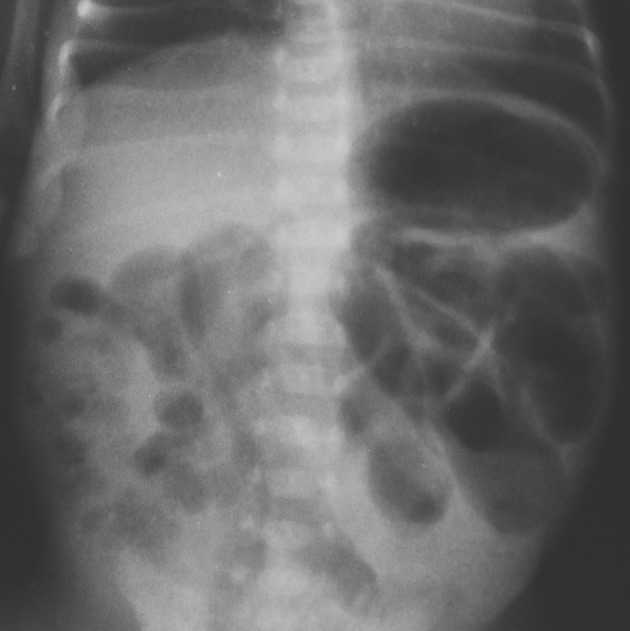
Radiografía abdominal de enterocolitis necrosante:
Esta imagen muestra una distensión intestinal difusa, gaseosa, con signos discretos de sospecha de neumatosis en el cuadrante inferior derecho.
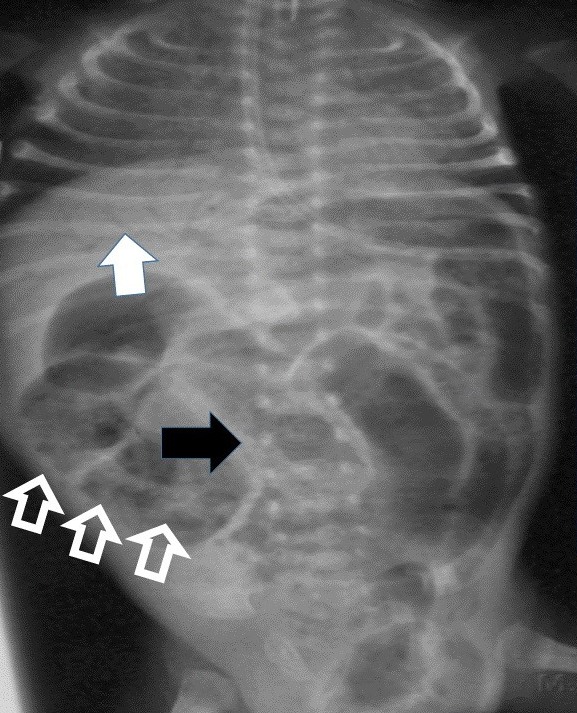
Radiografía de un paciente con enterocolitis necrosante:
La neumatosis intestinal aparece como una lucencia lineal (flecha negra) y como un aspecto “espumoso” sobre el intestino (flechas huecas). La flecha blanca indica la lucencia debida al gas venoso portal.
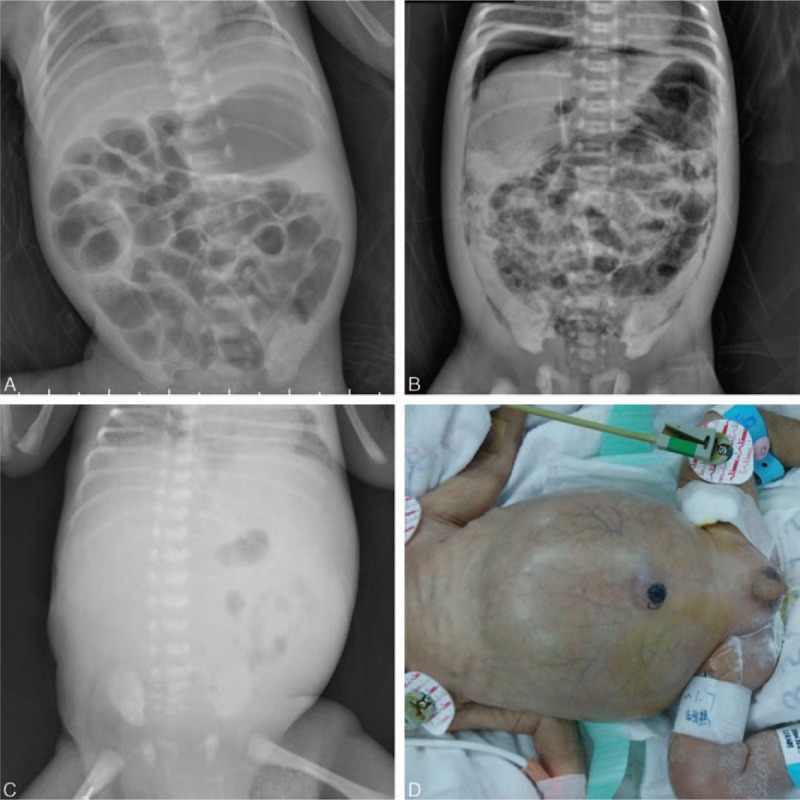
Hallazgos radiográficos de la enterocolitis necrosante:
A: Gas venoso portal y neumatosis intestinal
B: Neumoperitoneo (aire por debajo de ambos diafragmas) y neumatosis intestinal
C: Abdomen sin gas
D: Un bebé con abdomen distendido y eritema periumbilical
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes estudios son inespecíficos, pero pueden apoyar el diagnóstico y demostrar la gravedad de la enfermedad.
La siguiente tabla proporciona los LOS Neisseria criterios de estadificación utilizados para el reconocimiento de la enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante y evaluar su gravedad.
| Estadio | Clasificación | Signos clínicos | Signos radiológicos |
|---|---|---|---|
| IA | Sospecha de enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante |
|
Dilatación intestinal normal o leve |
| IB | Además de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos anteriores: hematoquecia | ||
| IIA |
|
Además de las conclusiones anteriores:
|
|
| IIB |
|
Además de las conclusiones anteriores:
|
Además de las conclusiones anteriores:
|
| IIIA |
|
Además de las conclusiones anteriores:
|
Además de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos anteriores: ascitis |
| IIIB |
|
Además de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos anteriores: neumoperitoneo |
Es necesario un tratamiento temprano y agresivo.
Tratamiento médico:
Intervención quirúrgica: