La enfermedad de Ménière es una afección caracterizada por episodios de vértigo, tinnitus Tinnitus A nonspecific symptom of hearing disorder characterized by the sensation of buzzing, ringing, clicking, pulsations, and other noises in the ear. Objective tinnitus refers to noises generated from within the ear or adjacent structures that can be heard by other individuals. The term subjective tinnitus is used when the sound is audible only to the affected individual. Tinnitus may occur as a manifestation of cochlear diseases; vestibulocochlear nerve diseases; intracranial hypertension; craniocerebral trauma; and other conditions. Cranial Nerve Palsies y pérdida de la audición, probablemente causados por hidropesía endolinfática del sistema laberíntico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el oído interno. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo incluyen antecedentes familiares de la enfermedad de Ménière, trastornos autoinmunes preexistentes, alergias y traumatismos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cabeza o el oído. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente, mediante audiometría, pruebas vestibulares y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones, mediante imagenología. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum modificación de la dieta y el estilo de vida, vasodilatadores, diuréticos, antihistamínicos, benzodiacepinas, antieméticos, glucocorticoides, intervención quirúrgica y/o auxiliares auditivos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad de Ménière es una tríada de vértigo episódico, tinnitus Tinnitus A nonspecific symptom of hearing disorder characterized by the sensation of buzzing, ringing, clicking, pulsations, and other noises in the ear. Objective tinnitus refers to noises generated from within the ear or adjacent structures that can be heard by other individuals. The term subjective tinnitus is used when the sound is audible only to the affected individual. Tinnitus may occur as a manifestation of cochlear diseases; vestibulocochlear nerve diseases; intracranial hypertension; craniocerebral trauma; and other conditions. Cranial Nerve Palsies y pérdida auditiva probablemente causada por hidropesía endolinfática del sistema laberíntico del oído interno.
El síndrome de Ménière es la enfermedad de Ménière secundaria a otras infecciones del oído interno.
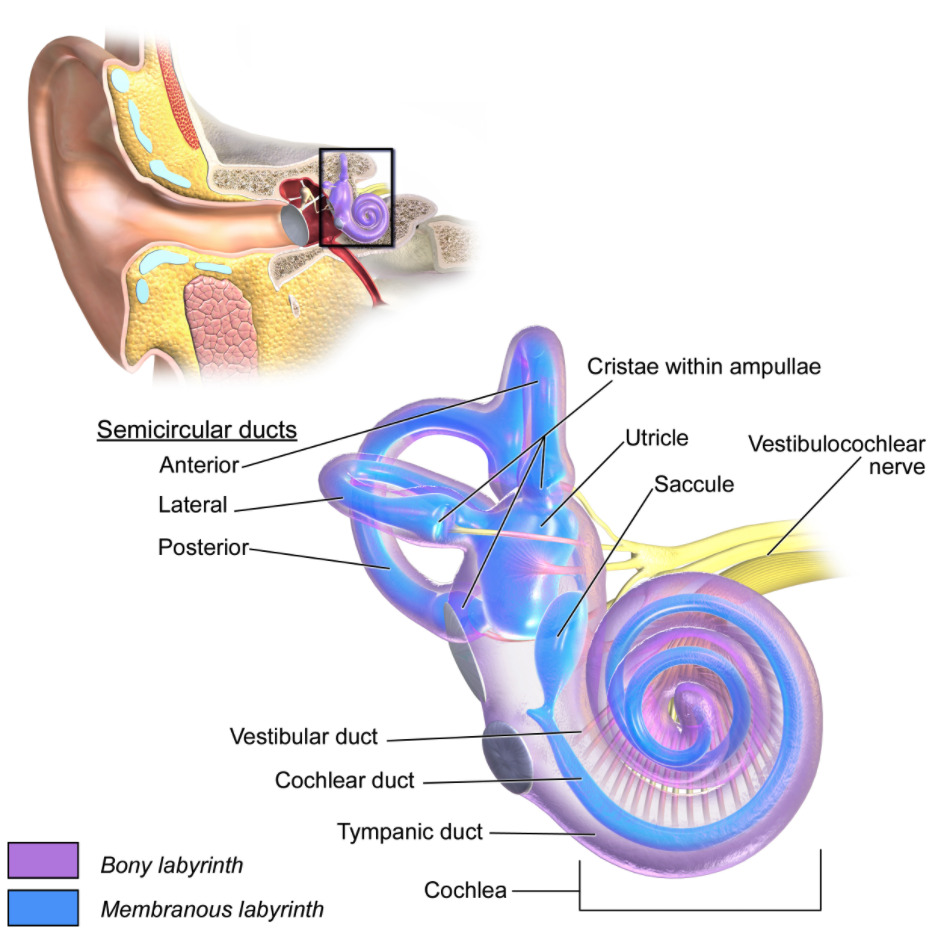
Anatomía del oído interno
Imagen: “El oído interno” por BruceBlaus. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Diagnóstico clínico realizado por la presencia de:
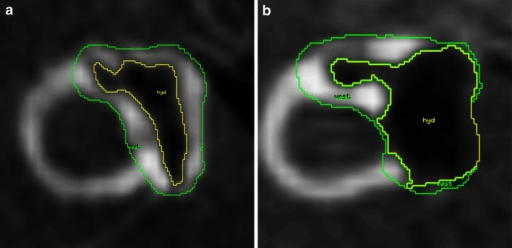
RM de la hidropesía endolinfática en pacientes con enfermedad de Ménière:
a: Hidropesía endolinfática correspondiente a leve
b: Hidropesía endolinfática correspondiente a significativa