El dolor Dolor Inflammation de tobillo representa hasta el 20% de los LOS Neisseria casos de dolencias musculoesqueléticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las consultas externas. Las etiologías más comunes del dolor Dolor Inflammation de pies y tobillos pueden clasificarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum artritis, traumatismos, esguinces y causas sistémicas. El diagnóstico es clínico con estudios de imagen y/o de laboratorio para confirmar la sospecha diagnóstica. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo, bolsas de hielo, compresión, elevación y antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE). La intervención quirúrgica rara vez es necesaria.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Epidemiología
El dolor Dolor Inflammation de pie es más frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum parte asociado con calzado de tacón alto o mal ajustado.
Clasificación
Historia clínica
Examen físico
Reglas de Ottawa para tobillos y pies:
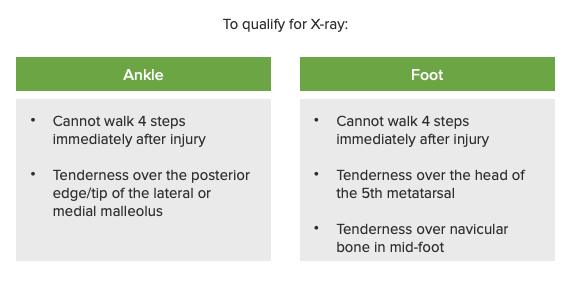
Normas de Ottawa para tobillos y pies
Imagen por Lecturio.La etiología del dolor Dolor Inflammation de tobillo o pie puede determinarse a partir de la localización anatómica del punto máximo de dolor Dolor Inflammation.
| Localización | Entidad | Características |
|---|---|---|
| Cara lateral | Esguince de tobillo ( dolor Dolor Inflammation agudo) |
|
| Cara medial |
|
|
| Cara posterior | Tendinitis Tendinitis Ankylosing Spondylitis de Aquiles ( dolor Dolor Inflammation agudo) |
|
| Ubicaciones variables | Trastornos infecciosos e inflamatorios |
|
| Localización | Entidad | Características |
|---|---|---|
| Antepié (dedos + metatarsos distales) | Juanetes (hallux valgus) |
|
| Uñas encarnadas |
|
|
| Neuroma de Morton |
|
|
| Callos y callosidades |
|
|
| Verrugas plantares |
|
|
| Fracturas metatarsales por estrés |
|
|
| Mediopié (huesos del tarso, arcos y ligamentos) | Osteoartritis |
|
| Pies elevados (pies cavos) y pies planos (pies planos) |
|
|
| Fractura navicular Navicular Foot: Anatomy por estrés |
|
|
| Retropié (astrágalo + calcáneo) | Fascitis plantar |
|
| Síndrome del túnel tarsiano |
|
|
| Fracturas de estrés del calcáneo y del astrágalo |
|
|
| Apofisitis calcánea (enfermedad de Sever) |
|
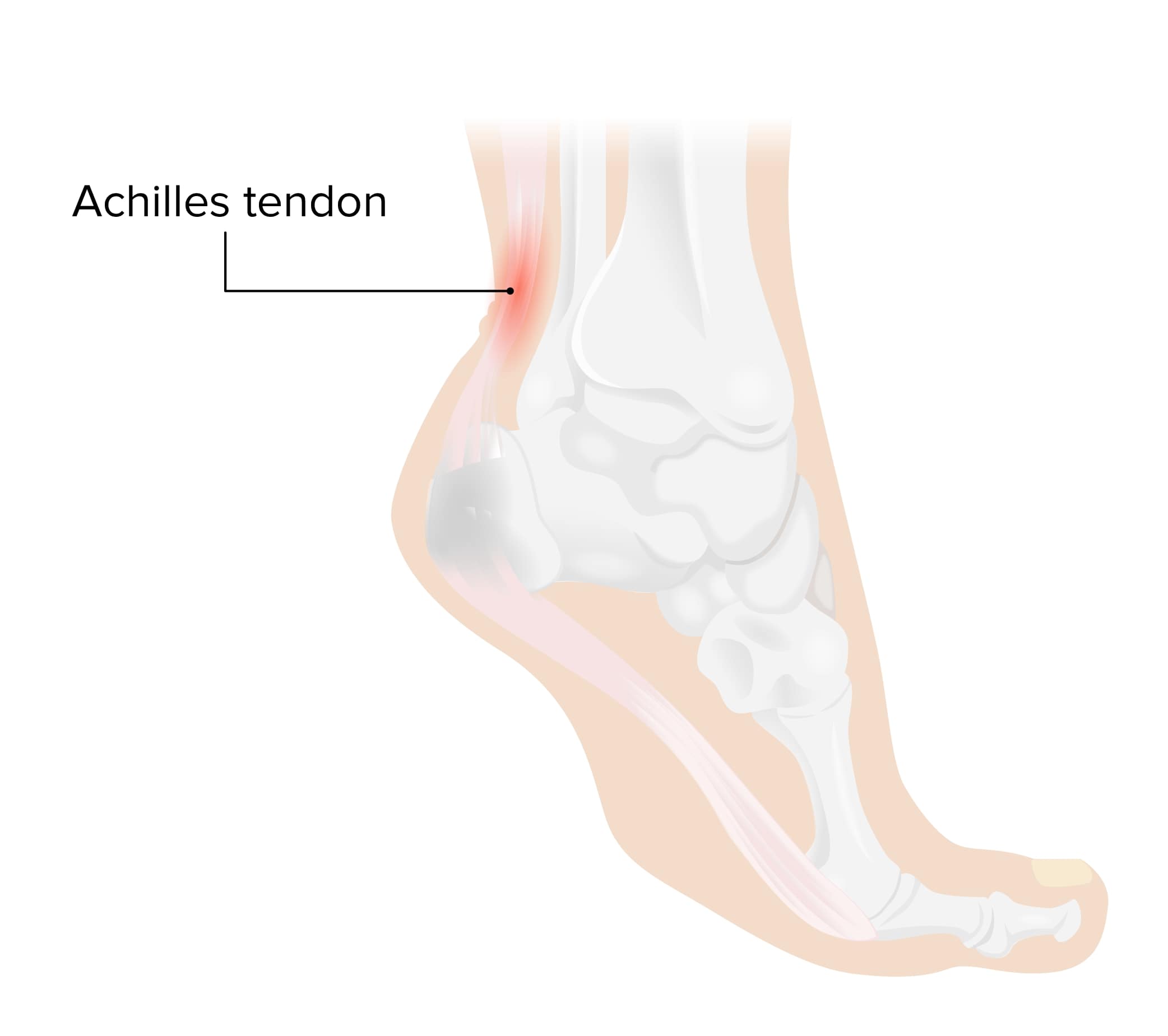
Tendinitis de Aquiles:
El tendón de Aquiles se encuentra en la parte posterior del tobillo y conecta los músculos de la pantorrilla con el hueso del talón. Este tendón es necesario para caminar, correr y saltar y soporta una gran tensión durante la vida diaria normal. La tendinitis de Aquiles se produce cuando los músculos y el tendón se utilizan en exceso, lo que provoca irritación e inflamación del tendón. Imagen de Lecturio.
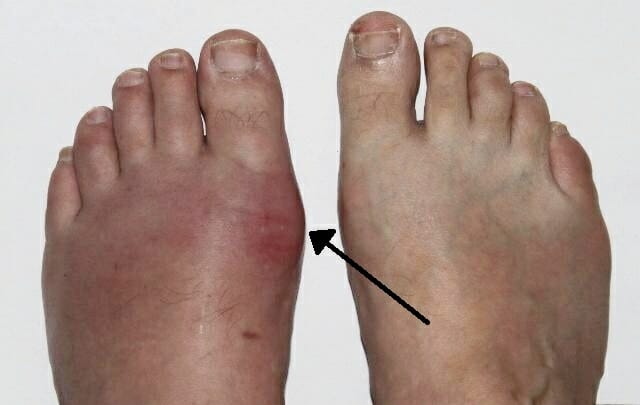
Eritema e inflamación de la 1ra articulación metatarsofalángica compatible con gota agudaith acute gout
Imagen: “Podagra” por Gonzosft. Licencia: CC BY 3.0 DE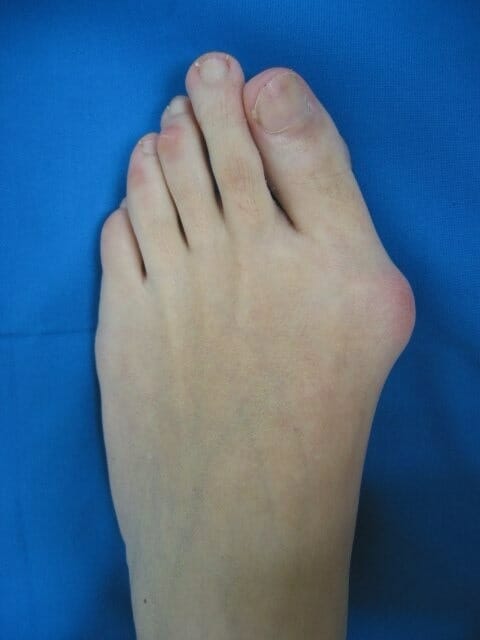
Deformación del hallux valgus:
La deformidad común y dolorosa se produce con la desviación lateral del hallux (el 1er dedo) sobre el 1er metatarsiano. El hallux valgus también puede asociarse a la eversión del dedo.
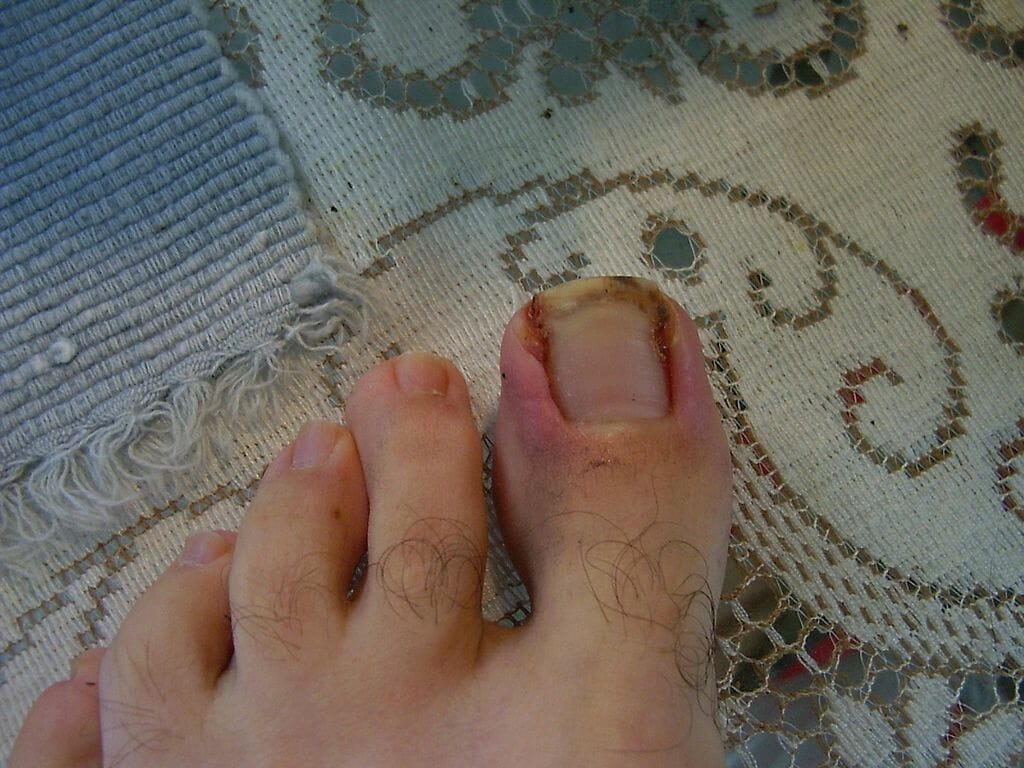
Uña encarnada del 1er dedo:
Las uñas encarnadas se desarrollan cuando una parte de la placa ungueal lateral perfora el pliegue ungueal lateral y la piel, provocando una reacción inflamatoria.
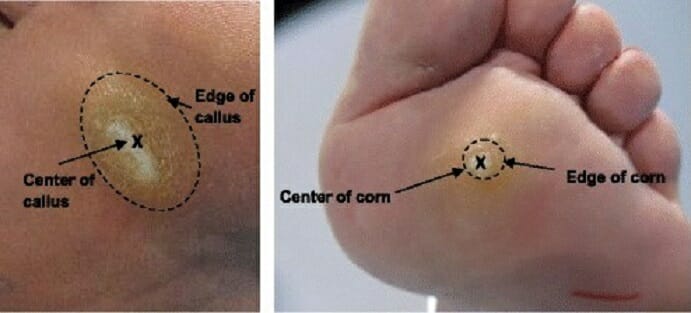
Puntos de referencia de una callosidad (izquierda) y un callo (derecha):
Las callosidades y los callos son algunas de las lesiones cutáneas más comunes de los pies y posibles fuentes de dolor en los mismos.
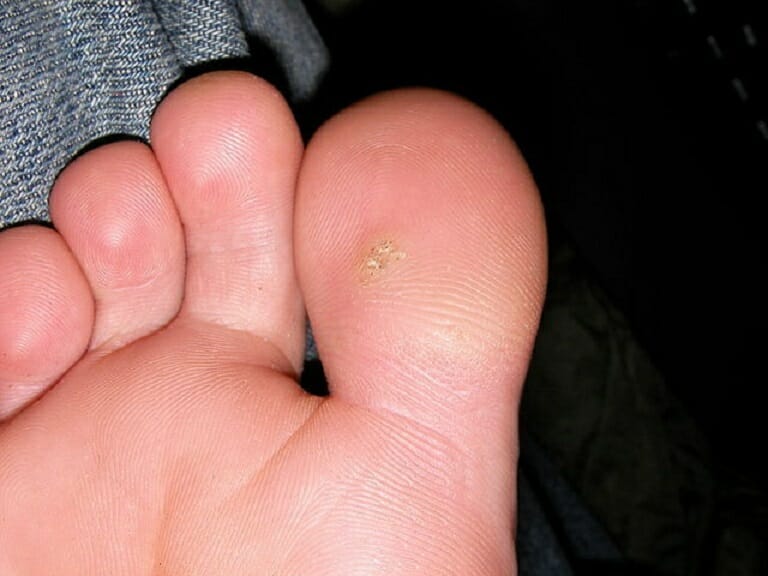
Verruga plantar en la parte inferior del dedo gordo del pie
Imagen: “Plantar wart on the bottom of the big toe (mine)” por Dewdude. Licencia: CC BY 2.5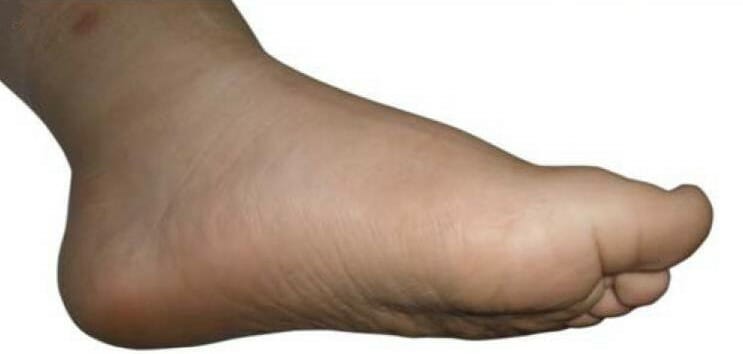
Pie plano
Imagen: “Pes planus typically seen in Alström syndrome” por Marshall J.D. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.5, editada por Lecturio.Estudio de diagnóstico:

Radiografías que demuestran una fractura por estrés del 5to metatarsiano (flechas):
a: vista anteroposterior (AP)
b: vista oblicua
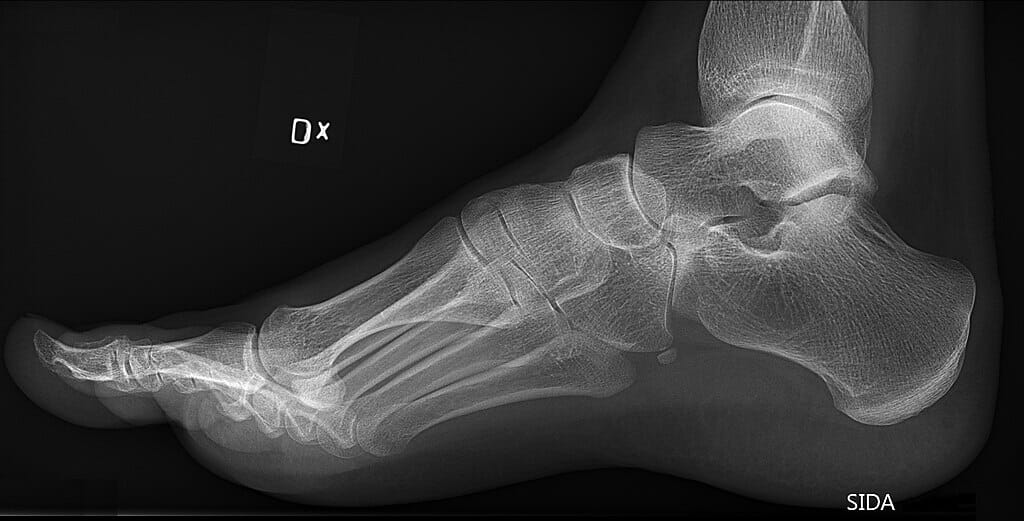
Radiografía de un pie con pie cavo (arco del pie alto)
Imagen: “Pes cavus and os peroneum on lateral foot X-ray” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0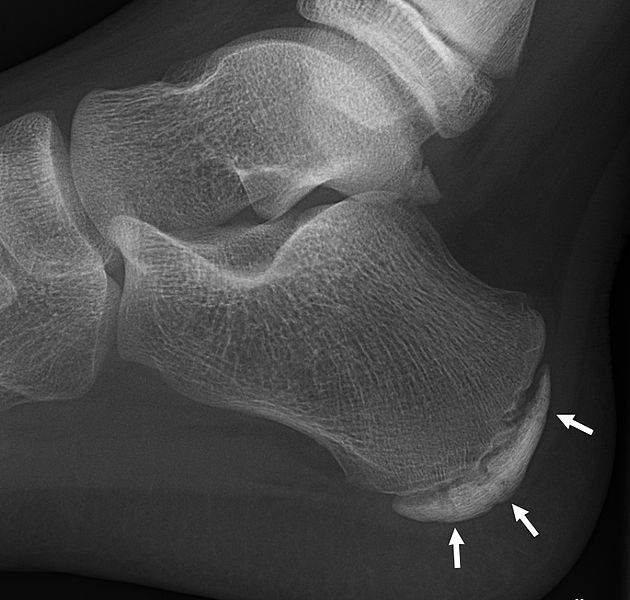
Radiografía del pie de un niño de 11 años, que muestra esclerosis y fragmentación de la apófisis del calcáneo. Sin embargo, las radiografías tienen poca sensibilidad y especificidad para la enfermedad de Sever, por lo que el diagnóstico suele hacerse clínicamente.
Imagen: “Sclerosis and fragmentation of the calcaneal apophysis” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0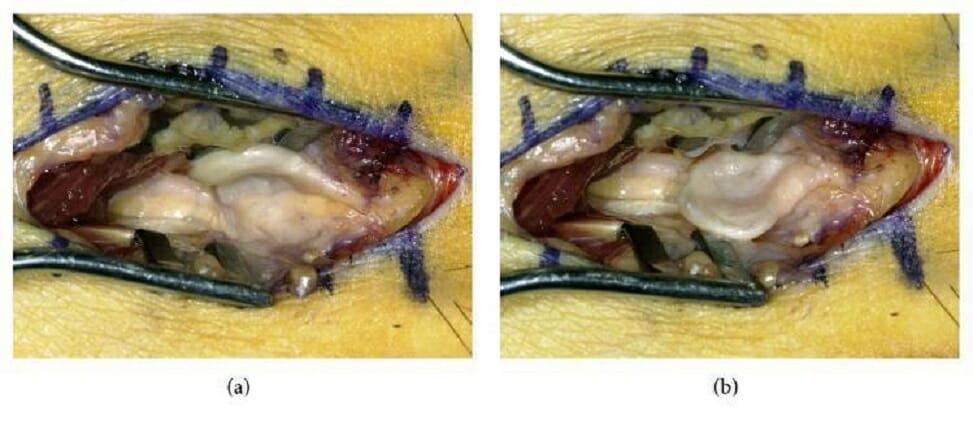
Fotografías intraoperatorias que muestran un neuroma de Morton (un neuroma interdigital del pie):
(a): Curso desviado en sentido dorsal del nervio interdigital y del neuroma
(b): Neuroma reclinado transversalmente mostrando la impresión en su centro (supuestamente realizada por las cabezas metatarsales adyacentes)
Las siguientes son afecciones comunes asociadas al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation de tobillos y pies: