El dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla es una presentación común para los LOS Neisseria médicos de atención primaria. El diagnóstico puede ser un desafío, ya que el dolor Dolor Inflammation puede surgir de la articulación, los LOS Neisseria tejidos circundantes o referirse a la articulación desde estructuras distantes. El diagnóstico diferencial del dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla es amplio y es útil categorizar los LOS Neisseria diversos diagnósticos relacionados con el momento (agudo o crónico). Un conocimiento profundo de la anatomía pertinente, examen físico apropiado y problemas frecuentes de la articulación de la rodilla son esenciales para el diagnóstico y el tratamiento adecuado del dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla. La terapia basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ejercicios es a menudo el tratamiento de primera línea de muchos trastornos de la rodilla, pero la intervención quirúrgica está justificada para diagnósticos específicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
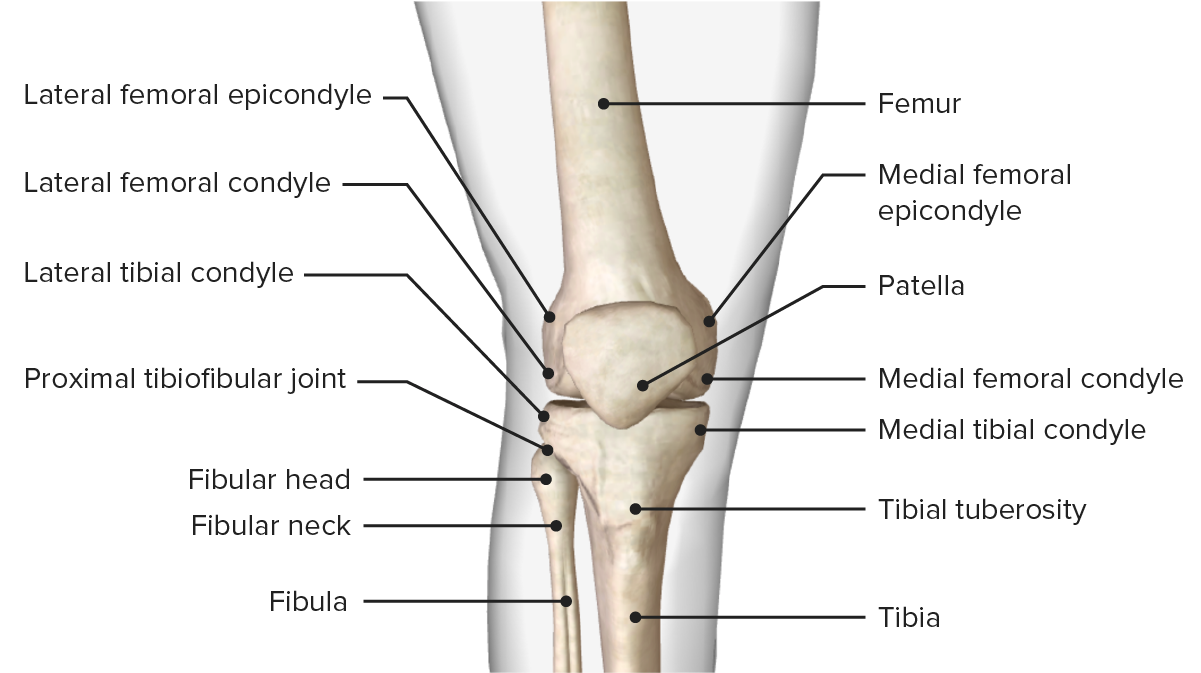
La estructura ósea de la articulación de la rodilla.
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio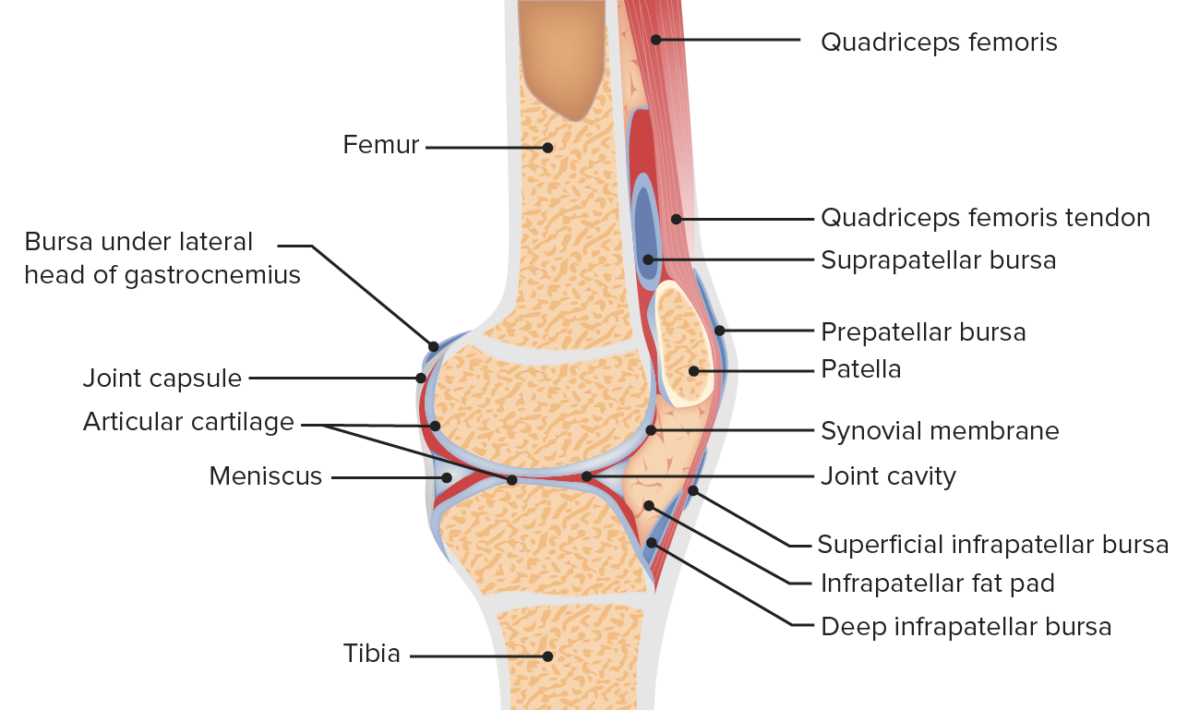
Vista sagital de la anatomía de la articulación femororrotuliana
Imagen por Lecturio.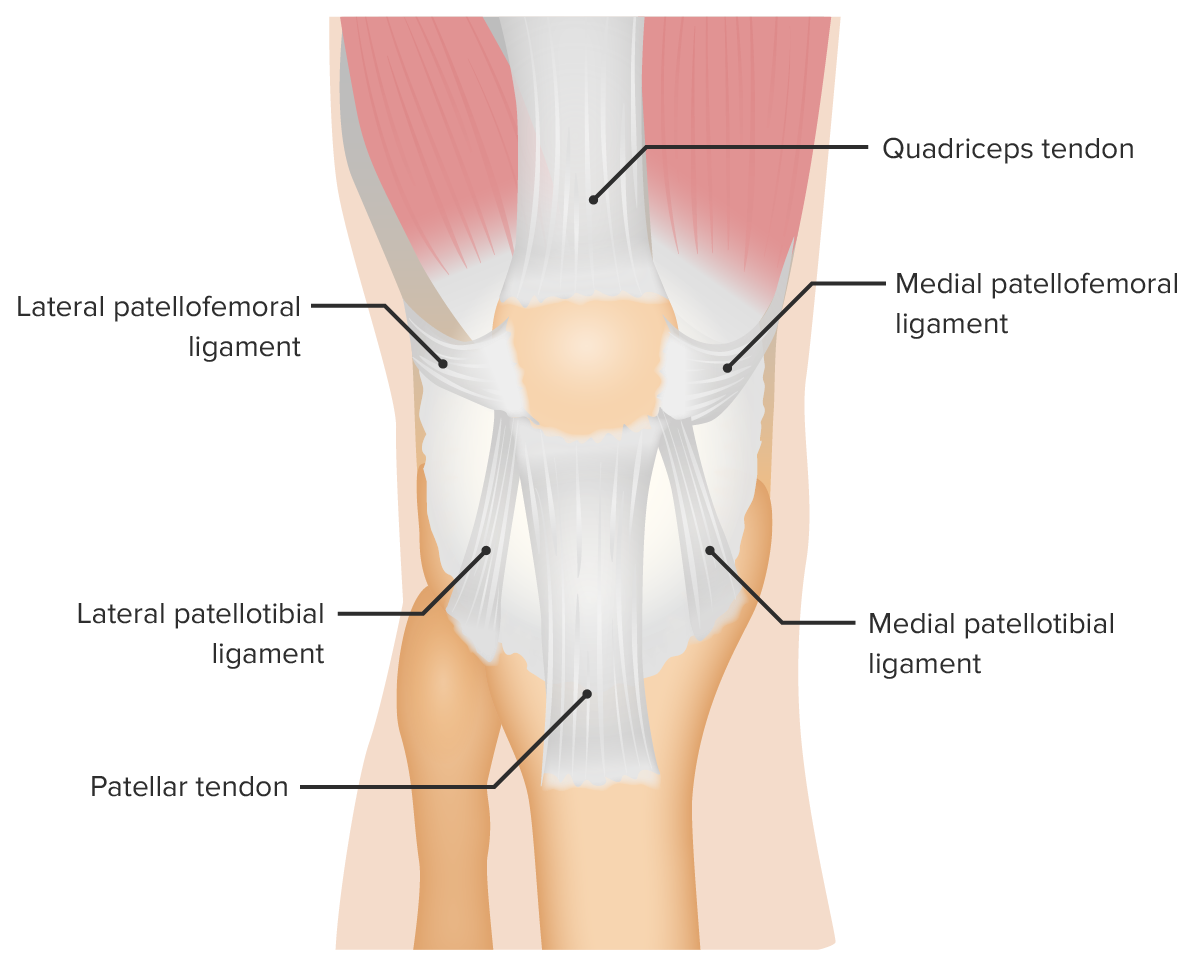
Vista anterior de los ligamentos de soporte de la articulación femororrotuliana
Imagen por Lecturio.Obtener una historia clara es fundamental para realizar el diagnóstico correcto y orientar la exploración:
El examen está dirigido por la duración y el tipo de lesión (aguda o crónica) y la edad del individuo. La comparación de la rodilla sana es importante:
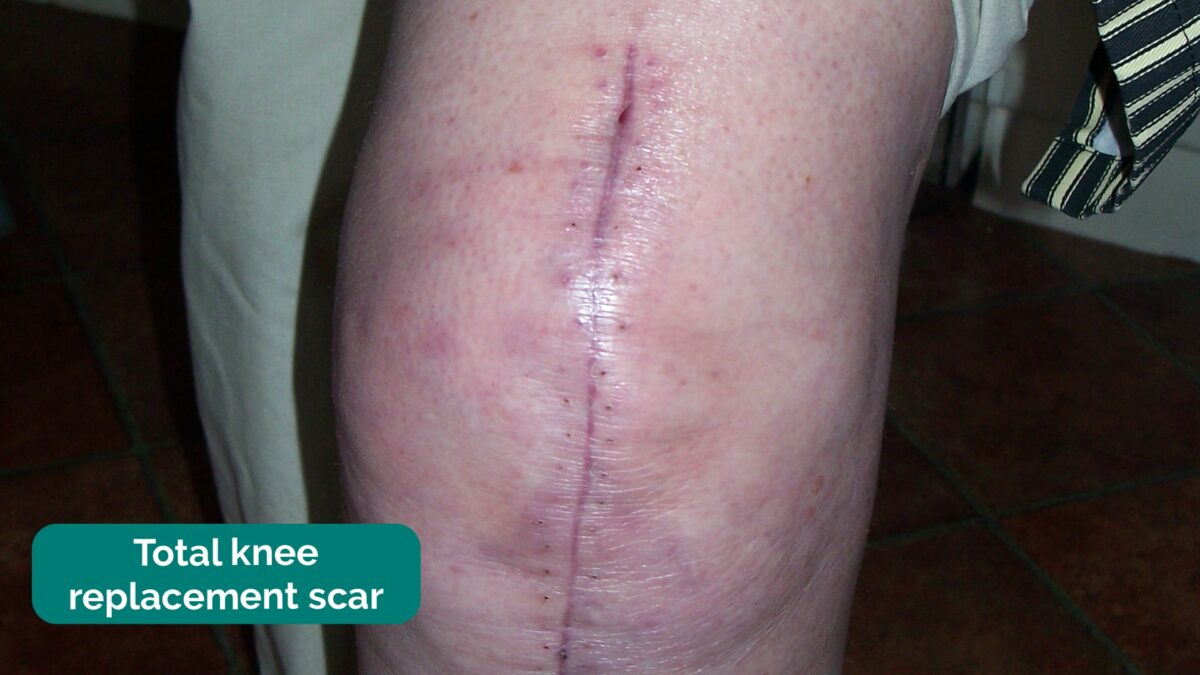
Cicatriz de artroplastia total de rodilla anotada en el examen del paciente
Imagen: “Total knee replacement scar” por Dave Haygarth; Geeky Medics. Licencia: CC BY 2.0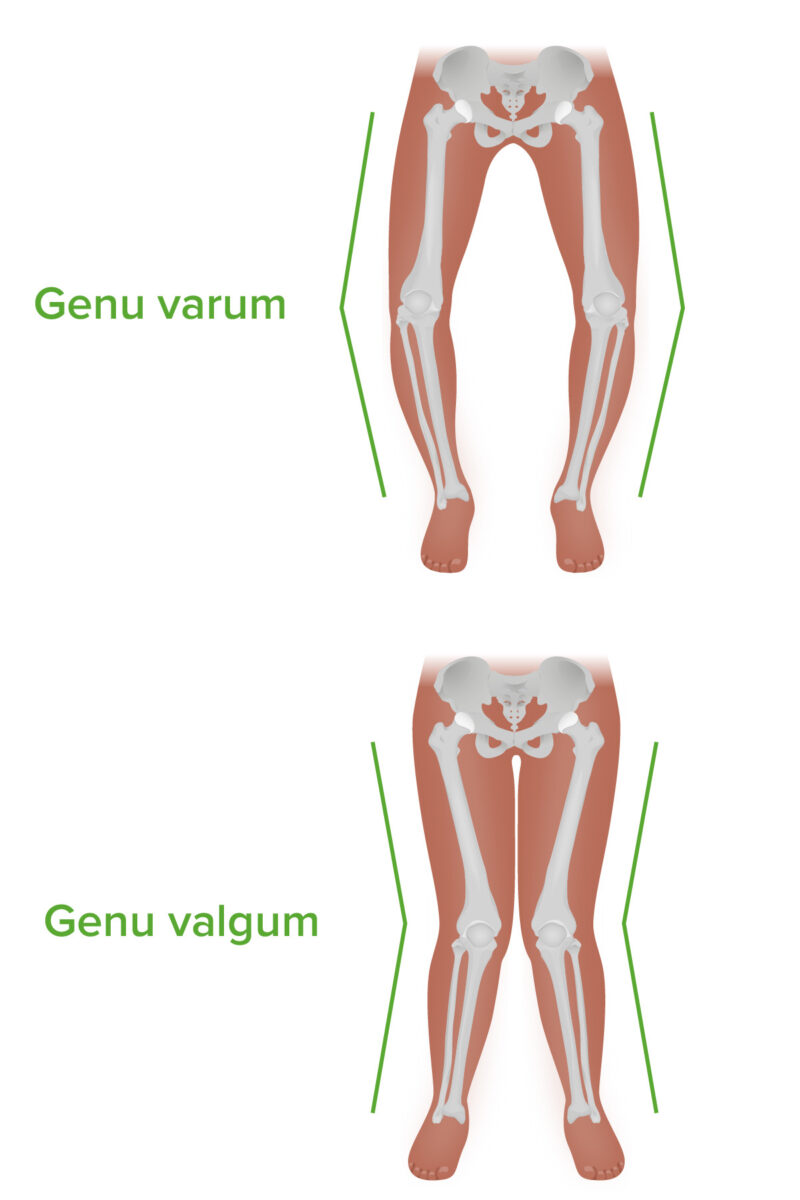
Genu varum y genu valgum: Nótese la diferencia de angulación en el plano coronal.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Lesión | Maniobra |
|---|---|
| Lesión del ligamento cruzado anterior (LCA) |
|
| Lesión de LCP |
|
| Lesión de LCM | Prueba de esfuerzo
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum valgo para la inestabilidad del LCM:
|
| Lesión de LCL | Prueba de esfuerzo
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum varo para inestabilidad del LCL:
|
| Desgarro meniscal |
|
| ITBS |
|
| PFPS |
|
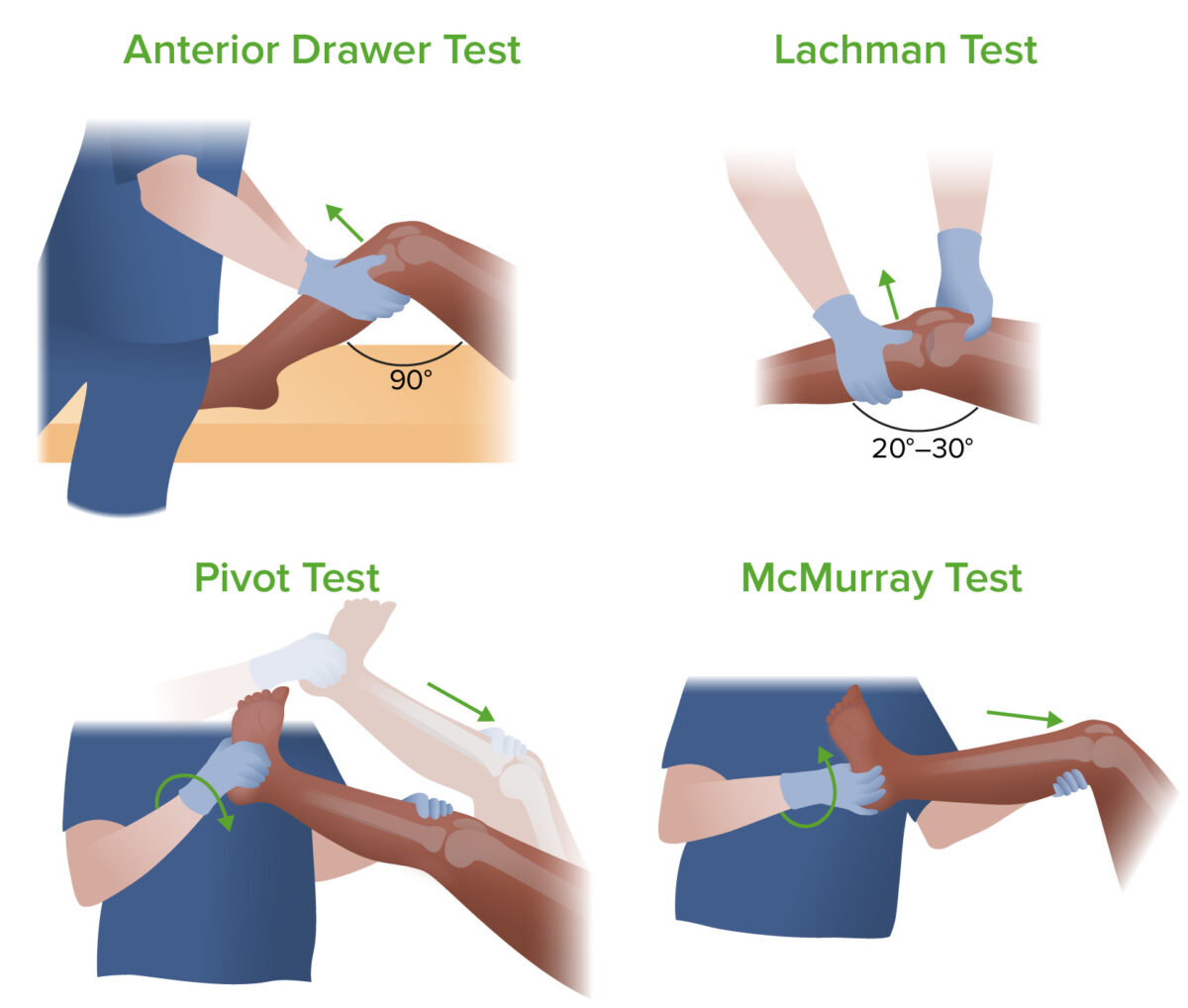
Cuatro exámenes para determinar la causa del dolor de rodilla: prueba del cajón anterior, prueba de Lachman, prueba de pivote y prueba de McMurray
Imagen por Lecturio.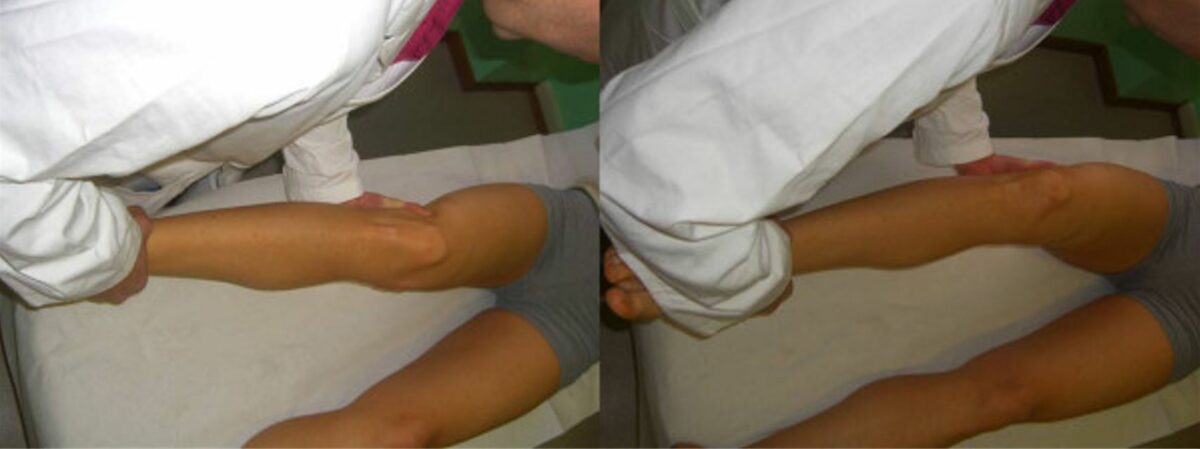
Pruebas de esfuerzo en valgo y varo
Imagen: “Valgus and varus stress tests” por Rossi R, Dettoni F, Bruzzone M, Cottino U, D’Elicio DG, Bonasia DE. Licencia: CC BY 2.0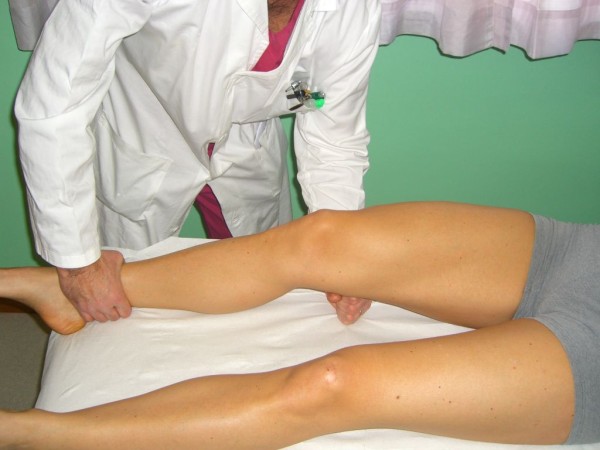
La prueba de Muller (también conocida como prueba activa de cuádriceps)
Imagen: “Quadriceps Active Test” por Rossi R, Dettoni F, Bruzzone M, Cottino U, D’Elicio DG, Bonasia DE. Licencia: CC BY 2.0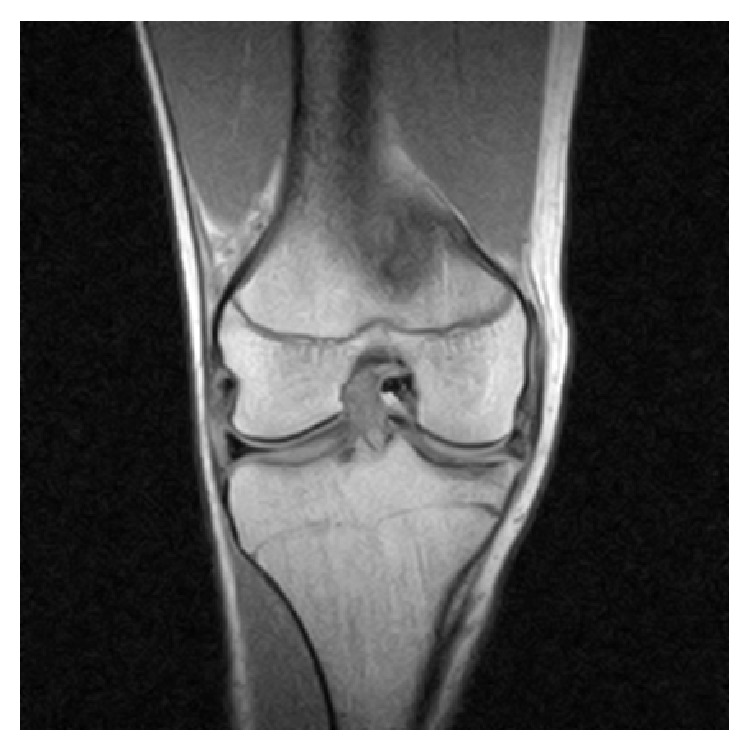
Resonancia magnética de la rodilla derecha que revela un desgarro del menisco medial intraarticular en forma de cubo con un fragmento desplazado ubicado en la muesca intercondilar
Imagen: “Coronal MRI of the right knee” de Ahmed Ali R, McKay S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0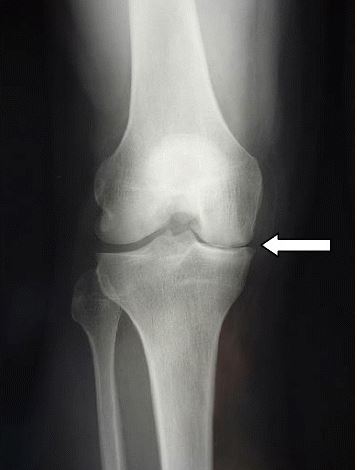
Radiografía que muestra el estrechamiento del espacio articular medial en un desgarro meniscal
Imagen: “Complete medial femorotibial thinning” por Sylvain Steinmetz et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0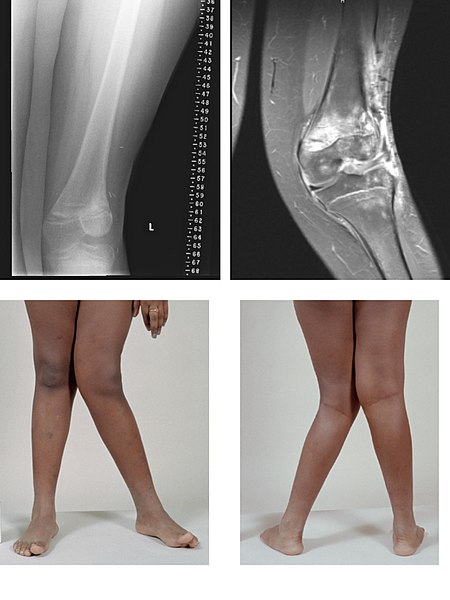
Imágenes de rayos X y resonancia magnética de la deformidad en valgo:
un caso grave de genu valgo de la rodilla izquierda después del tratamiento del cáncer de hueso
La evaluación del dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla es un desafío. Un enfoque para el diagnóstico diferencial es agrupar las diversas condiciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la agudeza de la presentación, la presencia o ausencia de derrame y las actividades precipitantes.
| Entidad | Mecanismo | Características | Diagnóstico |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desgarro del ligamento cruzado anterior (LCA) |
|
|
|
| Desgarro de LCP |
|
|
|
| Desgarro de menisco |
|
|
|
| Luxación rotuliana | Giro o cambio repentino de dirección |
|
|
| Desgarro del ligamento rotuliano |
|
|
|
| Desgarro del tendón del cuádriceps |
|
|
|
| Fractura intraarticular |
|
|
|
| Entidad | Mecanismo | Características | Diagnóstico |
|---|---|---|---|
| Esguince de LCM |
|
|
|
| Esguince de LCL | Fuerza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rodilla |
|
|
| Entidad | Características |
|---|---|
| Osteoartritis de rodilla |
|
| Artropatía por cristales |
|
| Artritis septica |
|
| Artritis reumatoide |
|
| Entidad | Características |
|---|---|
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla anterior | |
| Apofisitis del tubérculo tibial (Osgood-Schlatter) |
|
| SCFE SCFE Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is an orthopedic disorder of early adolescence characterized by the pathologic “slipping” or displacement of the femoral head, or epiphysis, on the femoral neck. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis |
|
| Bursitis prerrotuliana |
|
| Síndrome de dolor Dolor Inflammation femororrotuliano |
|
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation medial de rodilla | |
| Bursitis pes PES Removal of plasma and replacement with various fluids, e.g., fresh frozen plasma, plasma protein fractions (ppf), albumin preparations, dextran solutions, saline. Used in treatment of autoimmune diseases, immune complex diseases, diseases of excess plasma factors, and other conditions. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura anserina |
|
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla lateral | |
| ITBS |
|
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation de rodilla posterior | |
| Quiste poplíteo (de Baker) |
|
| Entidad | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Lesión del ligamento cruzado anterior (LCA) |
|
| Lesiones de LCP |
|
| Lesiones meniscales |
|
| Lesión de LCM |
|
| Osteoartritis |
|
| Artropatía por cristales: gota y CPPD | Tratamiento de la gota:
|
| Artritis séptica |
|
| PFPS |
|
| Quiste poplíteo (de Baker) |
|