Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos osmóticos aumentan la osmolaridad del líquido tubular, arrastrando agua hacia los LOS Neisseria túbulos colectores e impidiendo la reabsorción de agua, lo que da lugar a una diuresis osmótica. El principal diurético osmótico utilizado clínicamente es el manitol. La indicación principal del manitol es para el tratamiento del aumento de la presión intracraneal o intraocular, que puede tener efectos significativos sobre el volumen de líquido y la concentración de sodio corporal, por lo que debe tenerse precaución al AL Amyloidosis utilizar estos agentes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un diurético osmótico es un agente osmóticamente activo que se filtra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria túbulos renales, pero no se reabsorbe. La presencia de esta sustancia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria túbulos renales mantiene el agua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria túbulos, lo que provoca la diuresis.
El manitol es un alcohol de azúcar simple de 6 carbonos y no absorbible.
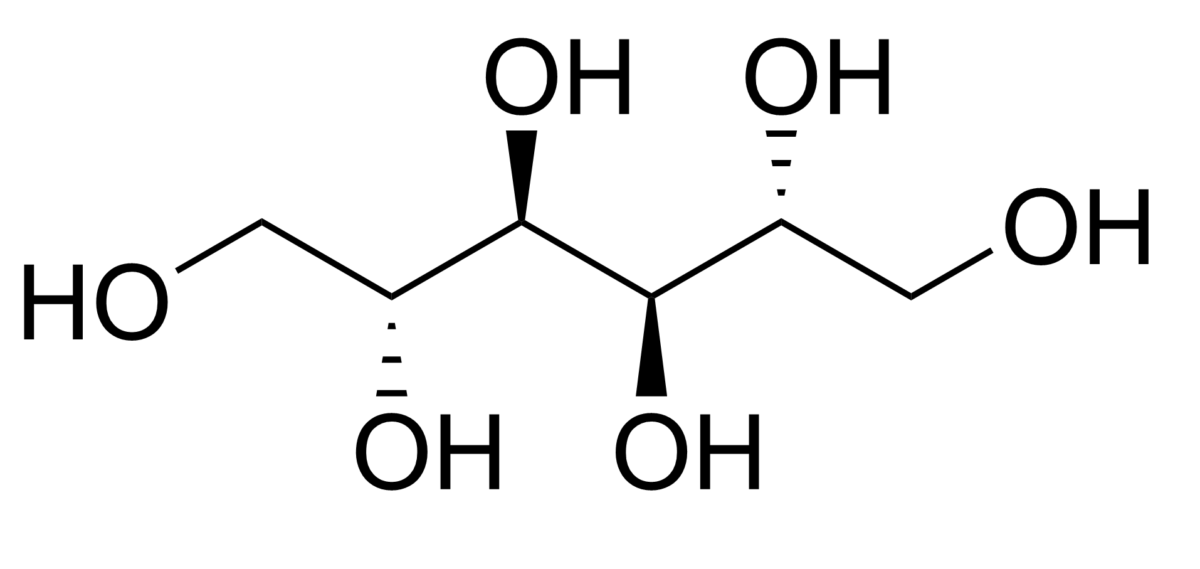
Estructura química del manitol
Imagen: “Chemical Structure of Mannitol” por Edgar181. Licencia: Dominio Público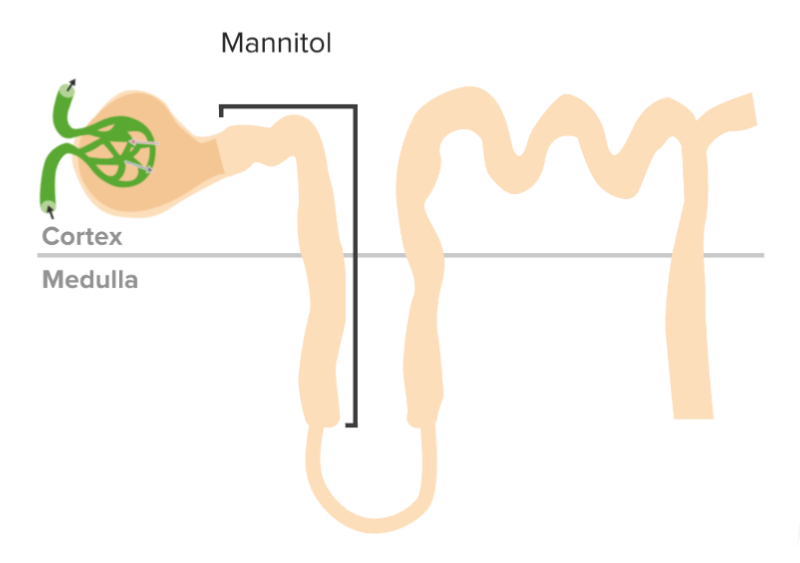
Mecanismo de acción de los diuréticos osmóticos
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Las principales indicaciones para el uso de manitol incluyen:
Algunos de los LOS Neisseria otros diuréticos más comunes son los LOS Neisseria diuréticos tiazídicos (e.g., la hidroclorotiazida), los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome (e.g., la furosemida), los LOS Neisseria diuréticos ahorradores de potasio (e.g., la espironolactona) y los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica (e.g., la acetazolamida).
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Efecto fisiológico | Indicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diurético tiazídico: Hidroclorotiazida | ↓ Reabsorción de NaCl en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el túbulo contorneado distal a través de la inhibición del cotransportador de Na+/Cl–. |
|
|
| Diurético de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome: Furosemida | Inhibe el cotransportador luminal de Na+/K+/Cl– en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama gruesa ascendente del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle |
|
|
| Diurético ahorrador de potasio: Espironolactona |
|
|
|
| Inhibidor de la anhidrasa carbónica: Acetazolamida | Inhibe tanto la hidratación del CO2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células epiteliales del túbulo contorneado proximal como la deshidratación del H2CO3 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lumen del túbulo contorneado proximal; provocando una excreción ↑ de HCO3– y Na+. |
|
|
| Diuréticos osmóticos: Manitol | ↑ Presión osmótica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filtrado glomerular → ↑ líquido tubular e impide la reabsorción de agua |
|
|
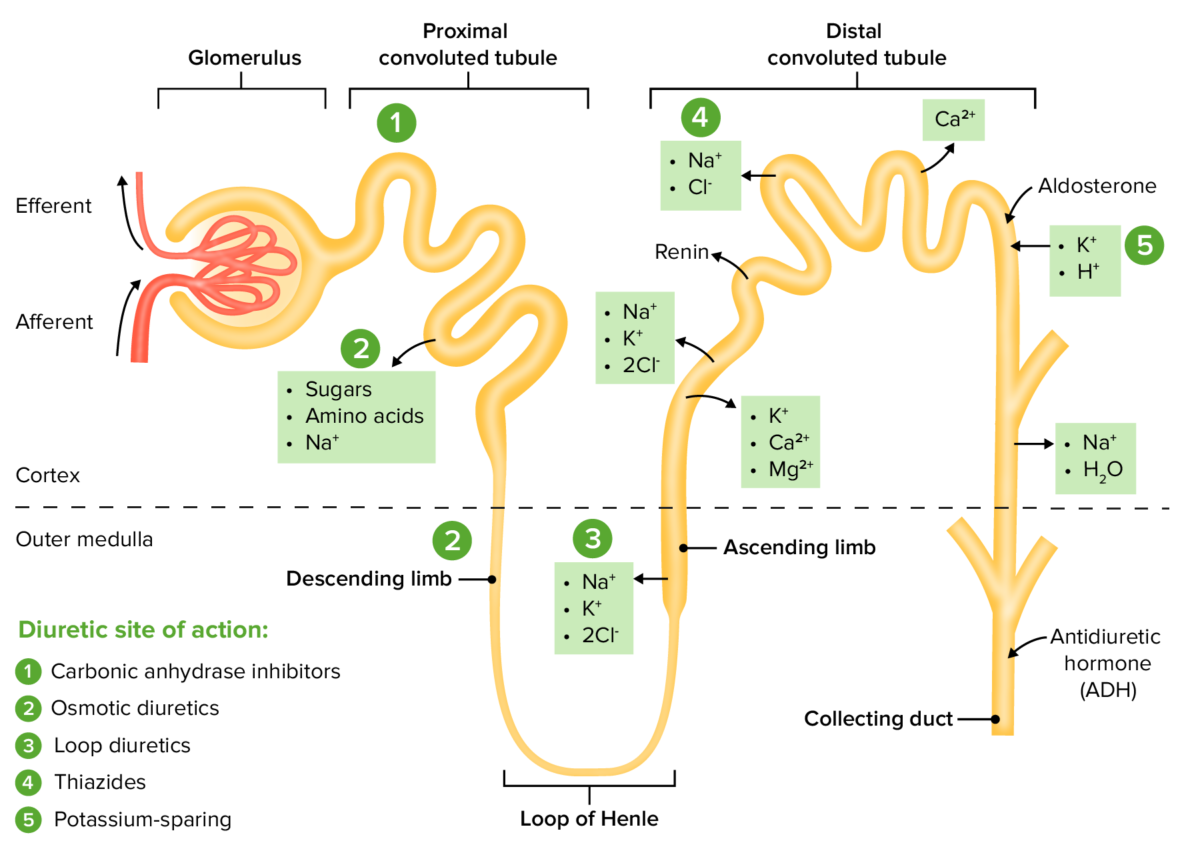
Sitios de acción, dentro de la nefrona, para las distintas clases de medicamentos diuréticos
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0