La deficiencia de alfa-1 antitripsina es un trastorno genético hereditario causado por mutaciones genéticas del gen SERPINA1, que provocan la producción defectuosa del inhibidor de la proteasa alfa-1 antitripsina. Estas mutaciones pueden dar lugar a deficiencia de la enzima causando enfermedades pulmonares, producción de una forma anormal de la enzima que provoque una disfunción hepática, o ambas. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar enfisema, neumotórax espontáneo, cirrosis, hepatitis o carcinoma hepatocelular. Al AL Amyloidosis momento no se dispone de cura. El tratamiento consiste es de soporte e incluye: la infusión de la proteína alfa-1-antitripsina, el tratamiento adecuado de las comorbilidades y el trasplante de hígado. El pronóstico puede variar según la forma de la enfermedad adquirida y la gravedad de los LOS Neisseria síntomas.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Enfermedad hepática:
Enfermedad pulmonar:
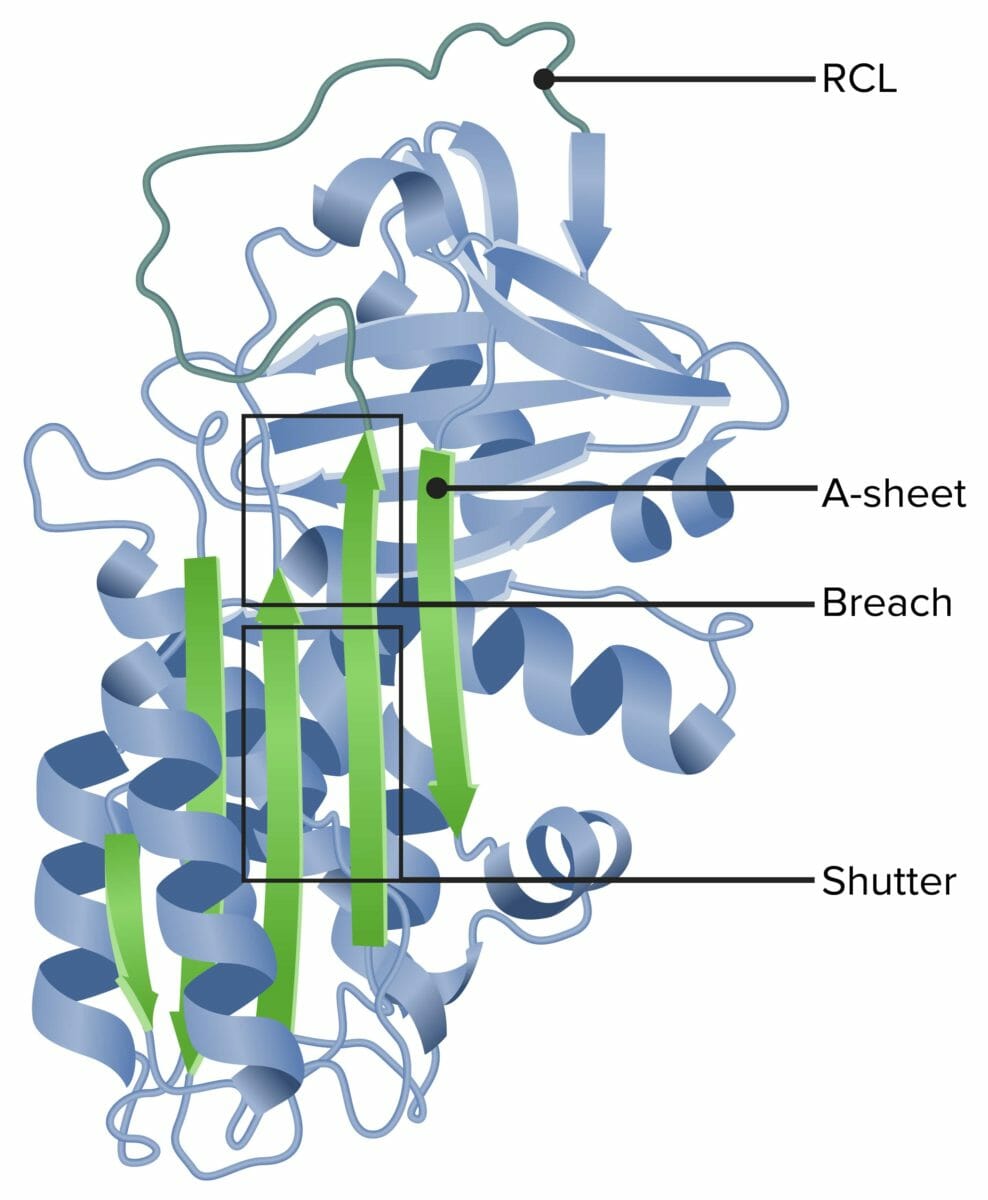
Alfa-1 antitripsina
RCL: bucle central reactivo (por sus siglas en inglés)
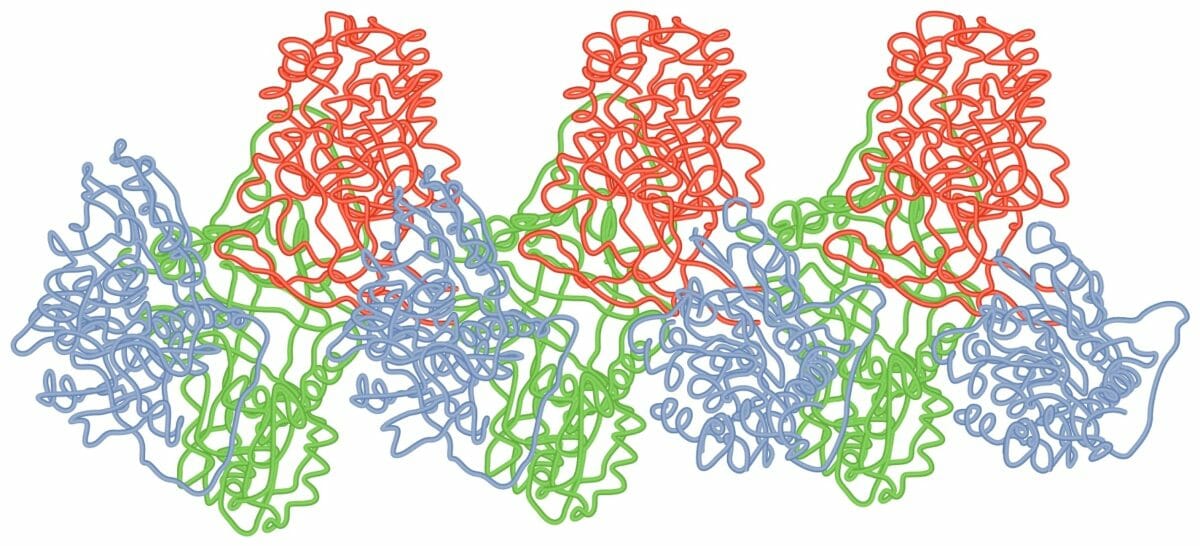
Polímero de bucle-lámina de las moléculas de alfa-1 antitripsina
Imagen por Lecturio.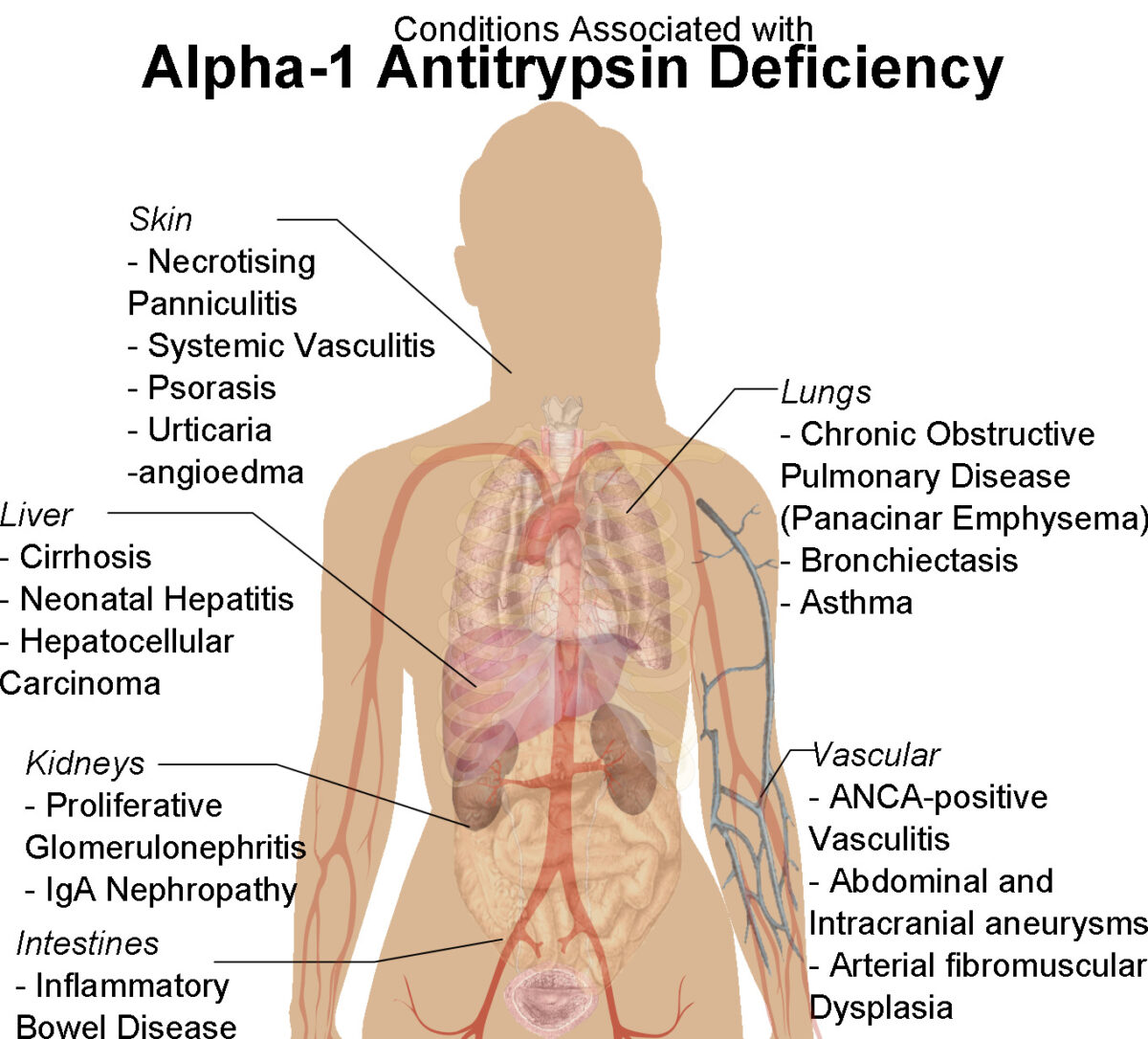
Diagrama de un contorno humano femenino con condiciones asociadas a la deficiencia de alfa-1 antitripsina
Imagen: “Human female shadow diagram with conditions associated with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0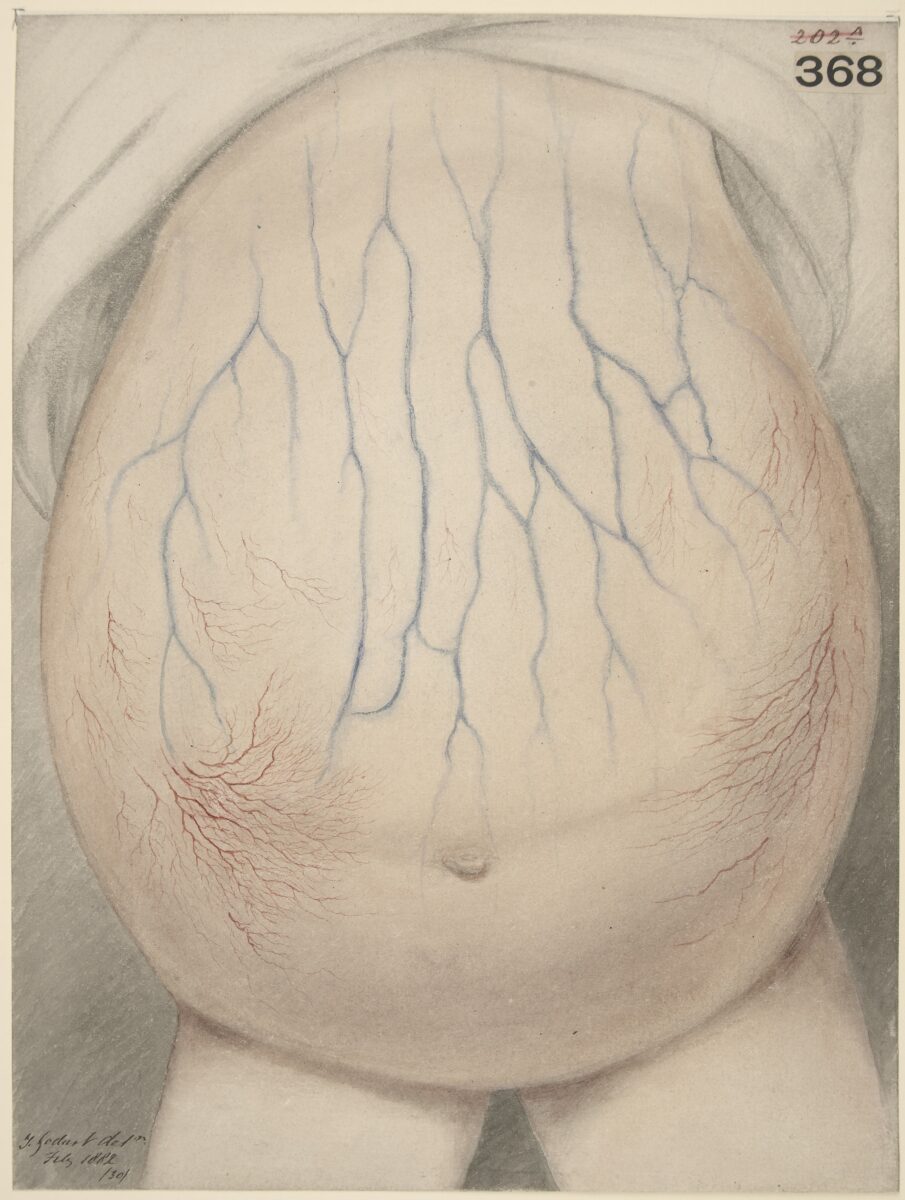
Abdomen de niño afectado por ascitis
Imagen: “Watercolour drawing of the abdomen of a child affected with ascites” por Wellcome Collection gallery. Licencia: CC BY 4.0