El carcinoma basocelular es la neoplasia maligna de piel más frecuente. Este cáncer surge de la capa basal de la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions. Las lesiones aparecen con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara como nódulos perlados, a menudo con vasos sanguíneos telangiectásicos y ulceración en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas de edad avanzada. El diagnóstico se establece mediante una biopsia. A pesar de tener un bajo potencial metastásico, el carcinoma basocelular debe tratarse adecuadamente porque es localmente agresivo y destructivo para los LOS Neisseria tejidos. La escisión quirúrgica completa es el principal método de tratamiento. El pronóstico a largo plazo es excelente con un tratamiento adecuado.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El carcinoma basocelular (carcinoma de células basales) es un cáncer de piel que surge de la capa basal de la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions y sus anexos.
| Tipo | Frecuencia | Histología | Presentación clínica |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinoma basocelular nodular | 80% |
|
|
| Carcinoma basocelular superficial | 15% | Tumores basaloides atípicos surgen como yemas de la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions. |
|
| Carcinoma basocelular morfeiforme | 5%–10% |
|
|
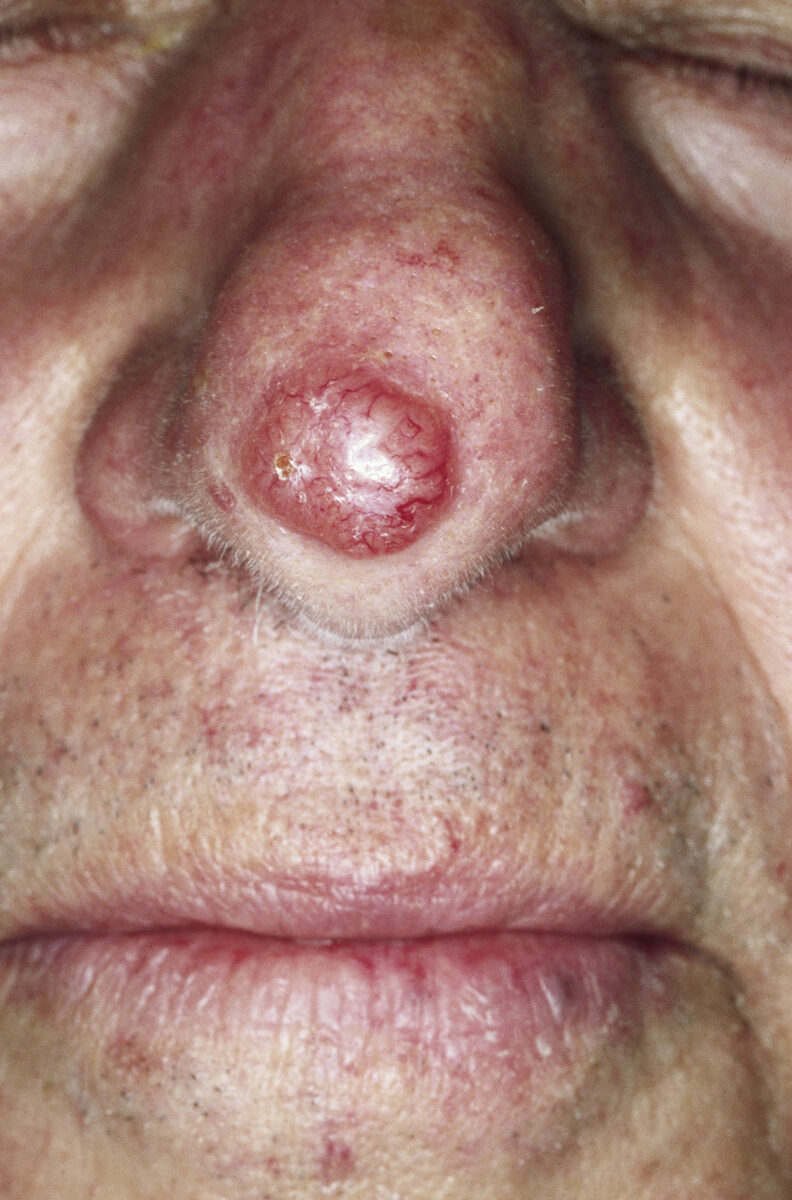
Carcinoma basocelular nodular de la nariz:
Nódulo perlado con vasos telangiectásicos visibles
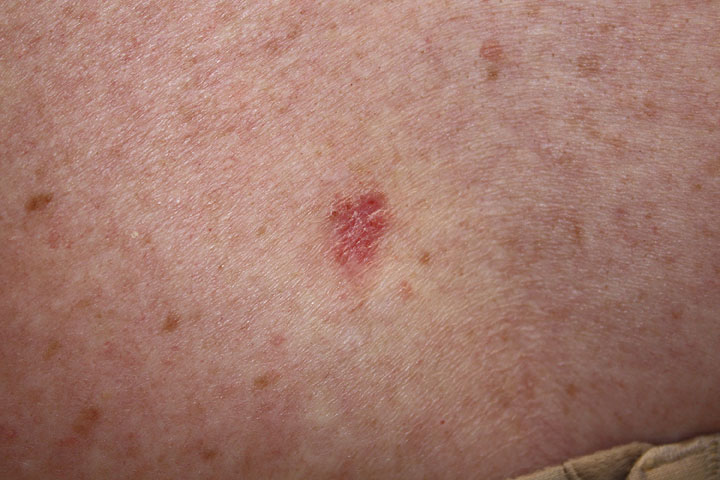
Carcinoma basocelular superficial:
Una lesión rosada y escamosa en la piel.
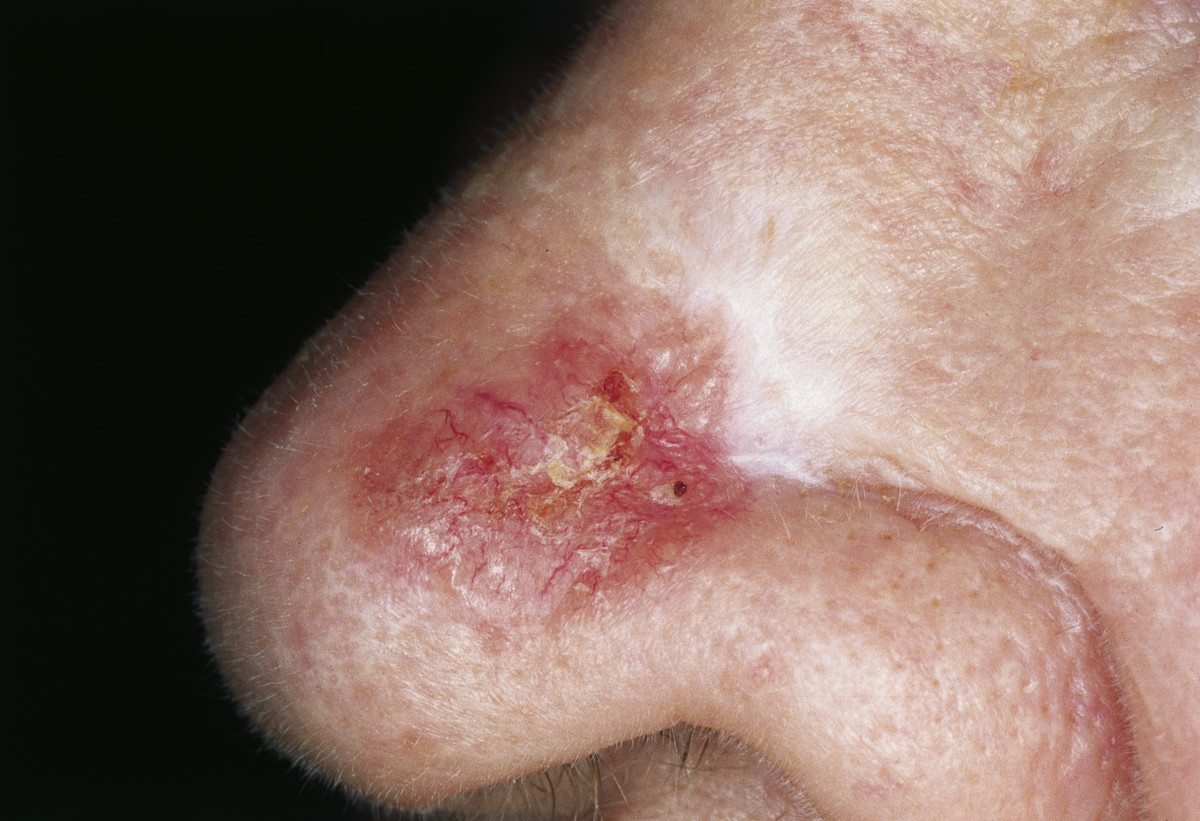
Carcinoma basocelular morfeforme:
Placa esclerótica, parcialmente rojiza con bordes irregulares y costra central
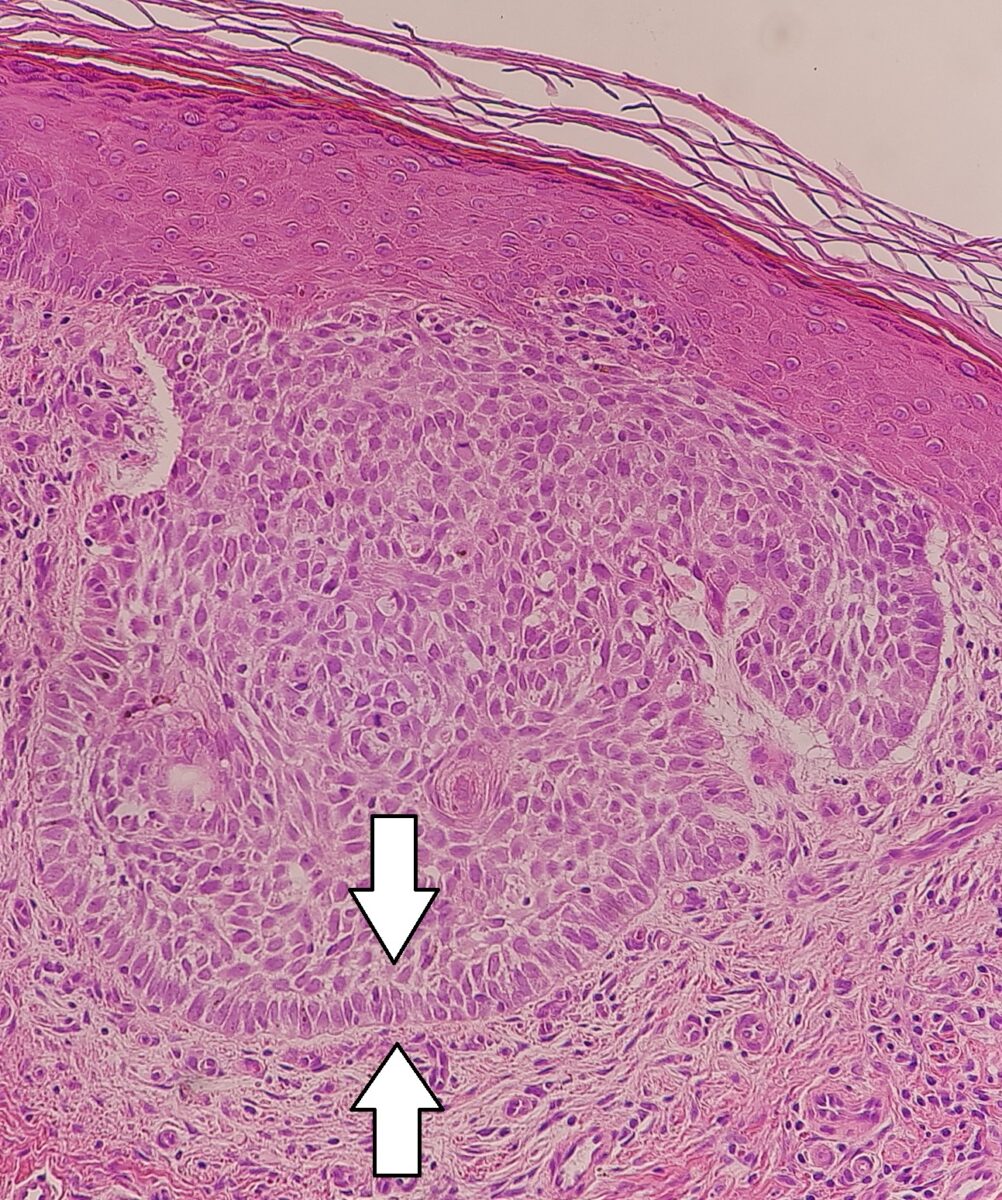
Carcinoma basocelular nodular:
Queratinocitos en empalizada en un carcinoma basocelular nodular
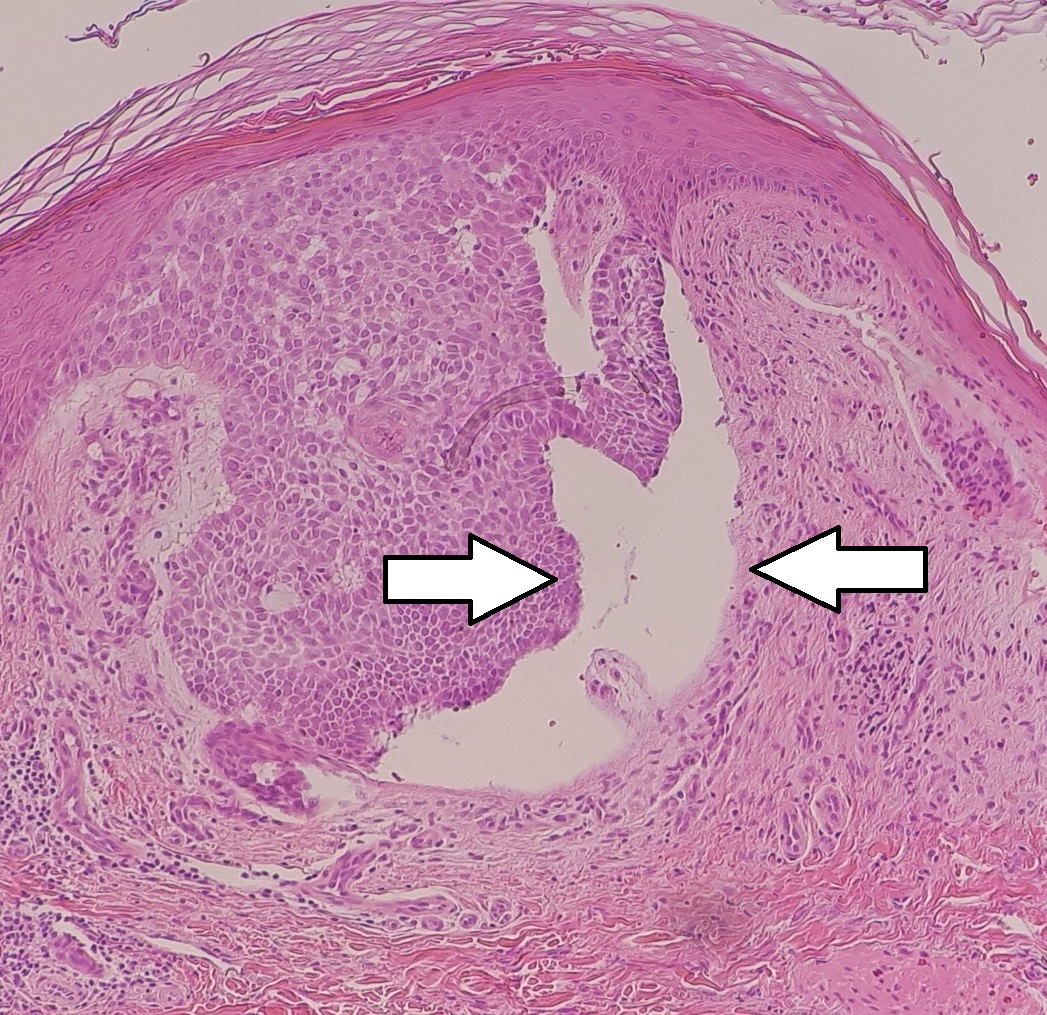
Carcinoma basocelular nodular:
Micrografía de un cáncer basocelular nodular con una hendidura
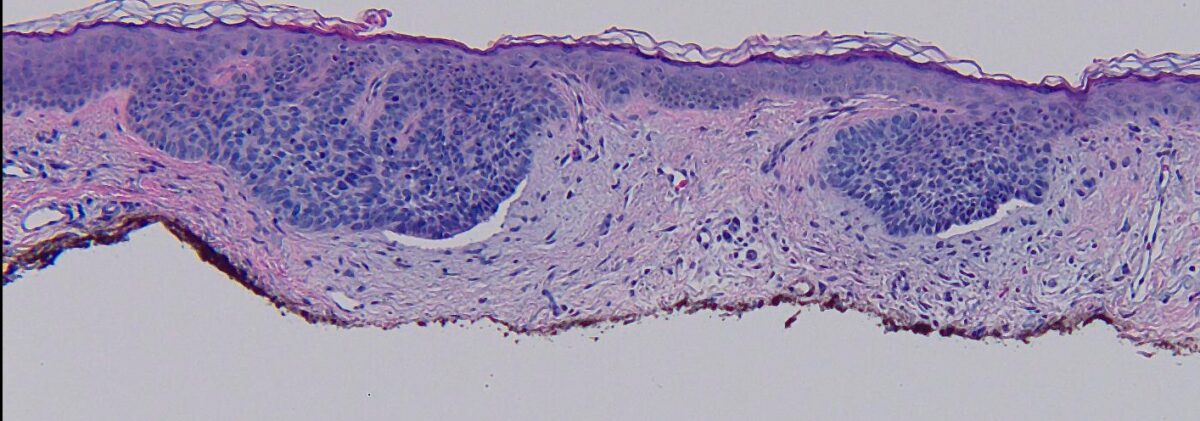
Micrografía de un carcinoma basocelular superficial:
Células tumorales en empalizada brotando de la epidermis
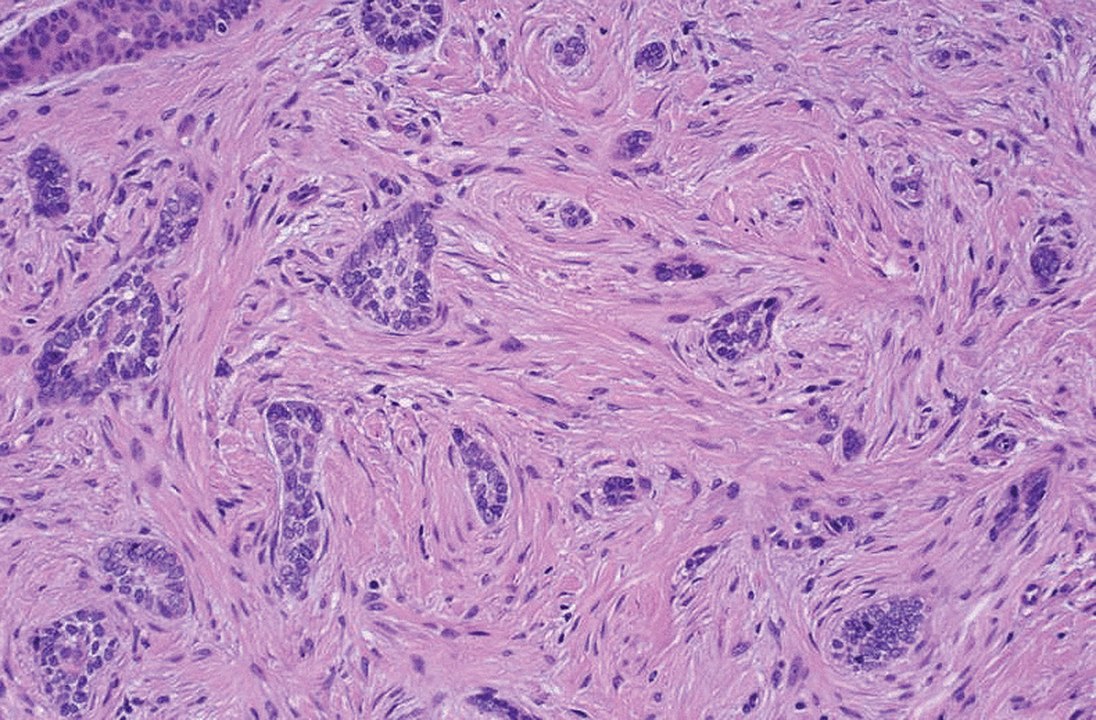
Carcinoma basocelular morfeiforme: cordones de células tumorales crecen en la dermis (infiltrativo)
Imagen : “Morpheaform basal-cell carcinoma” por Masahiro Nakayama, Keiji Tabuchi, Yasuhiro Nakamura and Akira Hara. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Antecedentes:
Examen físico:
Dermatoscopia:
Biopsia:
Evaluar el riesgo de recurrencia:
Cirugía:
Terapias alternativas:
Terapia para enfermedad avanzada: