Las arterias son colecciones tubulares de células que transportan sangre oxigenada y nutrientes desde el corazón a los LOS Neisseria tejidos del cuerpo. La sangre pasa a través de las arterias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum orden decreciente de diámetro luminal, comenzando en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la arteria más grande (la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy) y terminando en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las arteriolas pequeñas. Las arterias se clasifican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 tipos: arterias elásticas grandes, arterias musculares medianas y arterias y arteriolas pequeñas. Cada uno de estos tipos de arterias contiene 3 capas primarias: la túnica íntima, la túnica media y la túnica adventicia. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum particular, la túnica media contiene células musculares lisas (que permiten la vasoconstricción) y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria vasos más grandes, una cantidad significativa de elastina (que permite que estos vasos se estiren y retrocedan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a los LOS Neisseria cambios de presión durante la sístole y la diástole).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las arterias son colecciones tubulares de células que transportan sangre oxigenada y nutrientes desde el corazón a los LOS Neisseria tejidos del cuerpo.
Todas las arterias tienen las siguientes características:
Todas las arterias tienen la misma estructura básica y están formadas por tres capas principales: la túnica íntima, la túnica media y la túnica adventicia (también conocida como túnica externa).
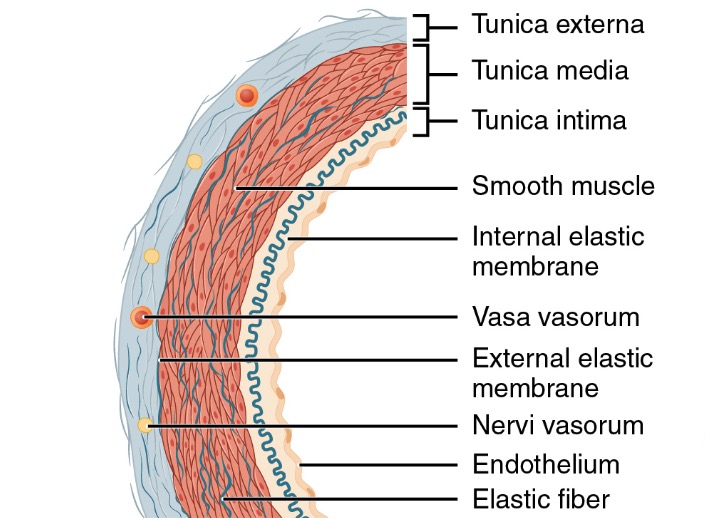
Estructura de una pared arterial
Imagen: “Structure of an artery wall” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0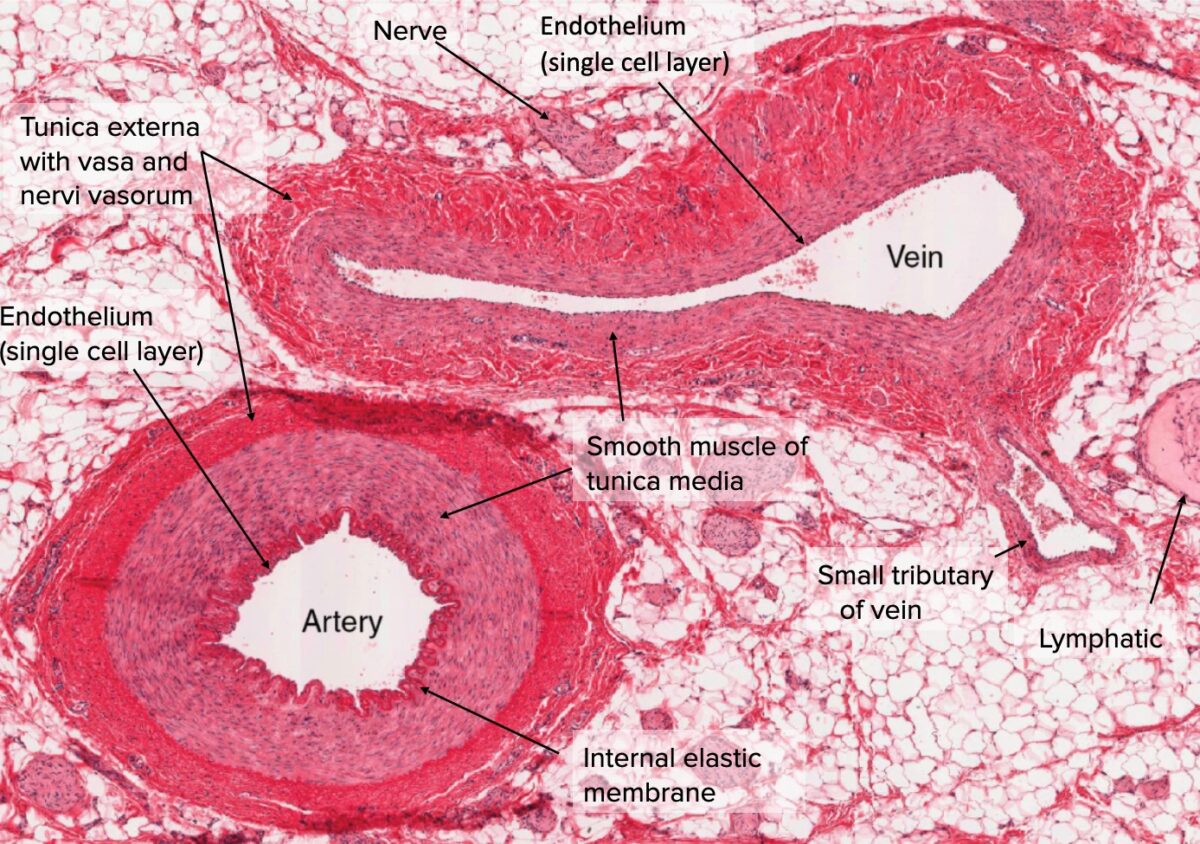
Sección transversal de arteria y vena
Imagen: “Types of Arteries and Arterioles” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.Hay 3 tipos principales de arterias, según su tamaño, función y composición general (conocida como diferenciación segmentaria). Las arterias generalmente existen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un continuo, con cambios graduales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la morfología de los LOS Neisseria vasos que descienden por el árbol arterial.
Los LOS Neisseria 3 tipos principales de arterias son:
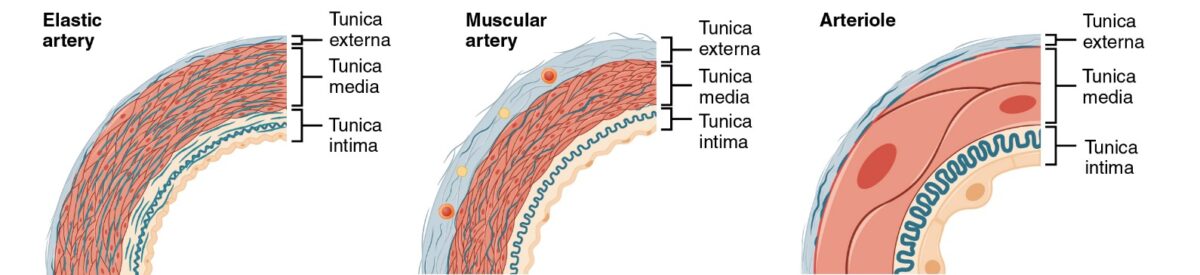
3 tipos principales de arterias
Imagen: “Types of Arteries and Arterioles” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Este grupo incluye las arterias más grandes del cuerpo; todas las arterias grandes/elásticas están cerca del corazón. La aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy es la arteria más grande del cuerpo.
Las arterias grandes/elásticas incluyen:
Características:
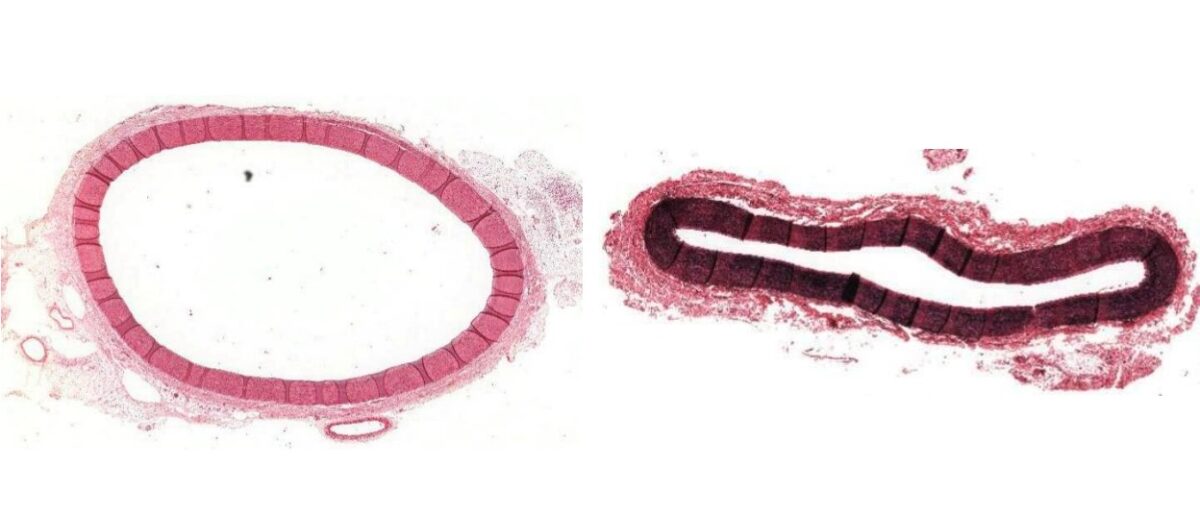
Tinción histológica de la aorta:
Izquierda: tinción hematoxilina & eosina de la aorta
Derecha: teñido para tejido elástico (color más oscuro), que demuestra la cantidad significativa de tejido elástico dentro de la túnica media en la aorta
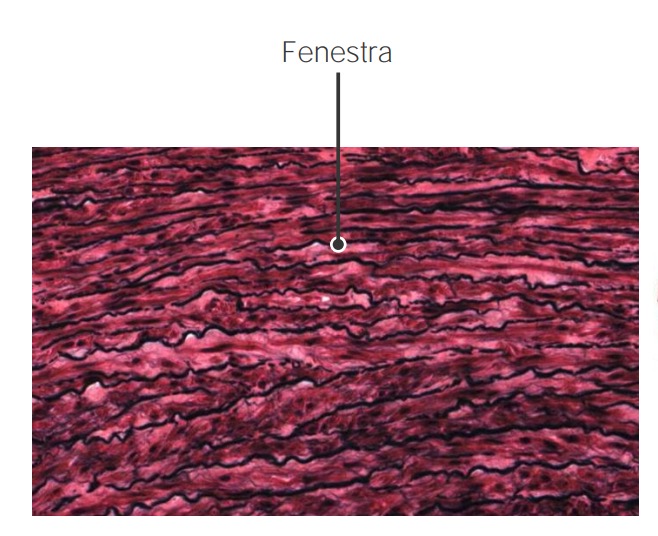
Fenestra (o “ventanas”) dentro de las fibras elásticas en la pared aórtica
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, PhD.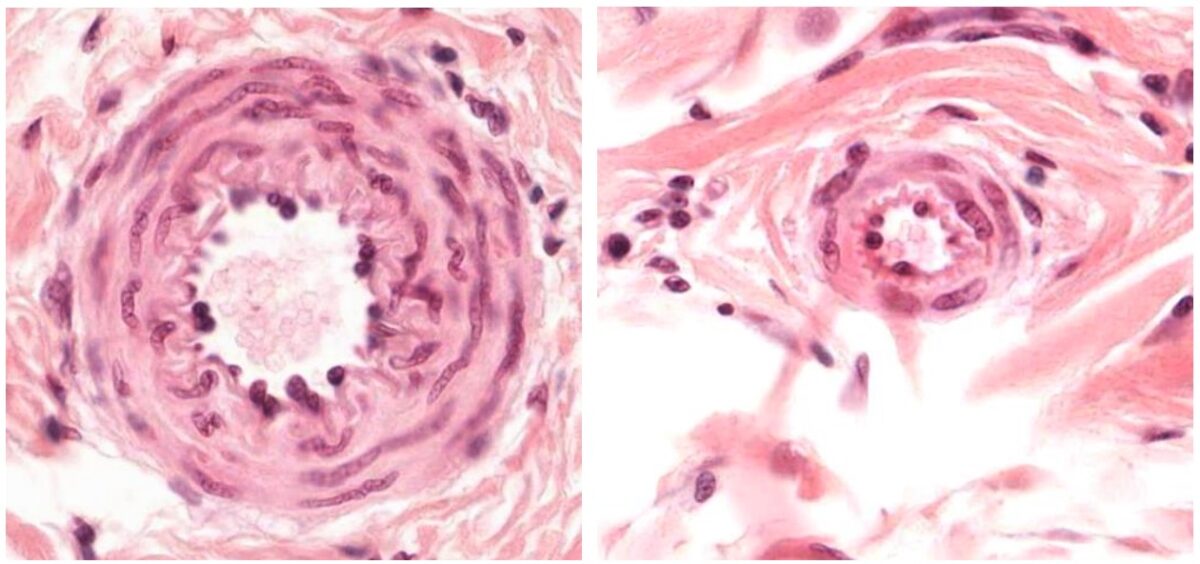
Cortes transversales de una arteria pequeña (izquierda) y una arteriola (derecha)
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, PhD.
Lecho capilar que muestra una arteriola, una metarteriola y esfínteres precapilares
Imagen: “Capillary Bed” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Las vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus son un grupo de enfermedades autoinmunes caracterizadas por inflamación de los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos mediada por el sistema inmunitario y daño de la pared. La pérdida de la integridad del vaso puede provocar hemorragia, así como isquemia y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage corriente abajo. Estos procesos pueden ser primarios o secundarios, y tienden a afectar solo vasos de un tipo específico o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una ubicación específica.
| Tipo de vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Ejemplos de afecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cada categoría |
|---|---|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de grandes vasos |
|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de vasos medianos |
|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de vasos pequeños |
|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de vasos de tamaño variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
|
| Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de un solo órgano |
|