El angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario, también conocido como deficiencia del inhibidor de la esterasa C1, es un trastorno autosómico dominante caracterizado por episodios recurrentes de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema grave ( angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema). El angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario suele afectar a extremidades, cara, tracto gastrointestinal y vías respiratorias superiores. La inflamación de la vía aérea puede restringir la respiración y provocar una obstrucción de la vía aérea potencialmente mortal. El angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tiene 3 subtipos que se distinguen por sus etiologías subyacentes y los LOS Neisseria niveles de inhibidor C1 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre. El tratamiento incluye la terapia con danazol Danazol A synthetic steroid with antigonadotropic and anti-estrogenic activities that acts as an anterior pituitary suppressant by inhibiting the pituitary output of gonadotropins. It possesses some androgenic properties. Danazol has been used in the treatment of endometriosis and some benign breast disorders. Antiestrogens, inhibidores de la calicreína e inhibidores de la esterasa C1. El angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario es autolimitado, pero puede ser mortal si se comprometen las vías respiratorias.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
El angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario es una enfermedad hereditaria que presenta episodios recurrentes de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema ( angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema), generalmente de la mucosa del sistema respiratorio y gastrointestinal, sin urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) ni picor.
Las mutaciones genéticas son la causa del angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario:
La fisiopatología básica de la inflamación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tiene que ver con la sobreproducción de bradicinina.
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tipo I | Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tipo II | Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tipo III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalencia | 80%–85% de los LOS Neisseria casos | 15%–20% | Muy raro; generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres |
| Causa | Reducción de la secreción de inhibidores de la esterasa C1 | Producción de inhibidores de la esterasa C1 no funcional |
|
| Fisiopatología | Exceso de producción de anafilatoxinas inflamatorias que afectan al AL Amyloidosis flujo de fluidos corporales entre el sistema vascular y los LOS Neisseria tejidos corporales | Exceso de producción de anafilatoxinas inflamatorias que afectan al AL Amyloidosis flujo de fluidos corporales entre el sistema vascular y los LOS Neisseria tejidos corporales |
|
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tienen episodios recurrentes:
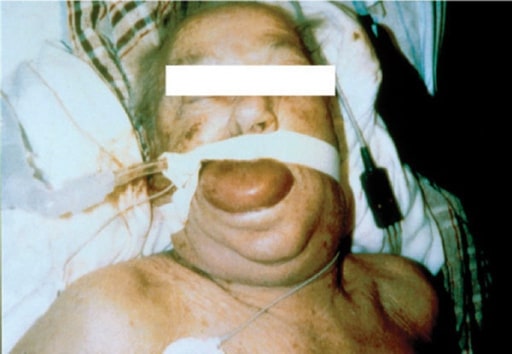
Edema facial, lingual y faríngeo severo en un paciente tratado con un inhibidor de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (IECA)
Imagen: “F3” por the National Allergy, Asthma, and Urticaria Centers of Charleston, Charleston, SC. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.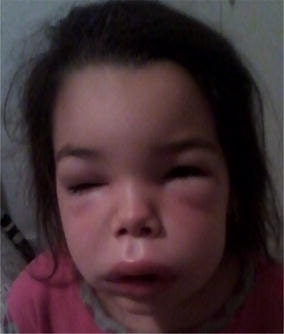
Angioedema de cara
Image: “Angioedema of the face” por S. Tolga Yavuz et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.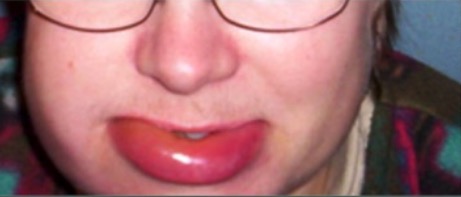
Angioedema hereditario
Imagen:“Typical features” por Department of Bacteriology and Immunology, Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.Reconocer el angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario suele ser difícil debido a la gran variabilidad de expresión de la enfermedad:
Los LOS Neisseria análisis de sangre suelen utilizarse para confirmar el diagnóstico:
| Tipo de angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema sin urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) | Proteína C1-INH | C1q | C4 y C2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tipo I | ↓ | Normal | ↓ |
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditario tipo II | N o ↑ (pero disfuncional) | Normal | ↓ |
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema adquirido con deficiencia de inhibidor de esterasa C1 (tipo I) | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema adquirido con deficiencia de inhibidor de esterasa C1 (tipo II) | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
El tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum controlar los LOS Neisseria episodios enfocado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síntomas específicos: