Los LOS Neisseria anestésicos intravenosos se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la práctica moderna de la anestesia desde el siglo XX. La anestesia moderna comenzó con anestésicos inhalados; sin embargo, se adoptaron los LOS Neisseria agentes intravenosos porque las dosis inyectadas o infundidas podían controlarse más estrechamente con poco medicamento desperdiciado. Actualmente, existen varios grupos de agentes (e.g., barbitúricos, benzodiazepinas y disociativos), pero los LOS Neisseria más utilizados son el fentanilo, el midazolam Midazolam A short-acting hypnotic-sedative drug with anxiolytic and amnestic properties. It is used in dentistry, cardiac surgery, endoscopic procedures, as preanesthetic medication, and as an adjunct to local anesthesia. The short duration and cardiorespiratory stability makes it useful in poor-risk, elderly, and cardiac patients. It is water-soluble at ph less than 4 and lipid-soluble at physiological pH. Benzodiazepines y el propofol Propofol An intravenous anesthetic agent which has the advantage of a very rapid onset after infusion or bolus injection plus a very short recovery period of a couple of minutes. Propofol has been used as anticonvulsants and antiemetics. Intravenous Anesthetics.
Last updated: Oct 22, 2022
Los LOS Neisseria anestésicos intravenosos incluyen:
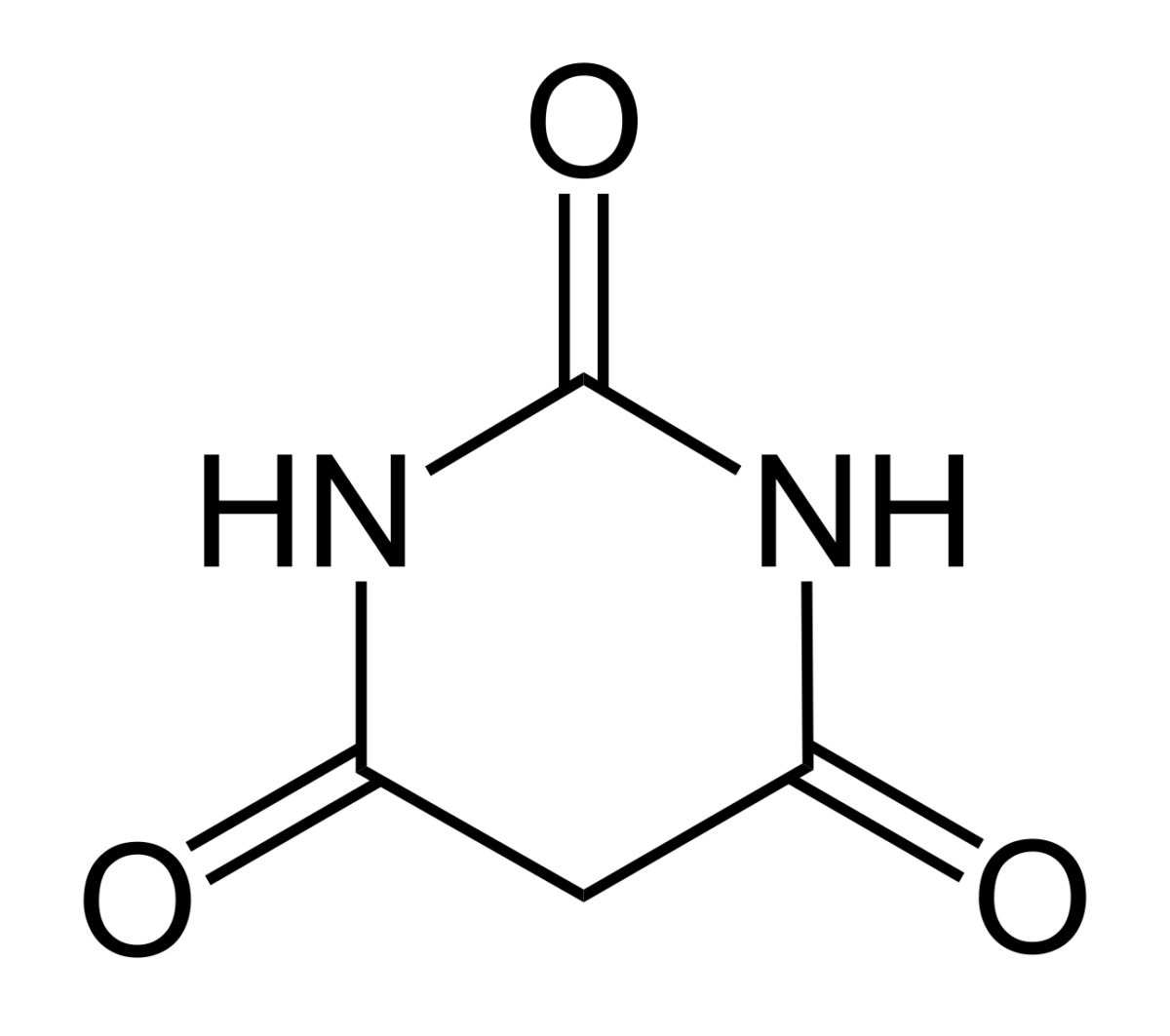
La estructura química del ácido barbitúrico
Imagen: “Barbituric Acid Structural formula” por Jü. Licencia: Dominio Público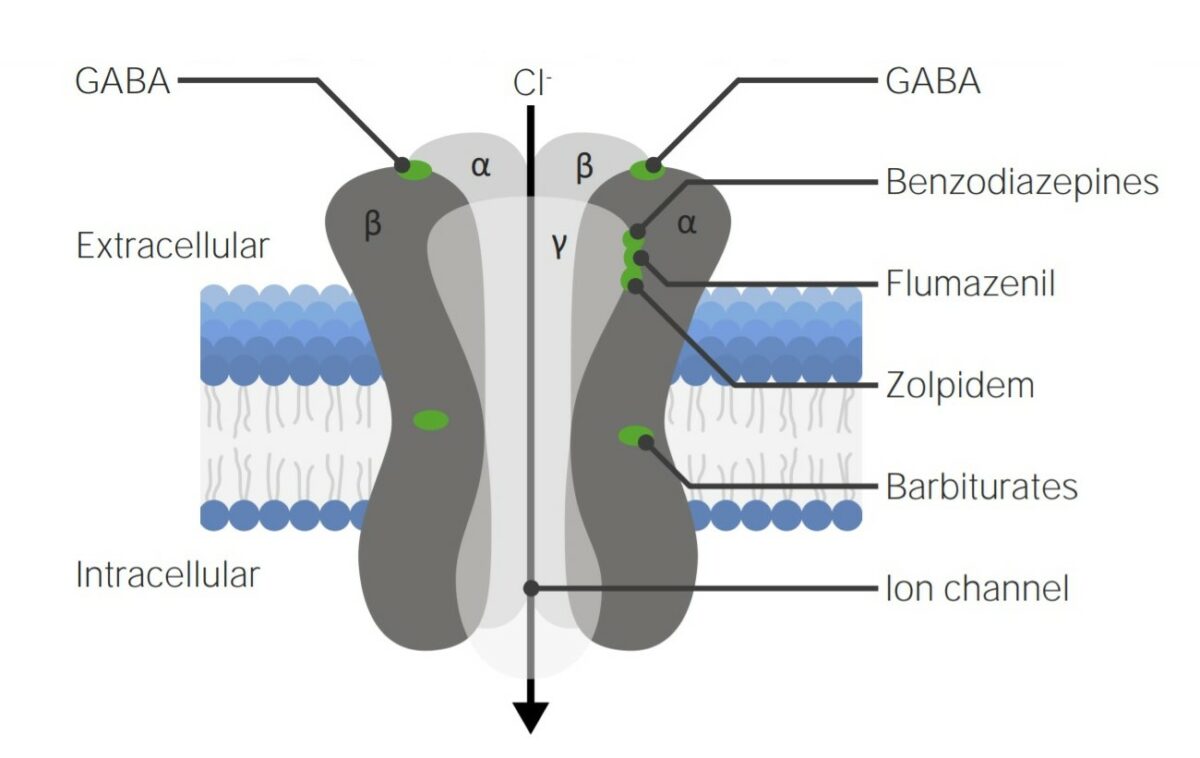
Diagrama del receptor del ácido γ-aminobutírico A (GABAA):
Obsérvese a los diferentes sitios de unión de las distintas familias de medicamentos.
Los LOS Neisseria barbitúricos son un grupo de medicamentos sedantes-hipnóticos con las siguientes indicaciones:
Efectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Contraindicaciones:
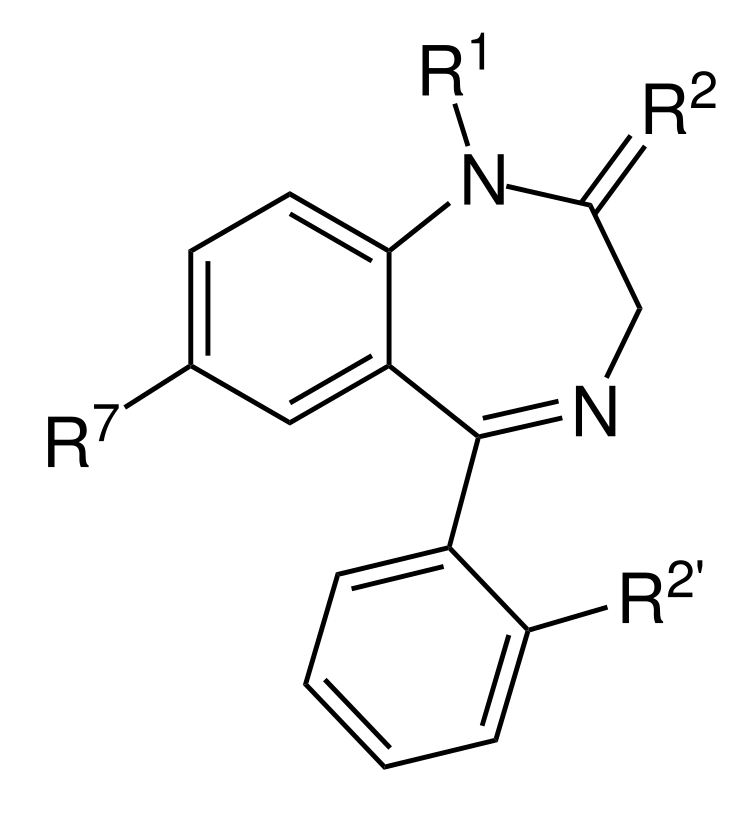
Estructura básica del anillo de la clase de las benzodiazepinas:
Los medicamentos dentro de la clase tienen grupos R variables.
La ocupación/activación del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors GABAA aumenta la frecuencia de apertura del canal de cloruro (Cl-) asociado, lo que provoca la inhibición del potencial de acción:
Efectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Contraindicaciones:
Presentación clínica:
Tratamiento:
La ketamina es similar a la fenciclidina, un alucinógeno.
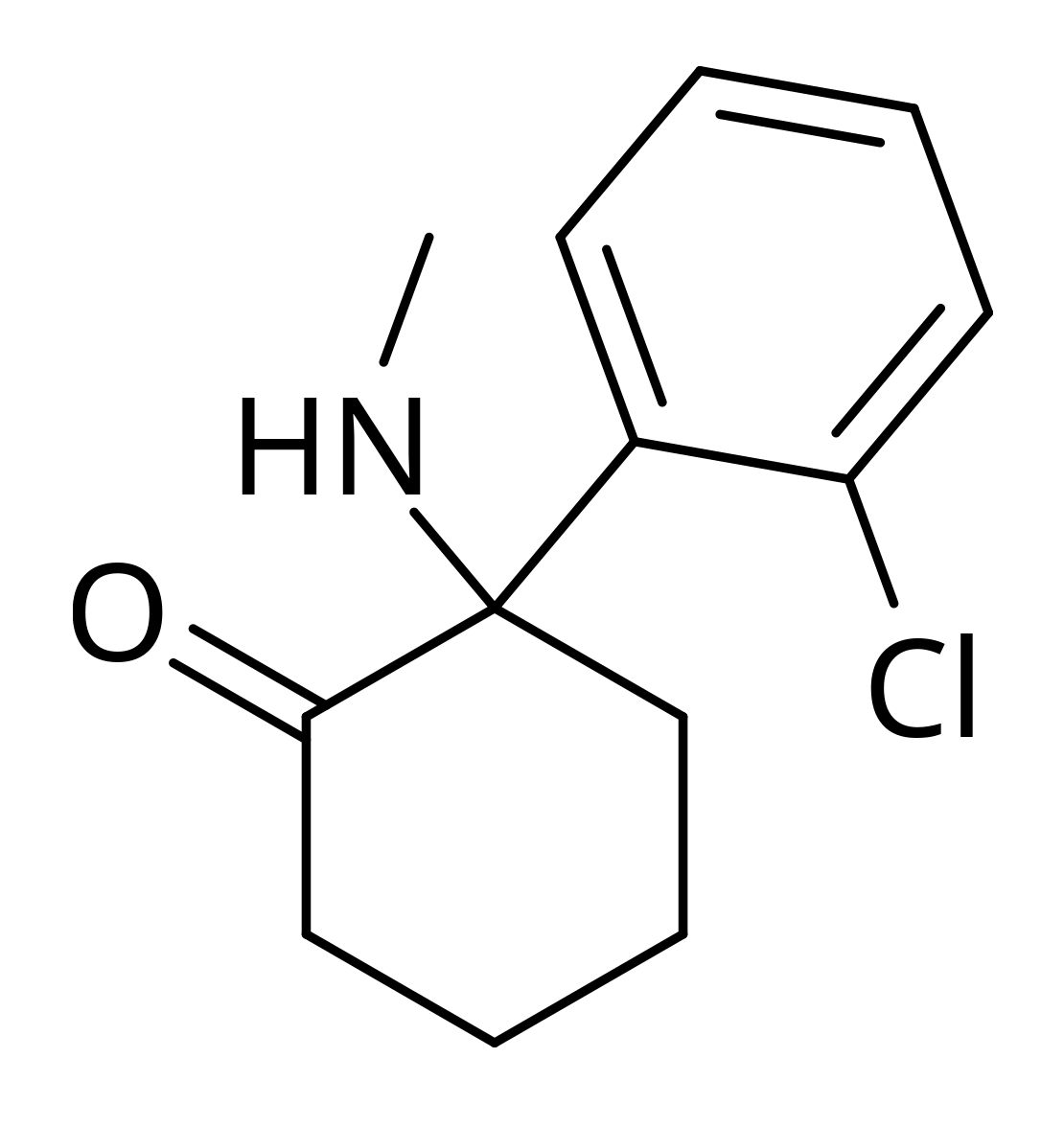
Estructura química de la ketamina
Imagen: “Structure of ketamine” por Brenton. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEfectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Contraindicaciones:
Administración cautelosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
El etomidato es un agente anestésico intravenoso con las siguientes características:
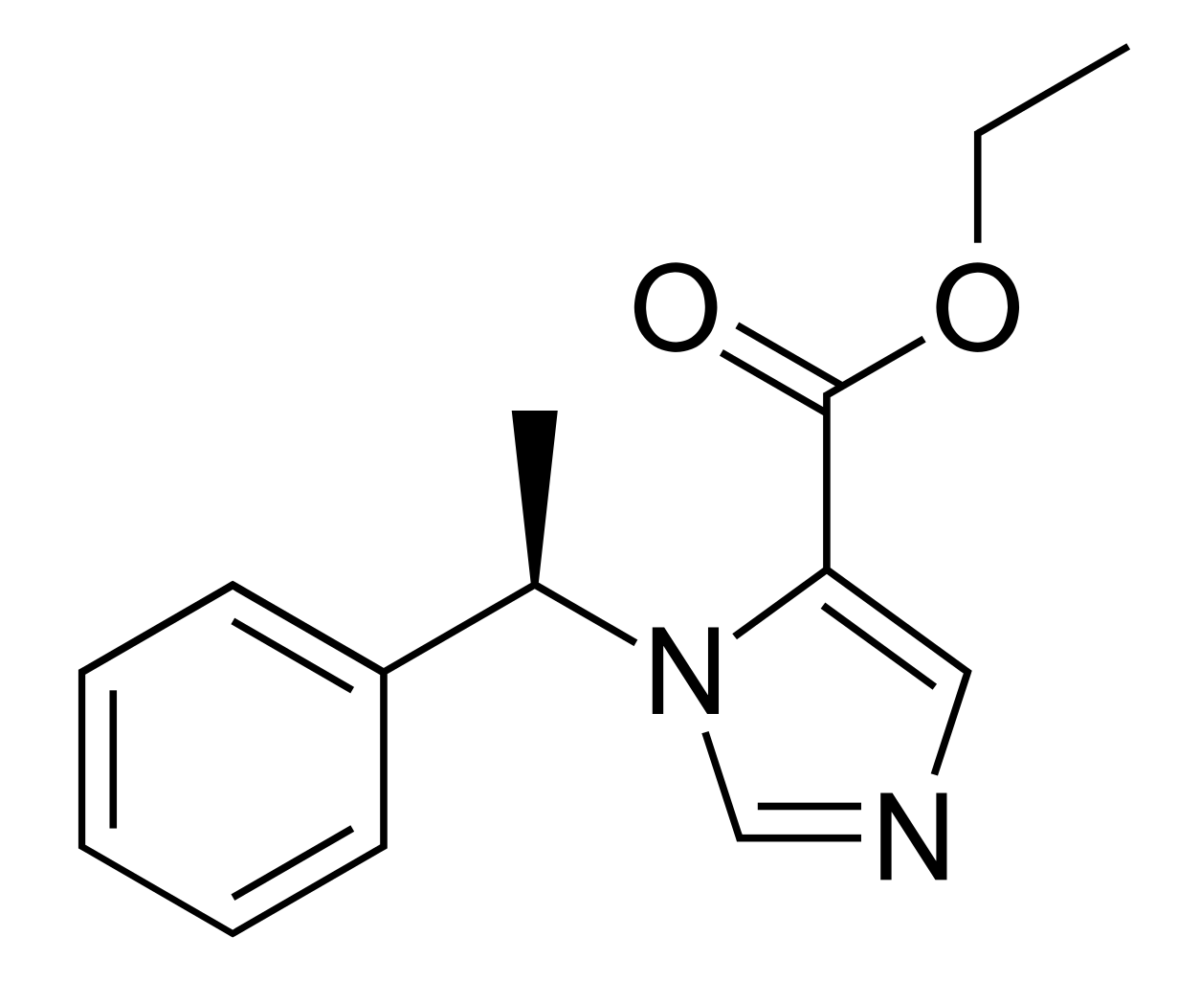
Estructura química del etomidato
Imagen: “Etomidate” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa ocupación/activación del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors GABAA aumenta la sensibilidad para que el GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS reduzca la neuroexcitación.
Efectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Uso cauteloso:
El propofol Propofol An intravenous anesthetic agent which has the advantage of a very rapid onset after infusion or bolus injection plus a very short recovery period of a couple of minutes. Propofol has been used as anticonvulsants and antiemetics. Intravenous Anesthetics es el agente de inducción más utilizado.
La estructura química del propofol Propofol An intravenous anesthetic agent which has the advantage of a very rapid onset after infusion or bolus injection plus a very short recovery period of a couple of minutes. Propofol has been used as anticonvulsants and antiemetics. Intravenous Anesthetics incluye un anillo de fenol sustituido con 2 grupos isopropilo.
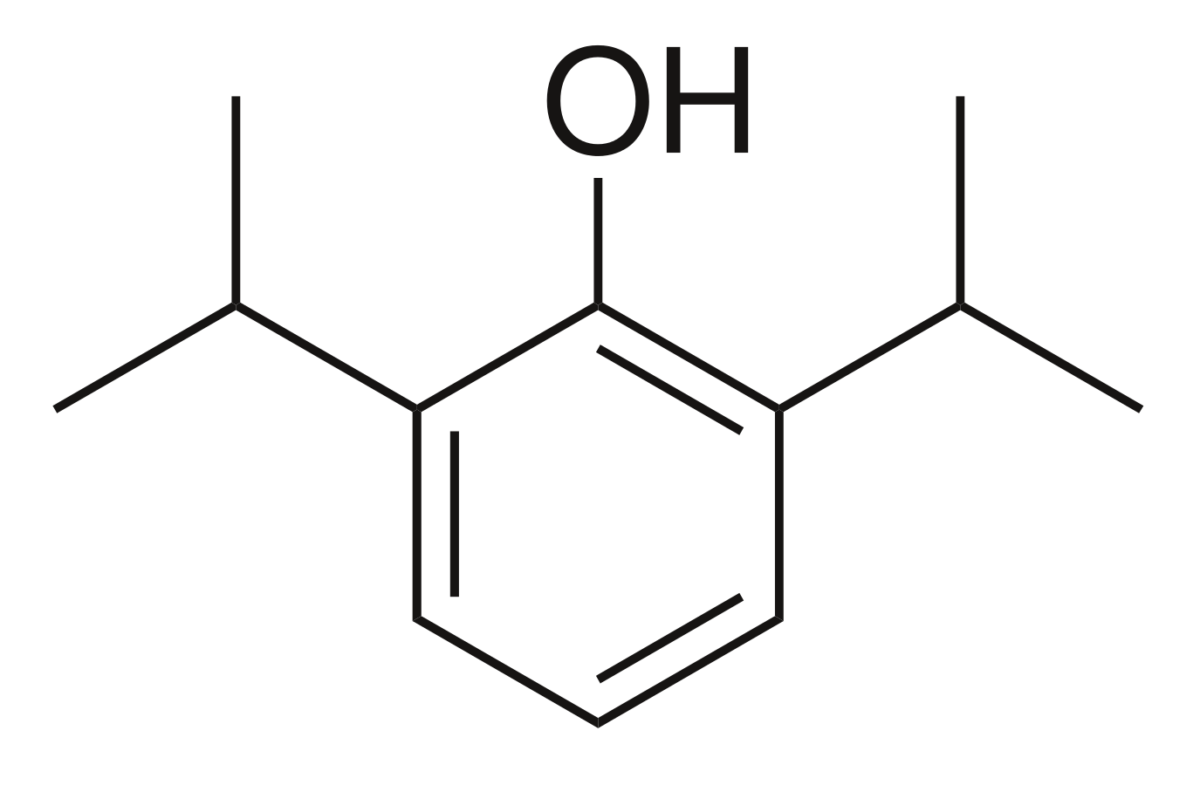
Estructura química del propofol
Imagen: “Propofol” por Harbin. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEfectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Contraindicaciones:
El síndrome de infusión de propofol Propofol An intravenous anesthetic agent which has the advantage of a very rapid onset after infusion or bolus injection plus a very short recovery period of a couple of minutes. Propofol has been used as anticonvulsants and antiemetics. Intravenous Anesthetics se produce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos con infusiones prolongadas de propofol Propofol An intravenous anesthetic agent which has the advantage of a very rapid onset after infusion or bolus injection plus a very short recovery period of a couple of minutes. Propofol has been used as anticonvulsants and antiemetics. Intravenous Anesthetics:
Presentación clínica:
Tratamiento:
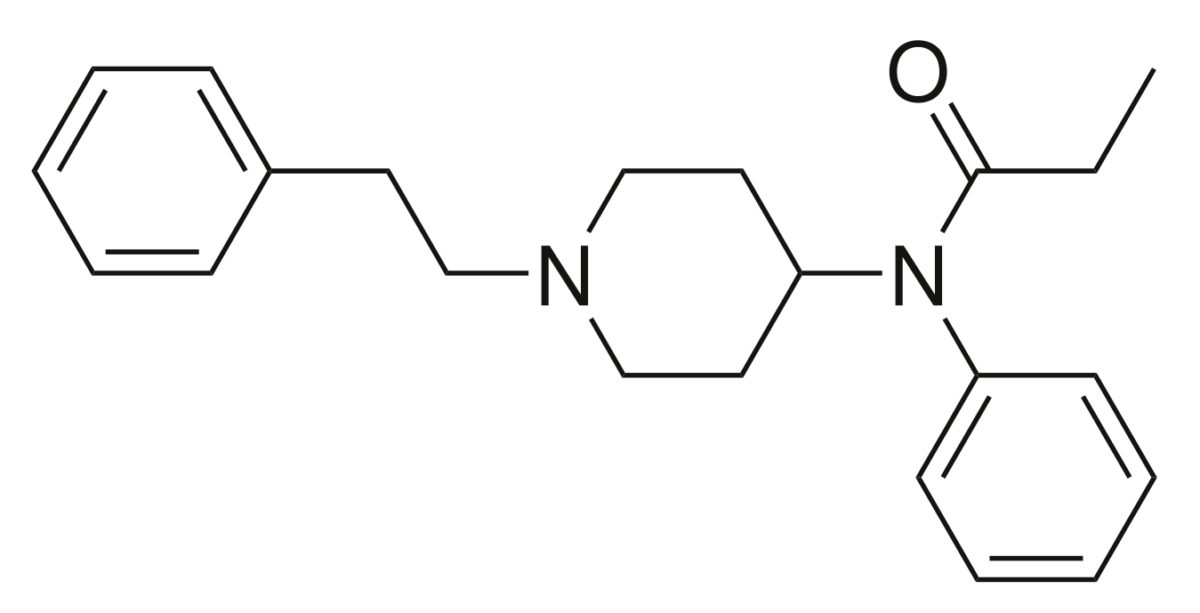
Estructura química del fentanilo
Imagen: “2D structure of fentanyl” por Harbin. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEfectos secundarios:
Interacciones medicamentosas:
Contraindicaciones:
Presentación clínica:
Tratamiento: