A neurofibromatose tipo 2 é uma doença neurocutânea que pode surgir de mutações no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics NF2 NF2 Neurofibromatosis type 2 is a neurocutaneous disorder that can arise from mutations in the NF2 gene located in chromosome 22 and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or occur from de novo mutations. The main clinical features are bilateral vestibular schwannomas, intracranial/spinal meningioma, and intramedullary and extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 localizado no cromossomo 22 e pode ser herdada de forma autossómica dominante ou ocorrer a partir de mutações de novo. As principais características clínicas são schwannomas vestibulares bilaterais, meningiomas intracranianos/espinhais e tumores espinhais intramedulares e extramedulares. Outras características podem incluir lesões oculares, como cataratas, lesões de pele e neuropatia periférica. O diagnóstico é clinico a partir da história e do exame físico e confirmado com RMN, testes Testes Gonadal Hormones moleculares e histopatologia. Recomenda-se a vigilância de tumores e o acompanhamento com rastreio de familiares em risco. O tratamento inclui intervenções cirúrgicas, radioterapia e/ou terapêutica com anticorpos monoclonais com bevacizumab Bevacizumab An anti-vegf humanized murine monoclonal antibody. It inhibits vegf receptors and helps to prevent pathologic angiogenesis. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A apresentação clínica da NF2 NF2 Neurofibromatosis type 2 is a neurocutaneous disorder that can arise from mutations in the NF2 gene located in chromosome 22 and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or occur from de novo mutations. The main clinical features are bilateral vestibular schwannomas, intracranial/spinal meningioma, and intramedullary and extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 pode variar amplamente entre indivíduos com mutações de novo e famílias portadoras de mutações genéticas. O início em idades mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome jovens está frequentemente associado a uma apresentação atípica com sintomas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome graves.
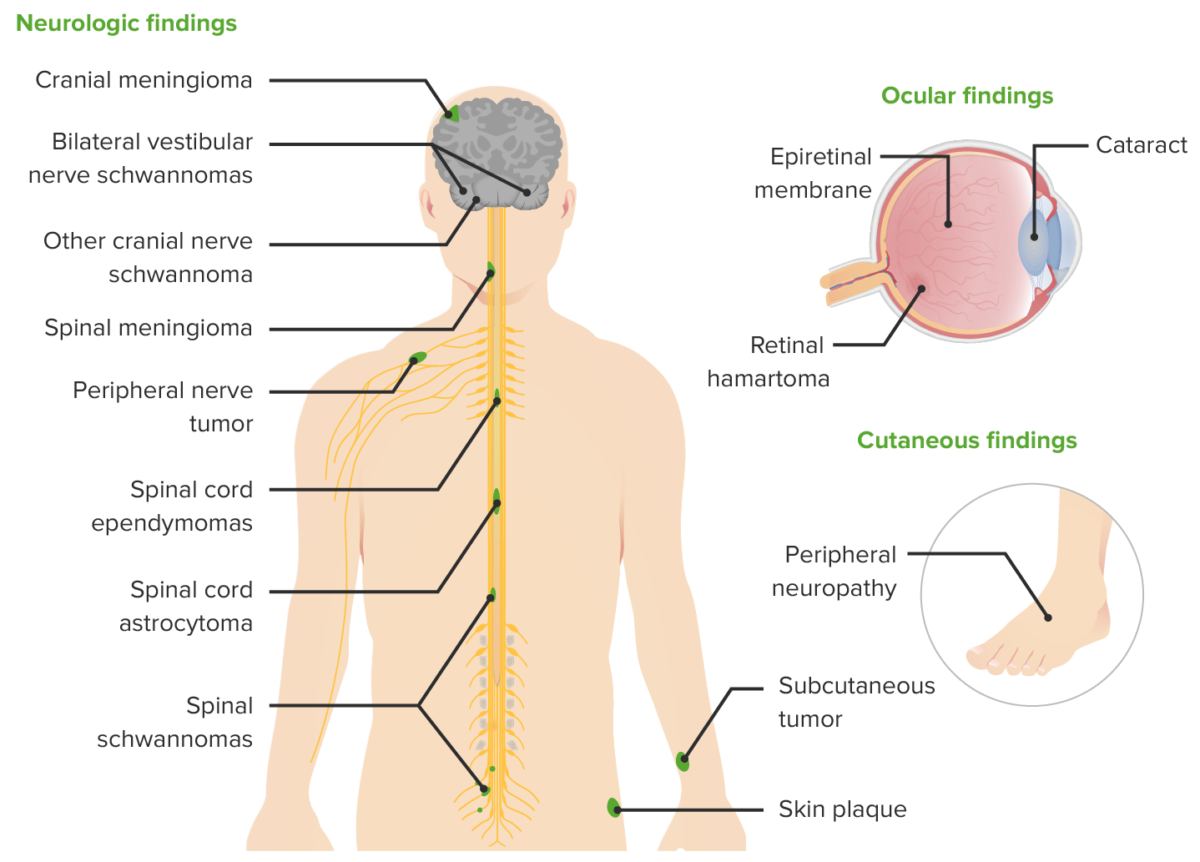
Manifestações clínicas da NF2
Imagem por Lecturio.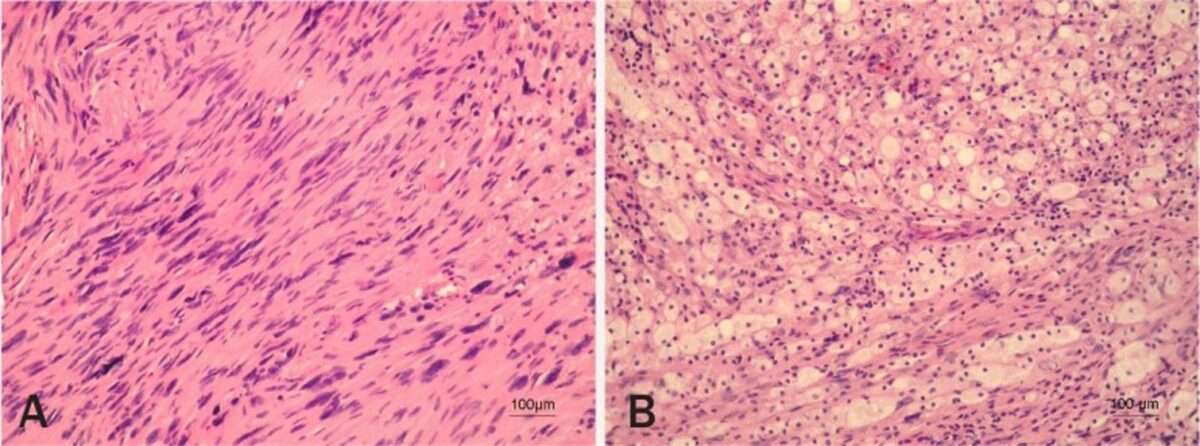
Histopatologia do Schwannoma Vestibular
Imagem: “Vestibular schwannoma” por Pećina-Slaus N, Zeljko M, Pećina HI, Nikuseva Martić T, Bacić N, Tomas D, Hrasćan R. Licença: CC BY 2.5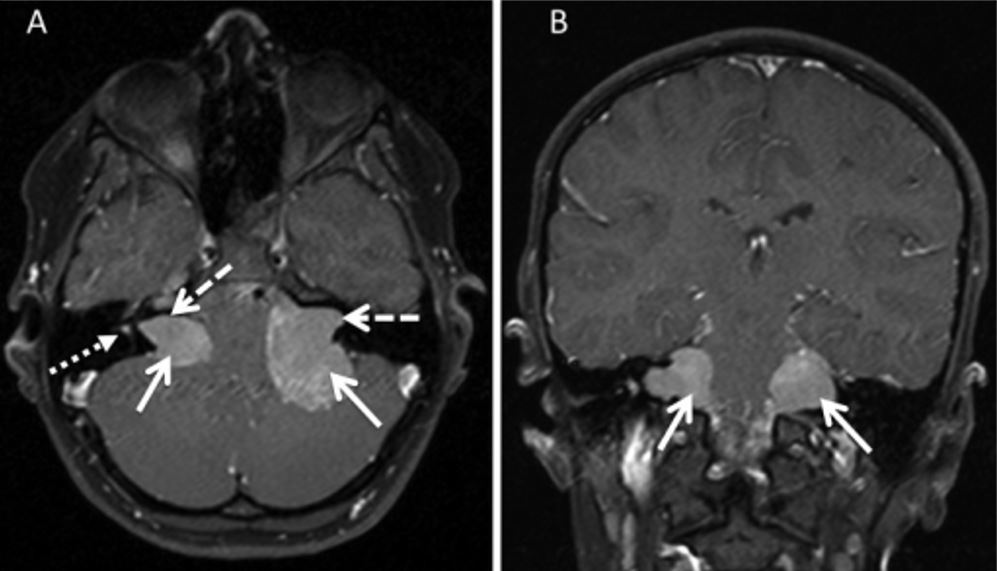
Schwannoma vestibular bilateral na RMN
Imagem: T1 spin echo sequences” por Stivaros SM, et al. Licença: CC BY 4.0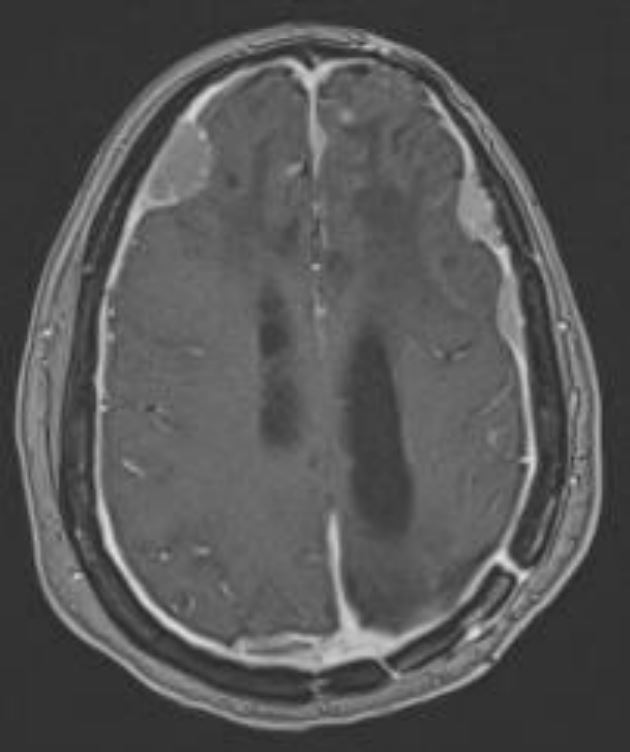
Meningioma intracraniano
Imagem de Roy Strowd, MD.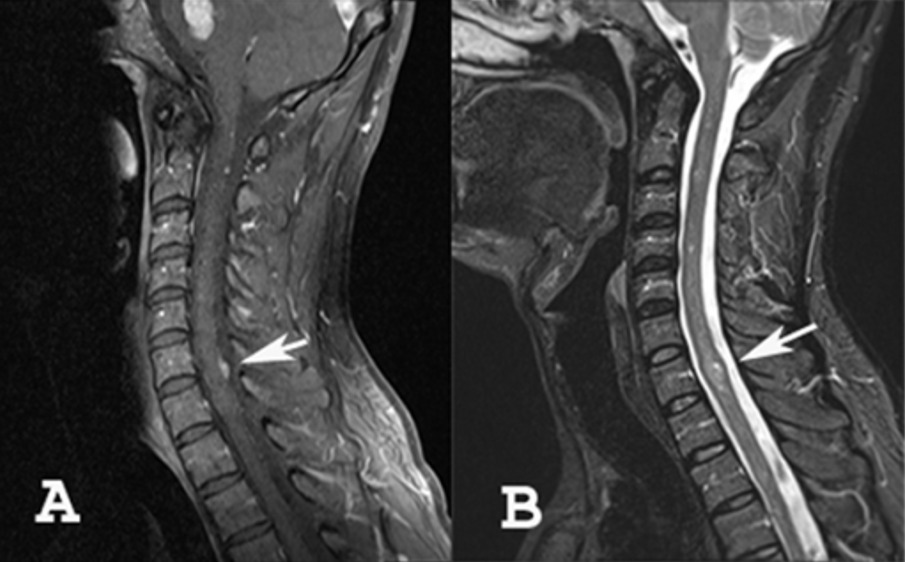
A: RMN a mostrar um meningioma da coluna cervical
B: RMN a mostrar um tumor intramedular (ependimoma ou astrocitoma)
A gestão da NF2 NF2 Neurofibromatosis type 2 is a neurocutaneous disorder that can arise from mutations in the NF2 gene located in chromosome 22 and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or occur from de novo mutations. The main clinical features are bilateral vestibular schwannomas, intracranial/spinal meningioma, and intramedullary and extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 é multidisciplinar e muitas vezes envolve contribuições de vários especialistas.