O interferão ( IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons) é uma citocina com propriedades antivirais (interfere com as infeções virais) e com vários papéis na imunoregulação. Os diferentes tipos são IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons tipo I (IFN-ɑ e IFN-β), IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons tipo II (IFN-ɣ), e IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons tipo III (IFN-ƛ). Os IFNs tipo I têm sido amplamente estudados; estas proteínas ligam-se aos recetores da superfície celular quando são estimulados por uma infeção viral. Após a estimulação, as vias são ativadas para produzir proteínas (por exemplo, ribonuclease Ribonuclease Enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester bonds within RNA. Interferons) que inibem a replicação viral. É criado um estado antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B tanto em células infetadas como nas não infetadas. O IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons Tipo I também tem propriedades antitumorais. A atividade antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B do IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons tipo II (IFN-ɣ) não é tão potente quanto a do tipo I, mas o IFN- ɣ é crucial na ativação de macrófagos. O recentemente descoberto IFN-ƛ destaca-se por ter atividade contra vírus intestinais. Com uma ampla gama de efeitos biológicos, os interferões são utilizados na terapêutica de doenças malignas, de infeções e outras doenças imunes (por exemplo, esclerose múltipla).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Os interferões são um grupo de proteínas pertencentes a uma classe de moléculas sinalizadoras conhecidas como citocinas e são libertados por uma variedade de células durante a resposta inflamatória.
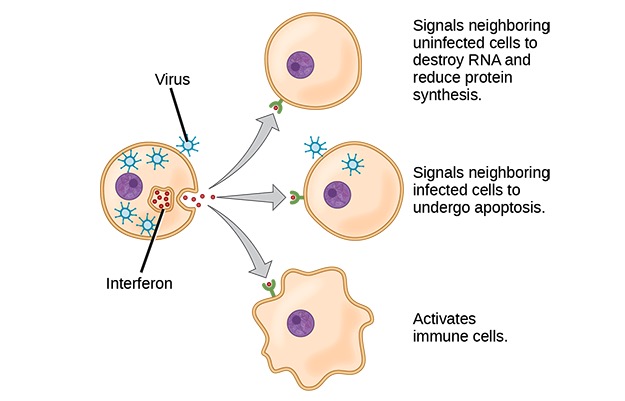
Interferões:
Os interferões são citocinas que são libertadas por células infetadas por um vírus, leucócitos e outras células imunitárias. Para limitar a infeção, as respostas das células ao interferão incluem inibição da síntese proteica, a ativação das células imunitárias e a indução de apoptose.
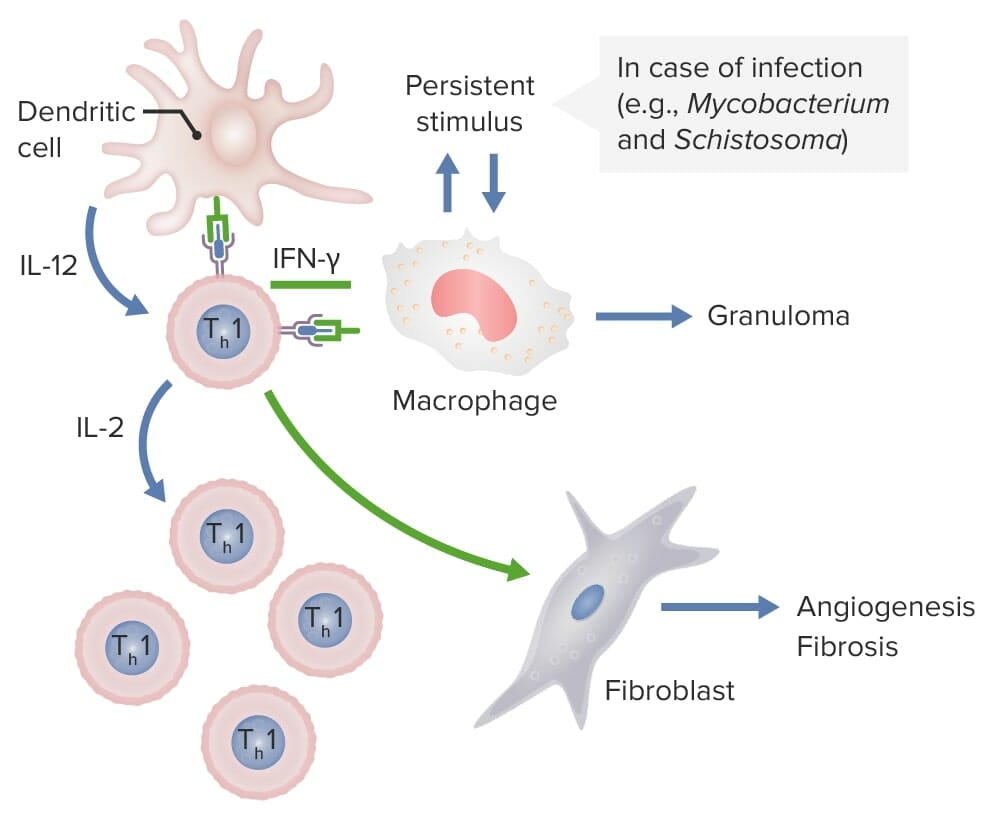
As células dendríticas libertam IL-12, o que ativa as células CD4 Th1. Estas células Th1 produzem IL-2, estimulando a produção de mais subconjuntos Th1 de linfócitos T. As células Th1 também libertam IFN-γ, o que ativa macrófagos e fibroblastos, que conduzem à angiogénese e à fibrose. Se esses macrófagos são persistentemente estimulados por agentes patogénicos como Micobacterium e Schistosoma, formam-se granulomas.
Imagem por Lecturio.| Outra designação | Localização cromossómica | Célula de origem | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-ɑ | Intrão-A | 9p22 | Leucócitos |
| IFN-β | IFN-b2 | 9p21 | Fibroblastos |
| IFN-ɣ | Fator ativador de macrófagos: interferão imunológico | 12q14 | Linfócitos, macrófagos, células NK, células dendríticas |
| IFN-ƛ | IL-28A, IL-28B IL-28A, IL-28B Interferons, IL-29, IFNA14 | 19q13.13 | Células epiteliais |
| Interferão | Doença(s) tratada(s) |
|---|---|
| Interferão-α |
|
| Interferão-β | Esclerose múltipla |
| Interferão-γ |
|