O fator de necrose tumoral ( TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), pela sigla em inglês) é uma citocina major, principalmente libertada por macrófagos em resposta a estímulos. Os fatores estimulantes incluem componentes microbianos, células mortas e lesões. Esta proteína pertence à superfamília do TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), um grupo de ligandos e recetores que desempenham funções de resposta inflamatória, morfogénese e proliferação celular. O fator de necrose tumoral interage com 2 recetores, que iniciam vias de transdução de sinal, causando diferentes respostas celulares (inflamação, sobrevivência celular ou apoptose). A ativação inadequada ou não restrita da sinalização do TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) produz inflamação crónica, como é possível observar em patologias autoimunes (e.g., artrite reumatóide, psoríase). O mecanismo de inibição do TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) tem sido utilizado no tratamento destas doenças inflamatórias.
Last updated: May 9, 2023
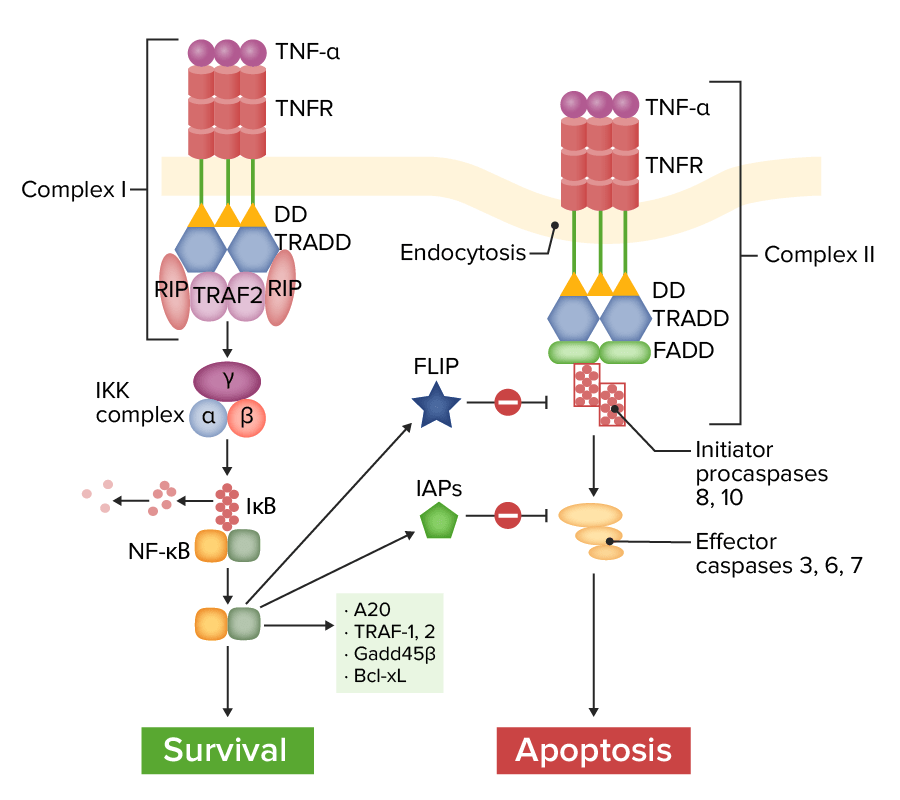
Via de sinalização do recetor 1 do fator de necrose tumoral (TNFR1, pela sigla em inglês):
Complexo I (à esquerda): Com a ligação do TNF-α, o TNFR recruta várias moléculas adaptadoras, resultando na ativação do fator nuclear kappa-B (NF-κB), que induz vários genes antiapoptóticos e sinais de sobrevivência. A proteína inibitória FLICE (FLIP) e o inibidor das proteínas da apoptose (IAPs) modulam e inibem a via da apoptose. Complexo II (à direita): Sem certas proteínas de adaptação (TRAF-2, RIP), o TNFR leva ao recrutamento de proteína associada ao domínio de morte Fas (FADD). A caspase-8 é ativada e libertada no citoplasma, ativando as caspases efetoras para induzir a apoptose.
IκB: inibidor de NF-κB
TRAF-2: recetor do fator associado ao TNF
RIP: proteína de interação do recetor
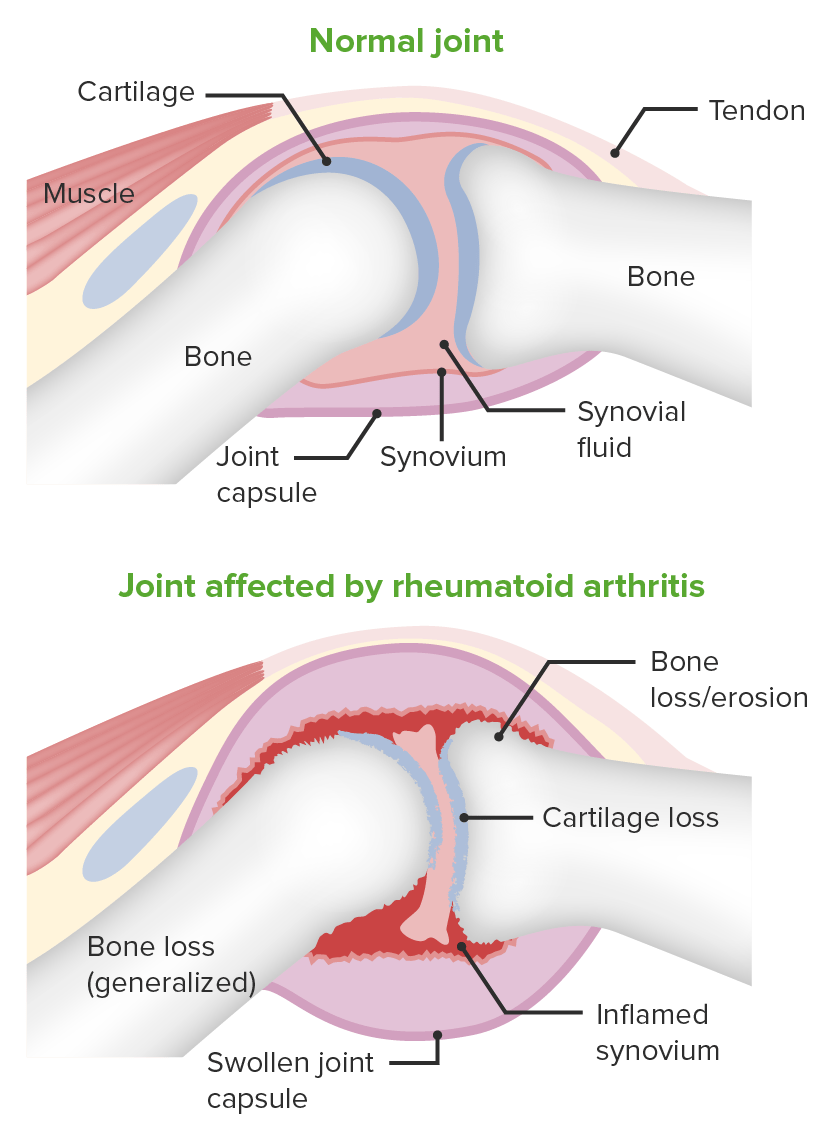
Imagem que demonstra a patologia da artrite reumatoide:
São mostradas as alterações no espaço articular
O fator de necrose tumoral apresenta múltiplos efeitos biológicos e, em certas condições (e.g., artrite reumatóide), foram observados níveis elevados de TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF). O mecanismo de inibição do TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) tem sido utilizado no tratamento de doenças inflamatórias.
| Tratamento anti-TNF | Mecanismo de ação | Indicações |
|---|---|---|
| Infliximab Infliximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody to tnf-alpha that is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticorpo quimérico recombinante (com uma região variável murina e uma região constante IgG1 humana) que se liga ao TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), impedindo a interação com o recetor |
|
| Etanercept Etanercept A recombinant version of soluble human tnf receptor fused to an IgG Fc fragment that binds specifically to tumor necrosis factor and inhibits its binding with endogenous tnf receptors. It prevents the inflammatory effect of tnf and is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis; psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Immunosuppressants | Proteína de fusão que se liga e neutraliza o TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) e a linfotoxina |
|
| Adalimumab Adalimumab A humanized monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to tnf-alpha and blocks its interaction with endogenous tnf receptors to modulate inflammation. It is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; psoriatic arthritis; Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticorpo monoclonal IgG1 humanizado que bloqueia a ligação do TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) aos recetores |
|
| Golimumab Golimumab Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticorpo monoclonal IgG1 humanizado com alta afinidade e especificidade para o TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
|
| Certolizumab Certolizumab Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticorpo monoclonal humanizado peguilado específico para o TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
|