Os agentes antivirais contra a gripe são importantes na prevenção e tratamento da infeção por influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza. A gripe é muitas vezes autolimitada, mas as populações de alto risco apresentam uma morbilidade e mortalidade significativas. Existem diferentes classes de fármacos que atuam sobre o vírus influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza. Os inibidores da neuraminidase Neuraminidase An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-2, 3, alpha-2, 6-, and alpha-2, 8-glycosidic linkages (at a decreasing rate, respectively) of terminal sialic residues in oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, colominic acid, and synthetic substrate. Antivirals for Influenza incluem oseltamivir Oseltamivir An acetamido cyclohexene that is a structural homolog of sialic acid and inhibits neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza (oral), zanamivir Zanamivir A guanido-neuraminic acid that is used to inhibit neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza (inalação) e peramivir Peramivir Antivirals for Influenza (IV); esta classe atua através da inibição da neuraminidase Neuraminidase An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-2, 3, alpha-2, 6-, and alpha-2, 8-glycosidic linkages (at a decreasing rate, respectively) of terminal sialic residues in oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, colominic acid, and synthetic substrate. Antivirals for Influenza, enzima envolvida na libertação de viriões recém-sintetizados pelas células infetadas pelo vírus Influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza. Ao bloquear o efeito enzimático, a libertação adicional do vírus para as células respiratórias adjacentes é reduzida. O baloxavir Baloxavir Antivirals for Influenza, um inibidor seletivo da endonuclease dependente de cap, inibe a síntese de mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3' end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure viral. Tanto os inibidores da neuraminidase Neuraminidase An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-2, 3, alpha-2, 6-, and alpha-2, 8-glycosidic linkages (at a decreasing rate, respectively) of terminal sialic residues in oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, colominic acid, and synthetic substrate. Antivirals for Influenza como o baloxavir Baloxavir Antivirals for Influenza têm atividade contra o vírus influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza e B. Os adamantanos, ou inibidores M2, incluem a amantadina e a rimantadina, que são ativos contra o vírus da influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza, mas pouco utilizados devido à sua resistência.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
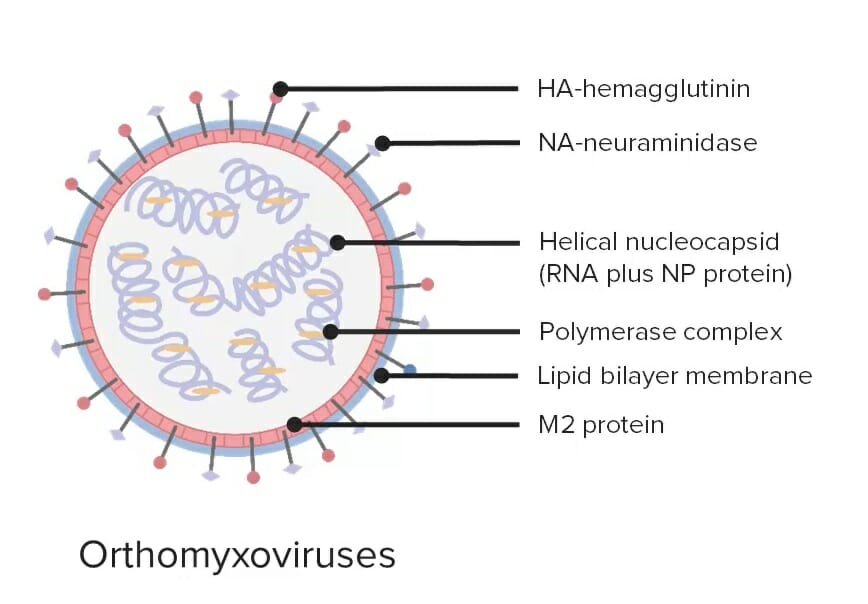
Um diagrama da estrutura do vírus Influenza
Imagem por Lecturio.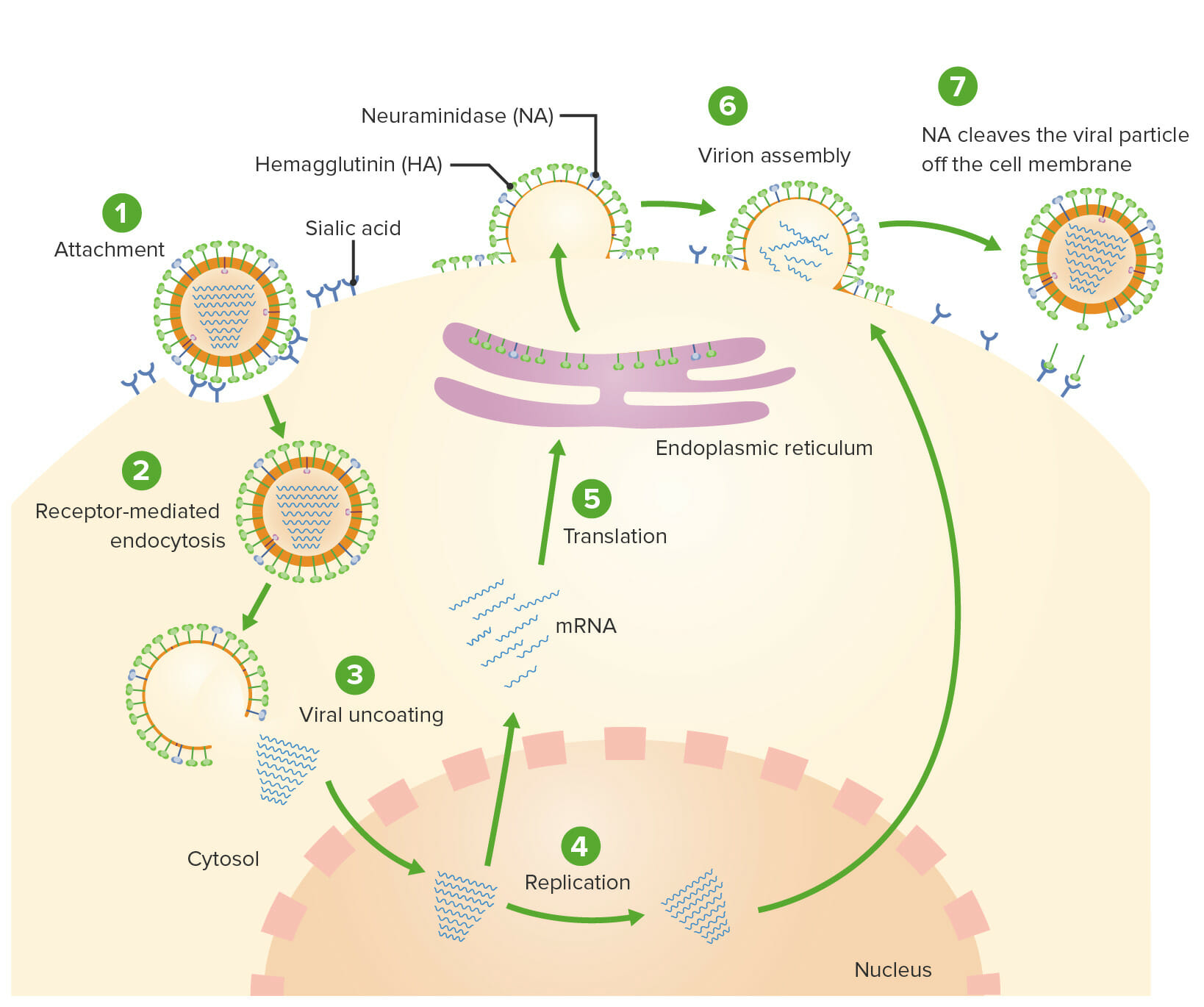
Replicação do vírus Influenza:
1: Uma partícula viral liga a sua hemaglutinina (HA) aos recetores contendo ácido siálico na superfície das células epiteliais respiratórias.
2: A partícula viral é internalizada via endocitose mediada por recetor.
3: Uma vez dentro da célula, a proteína M2 atua como um canal iónico, permitindo o influxo de partículas de hidrogénio, o que resulta na perda de revestimento (uncoating) do vírus.
4: O RNA viral move-se para o núcleo da célula, onde é replicado e se sintetiza RNA mensageiro (mRNA).
5: O mRNA é então traduzido em novas partículas virais usando a maquinaria celular.
6: As partículas virais e o RNA recém-replicado são levados à superfície celular e recompostos como viriões.
7: Conforme o novo vírus se destaca das células do epitélio respiratório, a hemaglutinina liga-se novamente a recetores contendo ácido siálico. A neuraminidase (NA) então quebra a ligação da nova partícula viral à célula epitelial respiratória, de forma a que possa infetar células próximas.
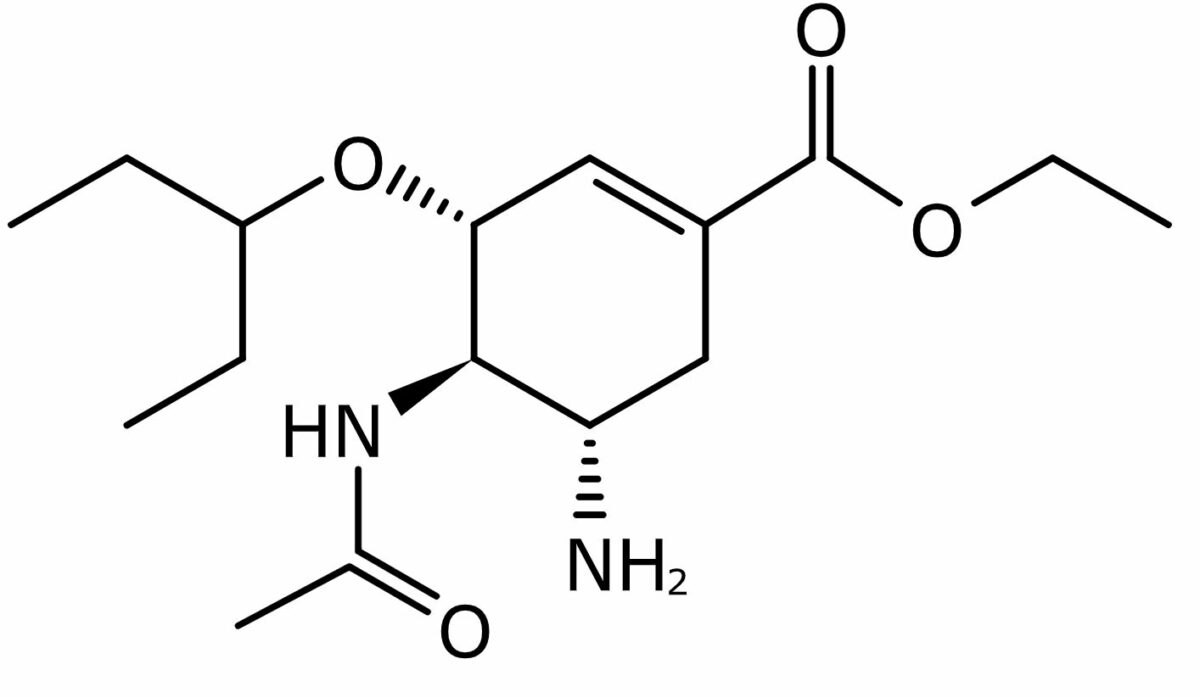
Oseltamivir, inibidor da neuraminidase
Imagem: “Oseltamivir” por BartVL71. Licença: Domínio Público
Peramivir, inibidor da neuraminidase
Imagem: “Peramivir” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público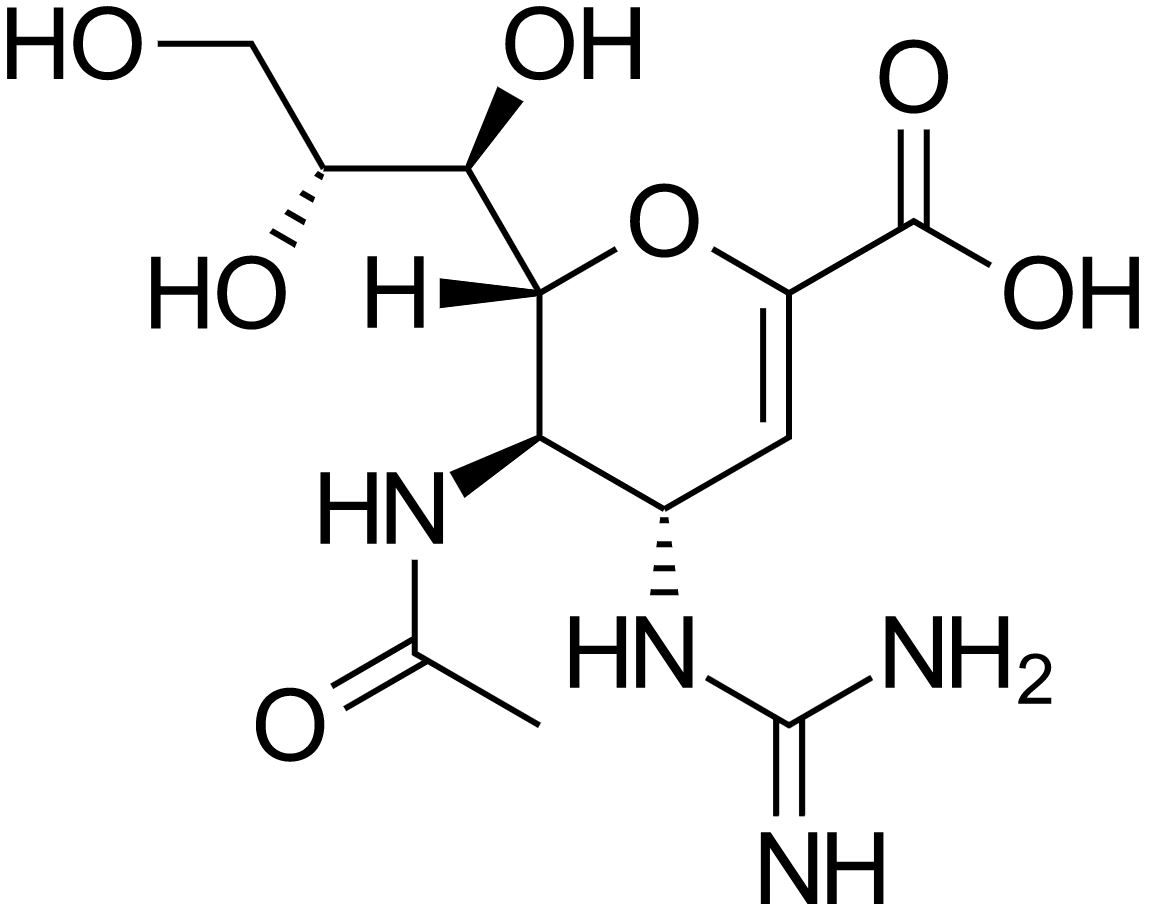
Zanamivir, inibidor da neuraminidase
Imagem: “Zanamivir structure” por Vaccinationist. Licença: Domínio Público| Categoria | Oseltamivir Oseltamivir An acetamido cyclohexene that is a structural homolog of sialic acid and inhibits neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza | Peramivir Peramivir Antivirals for Influenza | Zanamivir Zanamivir A guanido-neuraminic acid that is used to inhibit neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorção |
|
|
Inalação |
| Distribuição |
|
|
|
| Metabolismo | Sem metabolismo significativo | ||
| Excreção |
|
|
Até 15% absorvido e excretado na urina |
| Oseltamivir Oseltamivir An acetamido cyclohexene that is a structural homolog of sialic acid and inhibits neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza | Peramivir Peramivir Antivirals for Influenza | Zanamivir Zanamivir A guanido-neuraminic acid that is used to inhibit neuraminidase. Antivirals for Influenza | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
|
| Contraindicações |
|
|
|
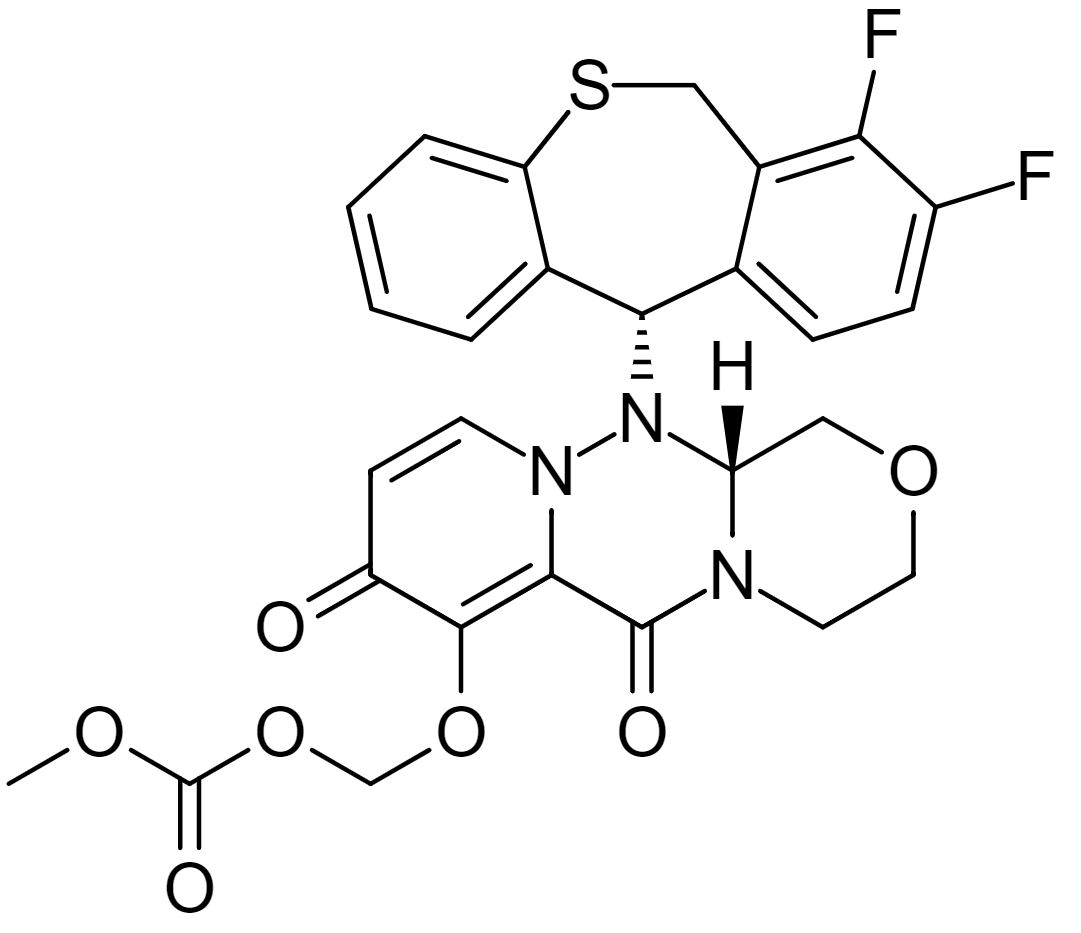
Estrutura química do baloxavir
Imagem: “Baloxavir marboxil” por Ed. Licença: Domínio Público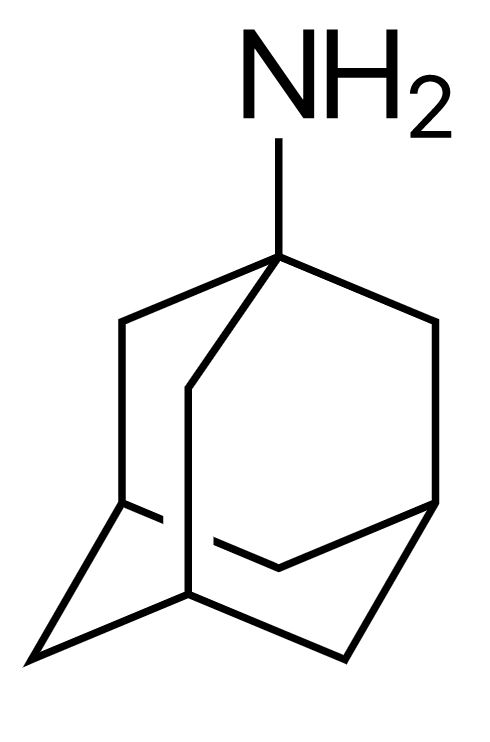
Estrutura da amantadina
Imagem: “Amantadine” por Ayacop. Licença: Domínio Público| Categoria | Amantadina | Rimantadina |
|---|---|---|
| Absorção | Boa biodisponibilidade oral | Boa biodisponibilidade oral |
| Distribuição |
|
|
| Metabolismo | Sem metabolismo significativo | Sofre metabolismo hepático |
| Excreção | Renal (excretado inalterado) | Renal |
| Inibidores da neuraminidase Neuraminidase An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-2, 3, alpha-2, 6-, and alpha-2, 8-glycosidic linkages (at a decreasing rate, respectively) of terminal sialic residues in oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, colominic acid, and synthetic substrate. Antivirals for Influenza | Baloxavir Baloxavir Antivirals for Influenza | Amantadina | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mecanismo de ação | Inibem a neuraminidase Neuraminidase An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-2, 3, alpha-2, 6-, and alpha-2, 8-glycosidic linkages (at a decreasing rate, respectively) of terminal sialic residues in oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, colominic acid, and synthetic substrate. Antivirals for Influenza, prevenindo a disseminação para células não infetadas | Inibidor da endonuclease, que impede a síntese de mRNA mRNA RNA sequences that serve as templates for protein synthesis. Bacterial mRNAs are generally primary transcripts in that they do not require post-transcriptional processing. Eukaryotic mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and must be exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Most eukaryotic mRNAs have a sequence of polyadenylic acid at the 3′ end, referred to as the poly(a) tail. The function of this tail is not known for certain, but it may play a role in the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus as well as in helping stabilize some mRNA molecules by retarding their degradation in the cytoplasm. RNA Types and Structure | Previne a atividade do canal M2, inibindo a perda do revestimento do genoma viral |
| Absorção |
|
Oral | Oral |
| Eliminação | Renal | Excreção biliar | Renal |
| Indicações | Prevenção e tratamento das gripes por influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza e B | Prevenção e tratamento das gripes por influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza e B | Tratamento e profilaxia da gripe por influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza (uso limitado devido às resistências) |
| Efeitos adversos relevantes |
|
Diarreia | Efeitos colaterais do SNC |