Viral Skin Infections in Patients with Darker Skin
by Ncoza DlovaViral skin infections represent a significant subset of dermatological conditions that affect patients across all age groups and backgrounds. These infections range from common, self-limiting conditions to potentially serious disorders requiring specific therapeutic interventions. Understanding these viral pathogens and their cutaneous manifestations is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate patient management in both primary care and specialist settings.
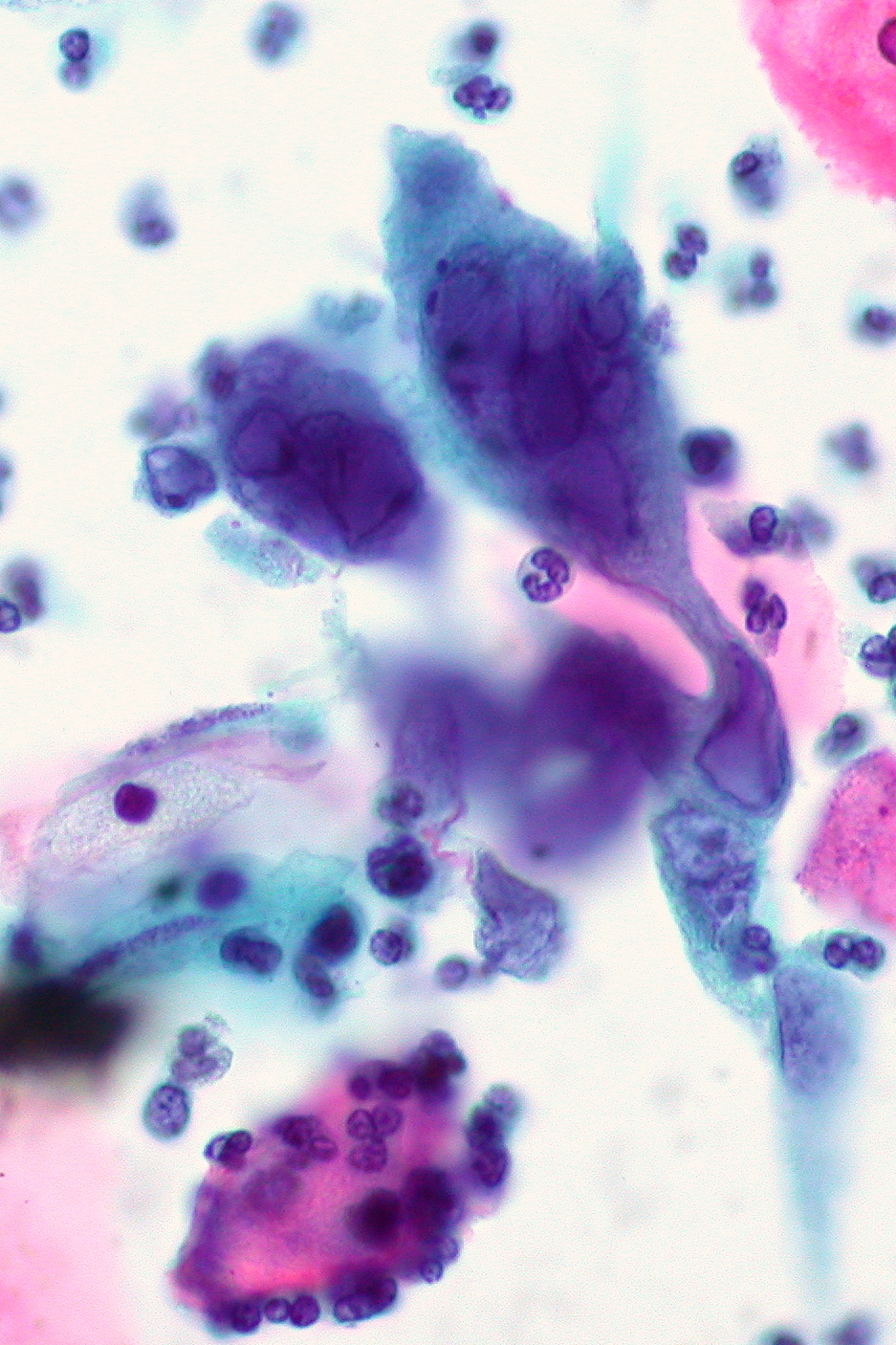
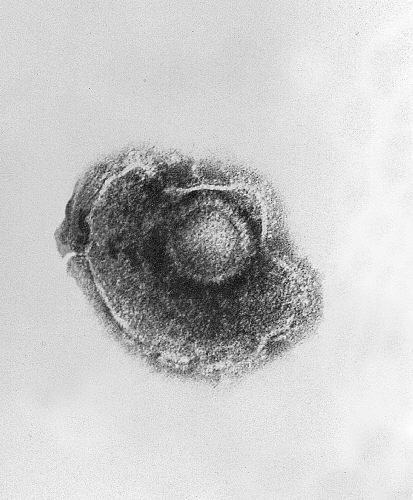
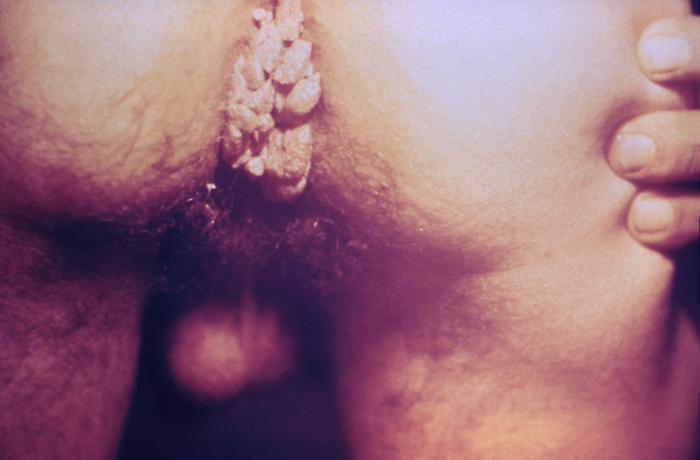
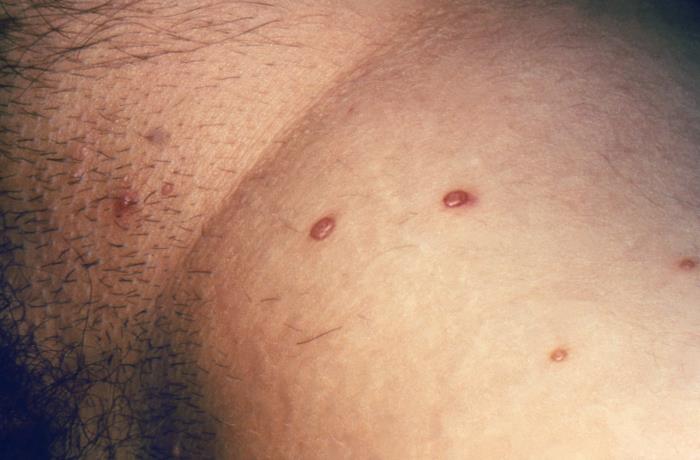
This course builds upon foundational knowledge in virology, immunology, and basic dermatology to explore the clinical spectrum of viral skin infections. Students will learn the underlying pathophysiology, characteristic presentations, diagnostic approaches, and evidence-based management strategies for key viral infections including herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, human papillomavirus, and molluscum contagiosum. The integration of basic science concepts with clinical reasoning skills will enable practitioners to recognize these conditions promptly, differentiate them from mimicking disorders, and implement appropriate treatment plans that improve patient outcomes.
This course builds upon foundational knowledge in virology, immunology, and basic dermatology to explore the clinical spectrum of viral skin infections. Students will learn the underlying pathophysiology, characteristic presentations, diagnostic approaches, and evidence-based management strategies for key viral infections including herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, human papillomavirus, and molluscum contagiosum. The integration of basic science concepts with clinical reasoning skills will enable practitioners to recognize these conditions promptly, differentiate them from mimicking disorders, and implement appropriate treatment plans that improve patient outcomes.
Course Details
- Videos 5
- Duration 0:30 h
- Quiz questions 16
- Concept Pages 3