Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Molluscum Contagiosum in Darker Skin
-
Slides Molluscum Contagiosum in Darker Skin.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
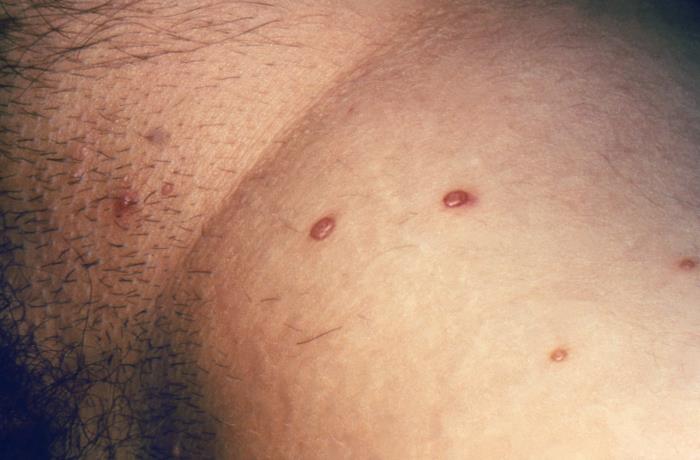
00:01 Welcome to our lecture on Molluscum Contagiosum. 00:06 Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection which is caused by Molluscum contagiosum virus, and this is a member of the Poxvirus family. It's more prevalent in tropical areas as well as overcrowded environments. 00:26 Those who are primarily affected are usually young children and sexually active adults. It can also affect immunosuppressed individuals, for example, those who have HIV cancer patients and on immunosuppressant drugs, as well as patients with a background of atopic dermatitis. 00:49 There are four major genotypes molluscum contagiosum virus 1 and 2 are the most common ones. 01:00 Infection is by direct skin-to-skin contact. 01:05 Also, it could be through inoculation, for example scratching or touching a lesion. It can also be true sexual transmission. 01:18 So how does molluscum contagiosum virus present? It can present with chronic or localized infection. 01:28 Once this firm, dome shaped papules It can also present with a shiny surface and central indentation, or what we call umbilication. 01:39 In darker skin colors, it may present with flesh or skin colored lesions with less erythema. 01:48 It may appear anywhere on the body except the palms and soles. 01:53 The common areas of involvement include the axillae, the trunk, antecubital region, the lower abdomen, genital region, and proximal thighs. 02:05 If it's multiple lesions, these may develop in intertriginous areas like the axillae and intercrural region. 02:14 It's also common, as I mentioned in people with a background history of atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis. 02:24 Giant molluscum usually is a large lesion up to 1 to 5 to 1.5cm in diameter. These lesions, which are up to 1.5cm in diameter, are usually seen in HIV positive or otherwise immunocompromised patients. 02:44 So in resolution, a characteristic molluscum dermatitis may be seen. 02:49 This is a sign that the molluscum contagiosum virus virus lesion is resolving. So you see erythema or dusky red erythema around the lesion of molluscum. 03:04 Complications include irritation, inflammation, and sometimes secondary infection. 03:11 If one has peri orbital lesions or lesions around the eyelids, it can cause conjunctivitis. 03:18 So do look for this complication. 03:21 It can also progress to cellulitis in HIV infected patients or those who are immunocompromised. 03:29 The diagnosis of Molluscum contagiosum virus is usually clinical, so clinical examination and history are usually enough for the diagnosis. Dermoscopy is also used by dermatologists looking for typical features of Molluscum contagiosum virus. 03:48 However, you need training to be able to detect this. 03:53 Skin biopsy is useful to confirm the clinical diagnosis when in doubt. So on histology, this is what we usually see. Keratinocytes with eosinophilic cytoplasm inclusion bodies. And these are known as molluscum contagiosum bodies or Henderson-Paterson bodies. 04:15 The differential diagnosis of Molluscum contagiosum virus includes Cryptococcus, which we see mainly in immunocompromised patients. Histoplasmosis is another differential diagnosis. 04:29 And lastly, it may look like basal cell carcinoma. 04:32 We've covered the differential diagnosis. 04:35 Now how do we treat patients with molluscum contagiosum virus infection. 04:40 It's usually a self-limited disease that heals spontaneously after several months. But many times the parents will want you to intervene or patients may want it to be treated. 04:50 So for young, immunocompetent children, especially those with numerous lesions, the most practical course may be to allow for spontaneous resolution. For adults with sexually transmitted molluscum and those with immunocompromised status, treatment is usually recommended. For topical agents, we can use cantharidin. This is applied directly on lesions. 05:19 The site is then covered with a plaster and should be washed off with soap and water after 2 to 6 hours. 05:28 The procedure can then be repeated every 2 to 4 weeks until the lesions clear. 05:34 The other option is to use tretinoin, which is vitamin A and a topical retinoid, which is applied on the lesion. 05:43 Trichloroacetic acid 100% concentration has also been found to be defective in some patients. 05:52 In terms of mechanical treatment, cryotherapy is another treatment option. 05:57 We use a spray gun which contains liquid nitrogen. 06:01 The spray gun is positioned at about 1 to 1.5 centimeters above the center of the skin lesion, and it's sprayed until an ice ball covers the lesion. 06:11 Apply two freeze thaw cycles, and this may be repeated weekly until the lesion clears. 06:20 Curettage and cautery is another option of treatment. 06:23 This is a type of electrosurgery in which a skin lesion is scraped off, and heat is applied to the skin surface. 06:31 In darker skinned prototypes, always remember there may be hypo or hyperpigmentation post-treatment, and always discuss this side effect with the patient so that they can anticipate it.
About the Lecture
The lecture Molluscum Contagiosum in Darker Skin by Ncoza Dlova is from the course Viral Skin Infections in Patients with Darker Skin.
Included Quiz Questions
Which virus family is responsible for causing Molluscum contagiosum?
- Poxvirus
- Papillomavirus
- Herpesvirus
- Polyomavirus
- Adenovirus
What is the characteristic feature that helps distinguish Molluscum contagiosum lesions from other viral skin infections?
- Central umbilication (indentation)
- Linear arrangement along scratch marks
- Vesicular fluid-filled appearance
- Dermatomal distribution pattern
- Yellow crusting on the surface
Which of the following conditions increases the risk of developing Molluscum contagiosum infection?
- Atopic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Vitiligo
- Acne vulgaris
What clinical sign indicates that a Molluscum contagiosum lesion is beginning to resolve?
- Development of erythema around the lesion (molluscum dermatitis)
- Development of a black eschar at the center
- Transition from dome-shaped to flat appearance
- Sudden increase in lesion size
- Formation of a keratotic plug on the surface
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |