Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hepatitis Treatment – Antiviral Drugs
-
Slides Hepatitis Treatment Antiviral Drugs.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
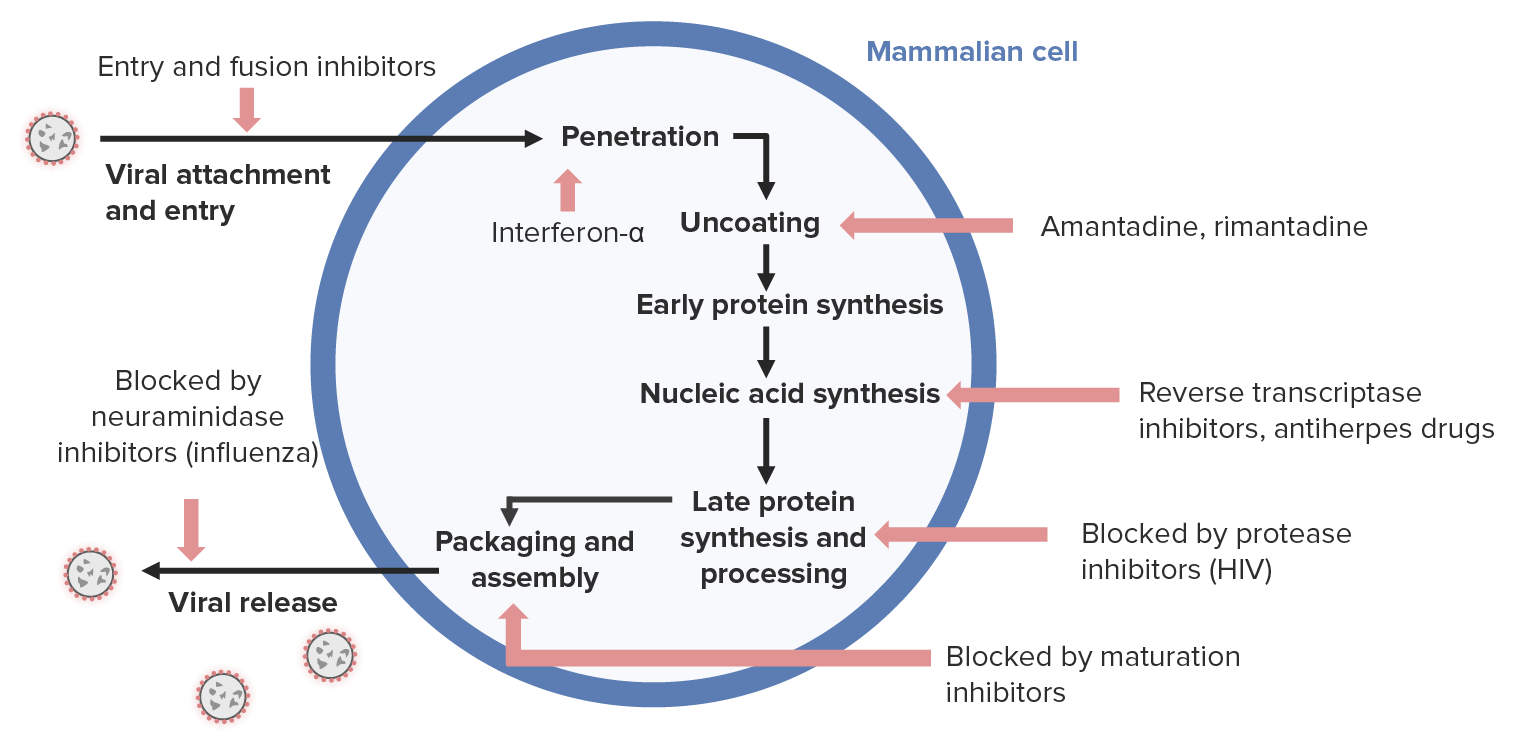
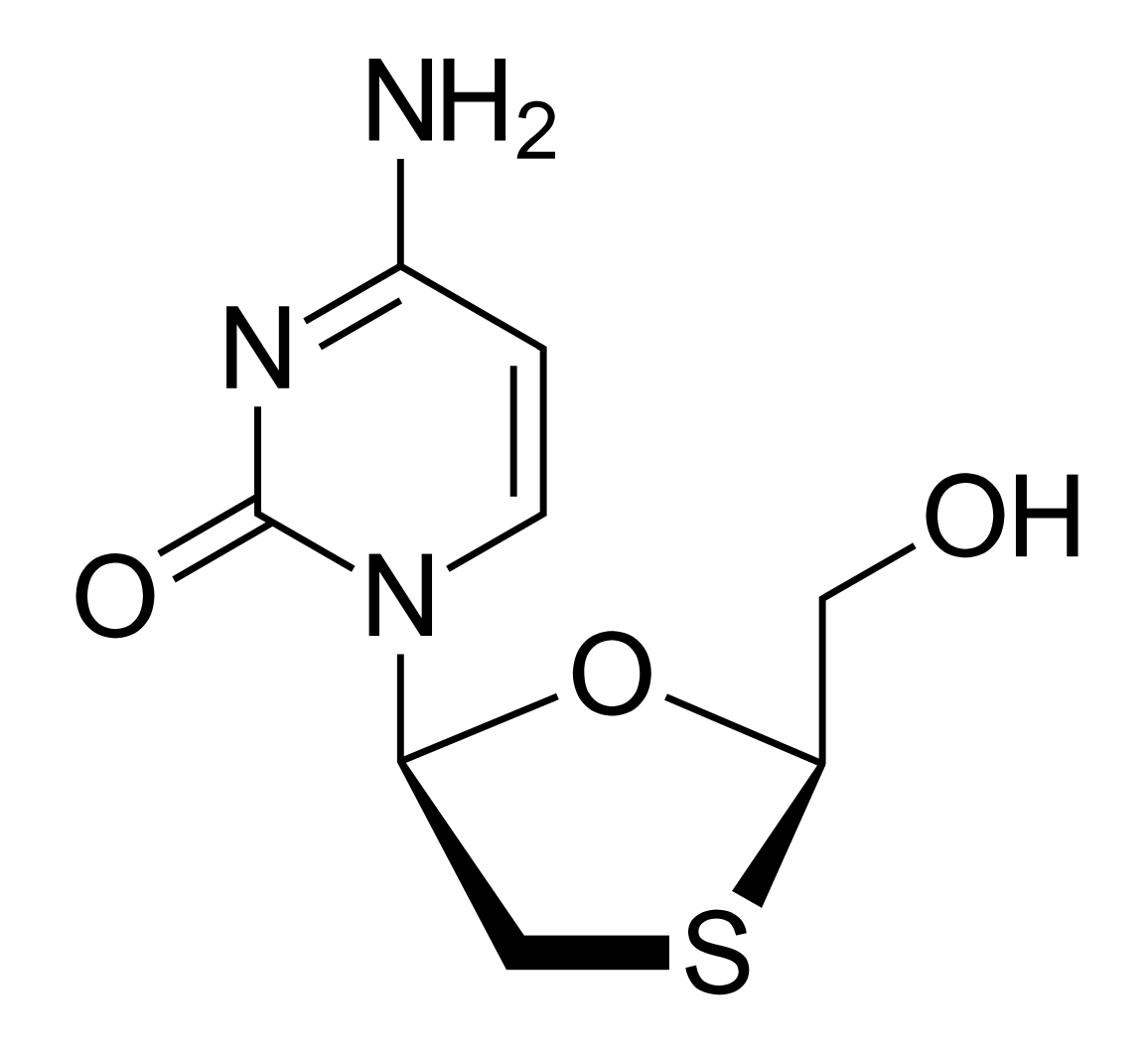
00:00 Let's move on to anti-hepatitis drugs. 00:03 Now the anti-hepatitis drugs really the main say of therapy has been the interferon alpha agents. 00:12 Now interferon alpha seems to work in viral penetration. 00:16 And by inhibiting viral penetration, you are inhibiting probably the first or second step in viral replication. 00:23 Anti-hepatitis B drugs are suppressive not curative. 00:28 So we are not necessary curing the patient with hepatitis B. 00:32 Anti-hepatitis C drugs are targeted for viral eradication. 00:38 And in fact we have seen eradication in many patients. 00:40 Let's talk about interferon alpha. 00:45 Now interferon alpha is a cytokine. 00:48 And it acts through the Janus kinases. 00:51 So Janus was mythical god, who had two heads. 00:58 And so we talk about Janus kinases as being those agents that seem to have a whole bunch of faces to them. 01:05 Now the Janus kinase is phosphorylate STAT that stands for Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription. 01:13 So we call these JAK STAT receptors. 01:18 And you can see the JAK portion down at the bottom. 01:21 Now this causes an increase production of antiviral proteins. 01:26 There is a specific activation of ribonuclease that degrades the viral messengerRNA when you activate these agents. 01:35 This promotes the formation of natural killer cells that destroy infected liver cells. 01:39 So that's why interferon alpha is such an important component of our immune system. 01:45 Now, intramuscular injections, interferon alpha are usually how we administer this medication. 01:52 The formulations vary from time and place. 01:56 Now the absorption is relatively slow. 01:59 It's given about two or three times per week. 02:01 We do have something called pegylated forms that can be given once a week. 02:06 Pegylated forms are first to encasing the inferon in certain types of almost mycells or liposomes. 02:13 The elimination is through hydrolysis and proteolysis in the kidney. 02:18 In terms of where we use these medications, they are most commonly used in chronic hepatitis B. 02:24 In less common uses, we've used it in Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV patients. 02:31 We've also used in papillomatosis and genital warts as well. 02:34 Although that's actually much less commonly used. 02:39 Now I have another category here called "Others" under anti-hepatitis drugs. 02:44 It's actually quite a large category. 02:46 Now we already spoke about interferon alpha. 02:49 So I'm not going to go through it again. 02:51 Now the other drugs that we use with hepatitis includes the DNA polymerase agents, the nucleoside inhibitors, the broad spectrum replication inhibitors and another set of drugs that I just call miscellaneous. 03:07 Let's take a look at the DNA polymerase inhibitors. 03:10 The prototypical drug of the DNA polymerase inhibitors is adefovir. 03:17 It inhibits DNA polymerase of hepatitis B virus which results in chain termination of -- results in chain termination after incorporation of the virus into the cell. 03:29 It has good oral bioavailability and it's unaffected by foods. 03:34 You can do dose reduction in renal dysfunction because it is excreted by the kidney. 03:39 It works quite well against viruses that are resistant to lamivudine which is another antiviral agent that I'll talk about. 03:50 In fact let's talk about lamivudine now. 03:52 It's a nucleoside inhibitor. 03:55 And if you recall nucleoside inhibitors are working on that very important step of nucleic acid synthesis. 04:01 It inhibits HIV reverse transcriptase. 04:04 It's a very long acting agent in hepatitis B infected cells. 04:08 Compared to say it's limited activity in HIV infected cells. 04:14 It's often used as monotherapy in hepatitis B. 04:19 It's relatively non-toxic and it causes a rapid suppression of hepatitis B viruses. 04:27 Other agents that are active against hepatitis include the broad spectrum replication inhibitors. 04:35 We also know this is ribavirin and it's actually quite a well known drug. 04:40 It inhibits replication of a wide range of DNA and RNA. 04:45 It effects influenza A and B. 04:48 It effects parainfluenza and respiratory syncytial virus. 04:53 It also is active against paramyxoviruses and hepatitis C as well as HIV. 04:59 In terms of the mechanisms of action, we're not entirely sure how this particular drug works. 05:06 We'll believe that it acts directly with guanine triphosphate to somehow cause an inhibition and capping of the viral messengerRNA. 05:13 It also blocks RNA dependent polymerases which is why we use it so often. 05:20 Now in terms of using this medication, remember that in order to improve it's absorption we actually want more acidity in the stomach. 05:32 So we tend to tell patients to avoid antacids when you're taking ribavirin. 05:37 It's eliminated by the kidney so we have to act dose reductions if there is renal failure. 05:43 We often use it with interferon alpha in chronic hepatitis C. 05:48 Remember that monotherapy with this particular agent is not very effective. 05:54 In terms of toxicity, there's a dose dependent hemolytic anemia that's associated with this drug. 06:00 And it is contraindicated in pregnancy. 06:05 Miscellaneous drugs use to treat hepatitis patients include the following. 06:12 Now we have nucleoside analogs that work against DNA polymerase. 06:20 We have agents that are approved for lamivudine resistance. 06:26 We have agents that inhibit RNA polymerase. This particular agent is quite active in hepatitis C virus. It is used in conjunction with ledipasvir to treat chronic hepatitis C infection. 06:37 Boceprevir is also a protease inhibitor and it's used with ribavirin as well.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hepatitis Treatment – Antiviral Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- INF-alpha
- Nucleoside Inhibitors
- Broad sprectrum Replication Inhibitors
- Miscellaneous
Included Quiz Questions
Which anti-hepatitis drug is a nucleoside inhibitor?
- Lamivudine
- Adefovir
- Interferon
- Tenofovir
Which statement regarding adefovir is NOT correct?
- It does not work against lamivudine-resistant strains of HBV.
- It has good oral bioavailability.
- It inhibits HBV DNA polymerase.
- Dose reduction is required in renal dysfunction.
- It results in chain termination after incorporation.
A patient comes to you with a chronic hepatitis C infection. He also has peptic ulcer disease and for which he is taking proton pump inhibitors. Which drug would you NOT prescribe?
- Ribavirin
- Adefovir
- Entecavir
- Tenofovir
- Lamivudine
Which anti-hepatitis drug is contraindicated in pregnancy?
- Ribavirin
- Lamivudine
- Zidovudine
- Emtricitabine
- Tenofovir
Customer reviews
3,7 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
1 |
3 customer reviews without text
3 user review without text