El sarampión (también conocido como rubéola) es causado por un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del ARN monocatenario, lineal y de sentido negativo de la familia Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus y del género Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus. Es altamente contagioso y se transmite solo entre los LOS Neisseria humanos a través de gotitas respiratorias o transmisión por contacto directo de una persona infectada. Por lo general, una enfermedad de la infancia, el sarampión comienza clásicamente con tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, coriza y conjuntivitis, seguidas de una erupción maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination. Las complicaciones incluyen diarrea, neumonía y encefalitis. El sarampión se puede prevenir mediante la vacunación y, gracias a esto, se había erradicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran parte hasta los LOS Neisseria últimos años. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se tratan con cuidados de apoyo, aunque en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes seleccionados pueden estar indicados los LOS Neisseria antivirales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARNm.
Representación gráfica tridimensional de una partícula del virus del sarampión de forma esférica
Imagen: “21074” por Allison M. Maiuri. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoAl AL Amyloidosis menos 1 complicación ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 30% de los LOS Neisseria casos:
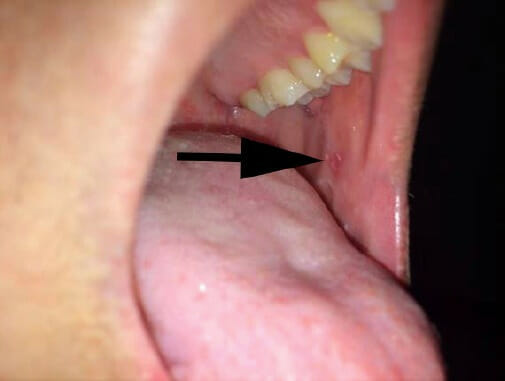
Un individuo con sarampión que muestra manchas de Koplik
Imagen: “Koplik spots” por Michael J Burns. Licencia: CC BY 4.0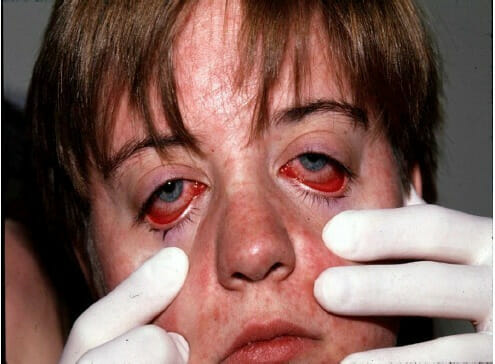
Un niño con conjuntivitis no purulenta y erupción facial por sarampión
Imagen: “Nonpurulent conjunctivitis and facial rash of measles one day after rash began” por Michael J Burns. Licencia: CC BY 4.0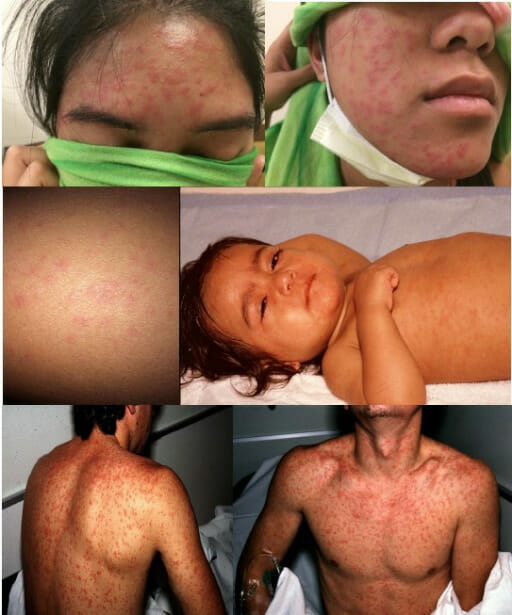
Erupción por sarampión
Imagen: “Measles rash” por Michael J Burns. Licencia: CC BY 4.0La enfermedad se diagnostica por sospecha clínica seguida de pruebas de laboratorio de confirmación. Los LOS Neisseria casos sospechosos deben aislarse hasta que se confirmen.
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus del sarampión |
|
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
Debido a cepas de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que producen toxina epidermolítica (exfoliativa) |
|
| 5ta enfermedad | Eritema infeccioso | Eritrovirus o parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (eritroparvovirus 1 de primates) |
|
| 6ta enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del herpes humano 6B o 7 |
|