El alcohol es una de las sustancias adictivas más utilizadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mundo. El trastorno por consumo de alcohol se define como el consumo patológico de alcohol que conduce a un deterioro del funcionamiento diario. La intoxicación aguda por alcohol se presenta con deterioro de las funciones motoras y del habla y puede tratarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos con cuidados de soporte. La abstinencia del consumo crónico de alcohol puede tener consecuencias fatales, como delirio y convulsiones y se trata con benzodiacepinas. El trastorno por consumo de alcohol crónico afecta a casi todas las partes del cuerpo humano y tiene un impacto grave en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la salud mental y física de una persona. El trastorno por consumo de alcohol se puede controlar con psicoterapia y medicamentos; sin embargo, el pronóstico suele ser malo, con altas tasas de recaída y complicaciones.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El trastorno por consumo de alcohol es un patrón crónico (> 12 meses) problemático de consumo de alcohol que causa una angustia significativa.
Existen diversas definiciones de diferentes organizaciones para la clasificación del consumo de alcohol.
Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas de la intoxicación aguda por alcohol difieren según el nivel de alcohol en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre.
Intoxicación leve:
Intoxicación moderada:
Intoxicación severa:
Diagnóstico:
Evaluación del Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol (CIWA-A):
Diagnóstico:
| Signos y síntomas | Ingesta más reciente | |
|---|---|---|
| Leve |
|
6–24 horas |
| Convulsiones | Convulsiones tonicoclónicas generalizadas (únicas o múltiples) | 12–48 horas |
| Alucinaciones | Predominantemente visuales (también pueden ocurrir de otros tipos) | 12–48 horas |
| Delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium tremens |
|
> 48 horas |
El tamizaje del abuso de alcohol debe incorporarse a las visitas de rutina.
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Características |
|---|---|---|
| Naltrexona | Antagonistas de los LOS Neisseria receptores de opioides |
|
| Acamprosato | Modula la transmisión de glutamato |
|
| Disulfiram | Inhibe la aldehído deshidrogenasa |
|
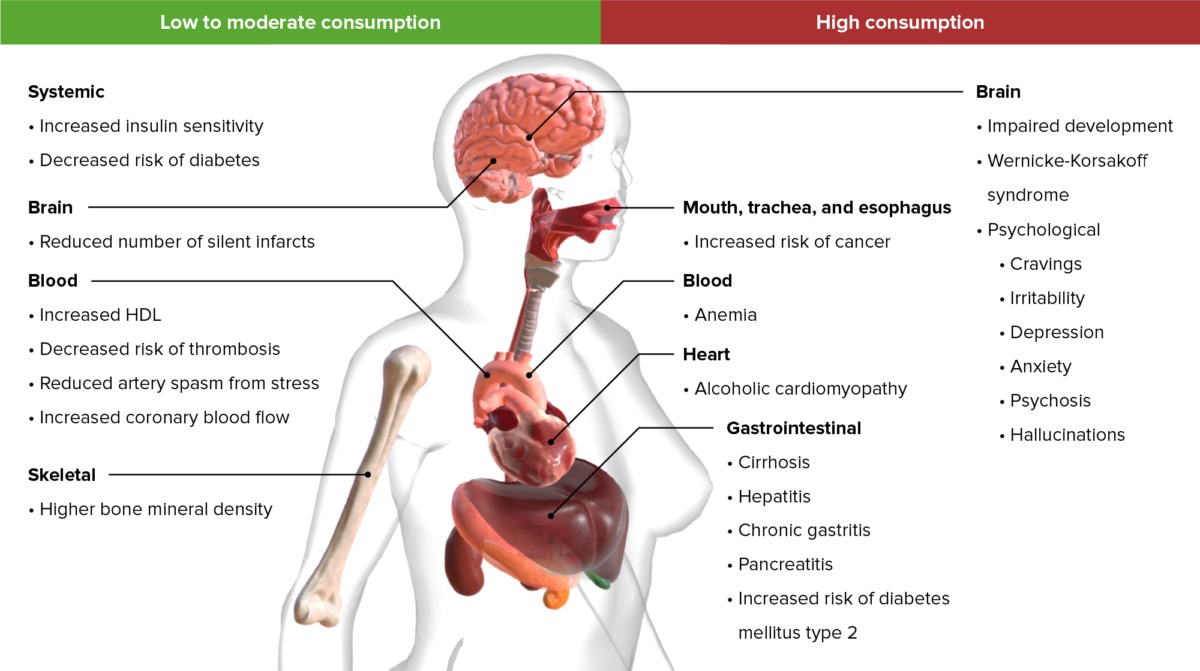
Efectos importantes a largo plazo resultantes de un consumo bajo o alto de alcohol
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioConsumo de alcohol durante el embarazo: