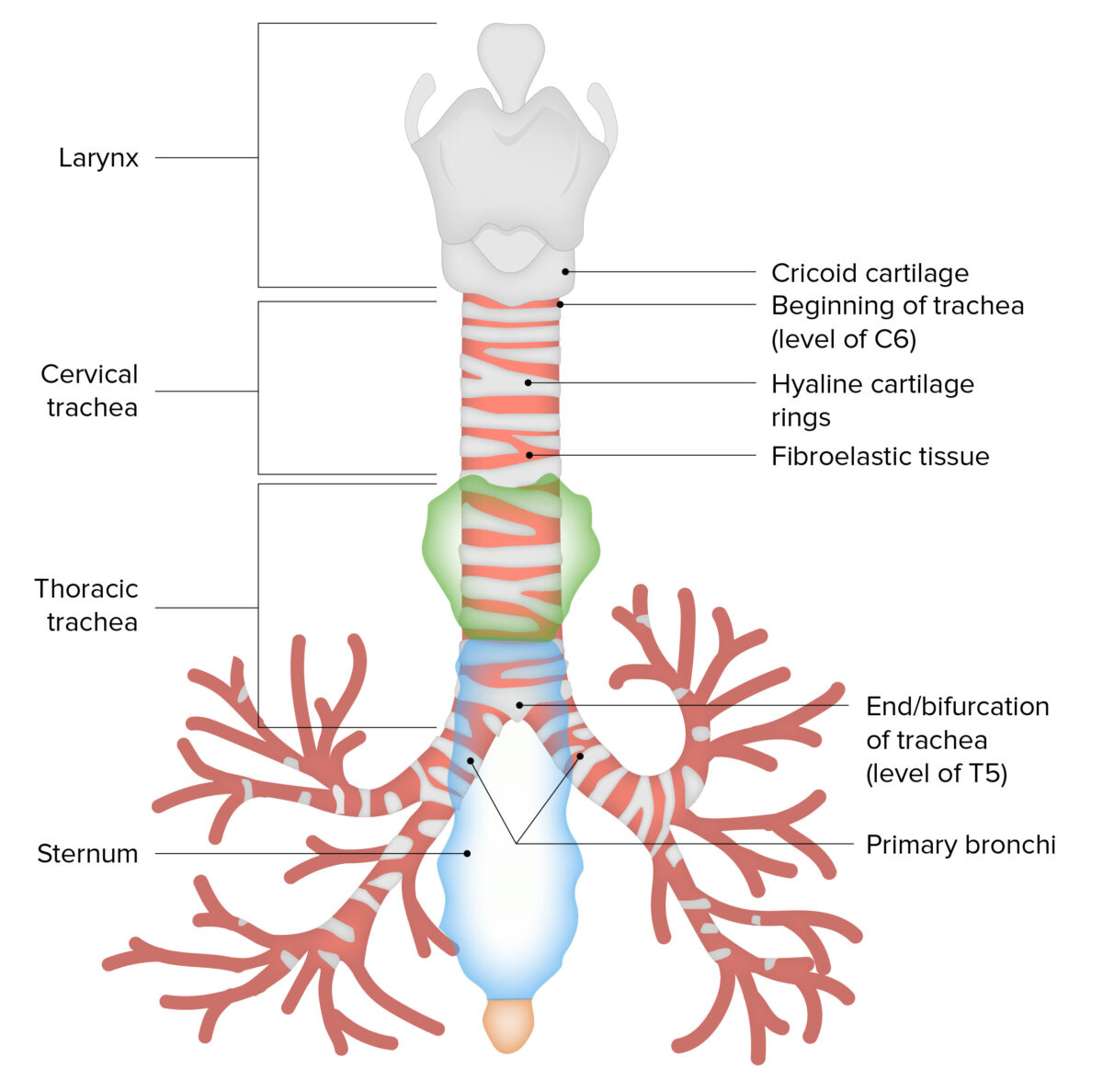
La tráquea es una estructura tubular que forma parte del tracto respiratorio inferior. La tráquea se continúa superiormente con la laringe e inferiormente se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el árbol bronquial dentro de los LOS Neisseria pulmones. La tráquea está formada por un armazón de soporte de 16–20 anillos semicirculares, o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de C, hechos de cartílago hialino y reforzados por tejido conectivo colagenoso. La pared posterior de la tráquea está libre de cartílago. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esta zona, la paries membranaceus Paries membranaceus Trachea: Anatomy forma una placa de músculo traqueal liso y tejido conectivo, y constituye el límite con el esófago que discurre dorsalmente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La tráquea se desarrolla como parte del árbol traqueobronquial al AL Amyloidosis brotar del intestino anterior del tubo intestinal embrionario.
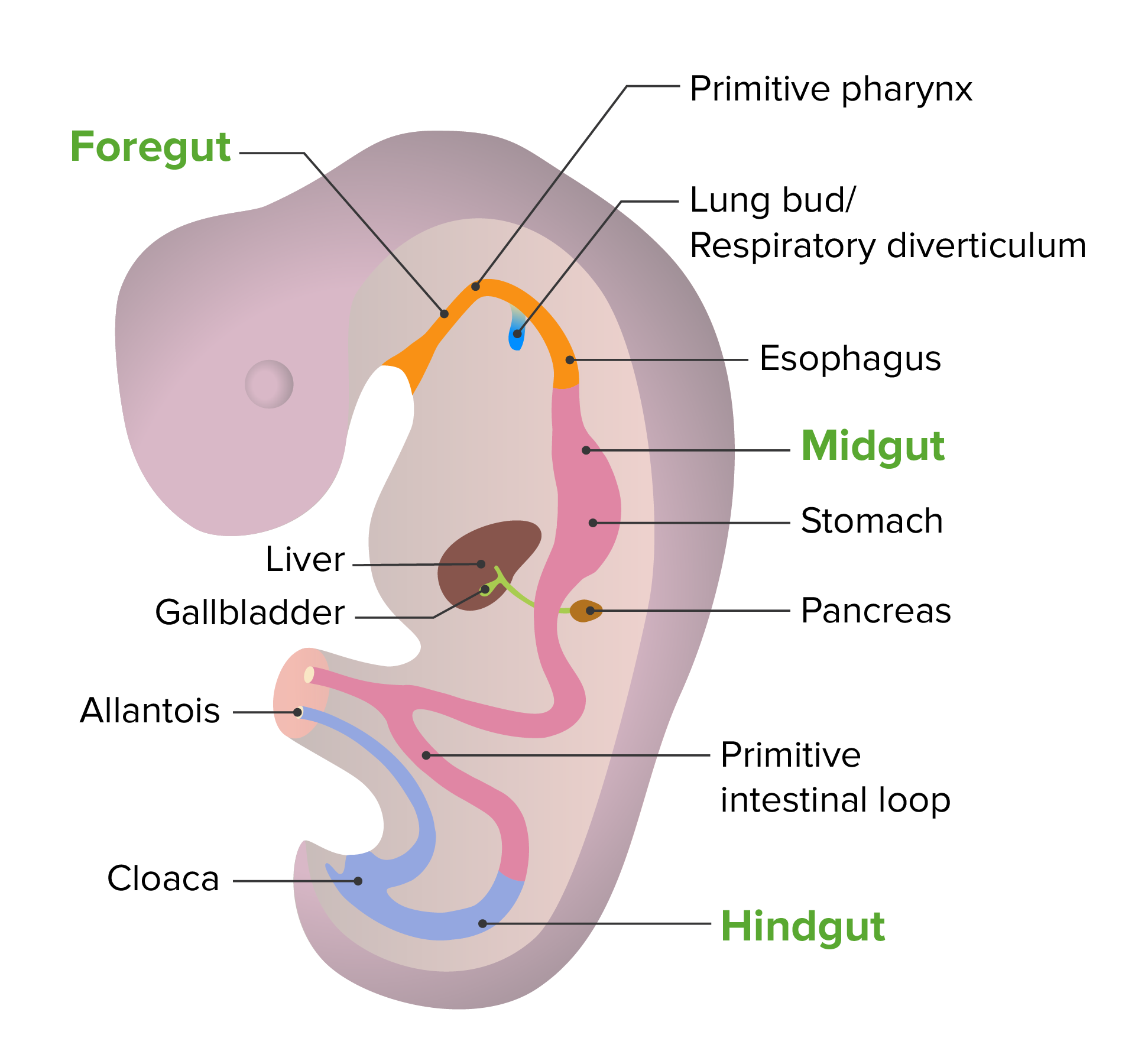
Desarrollo embrionario del tubo intestinal
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0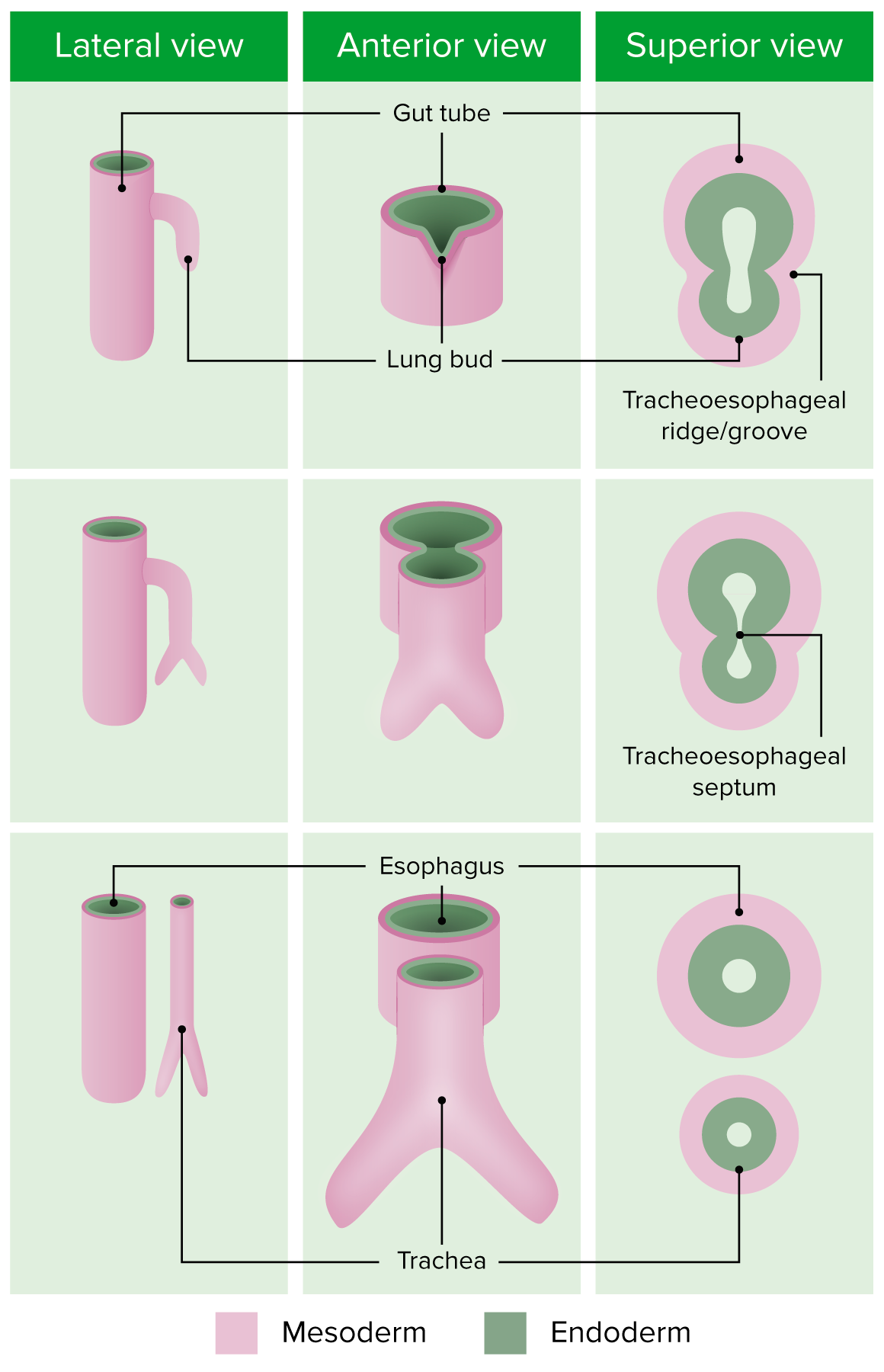
Desarrollo embrionario del árbol bronquial
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0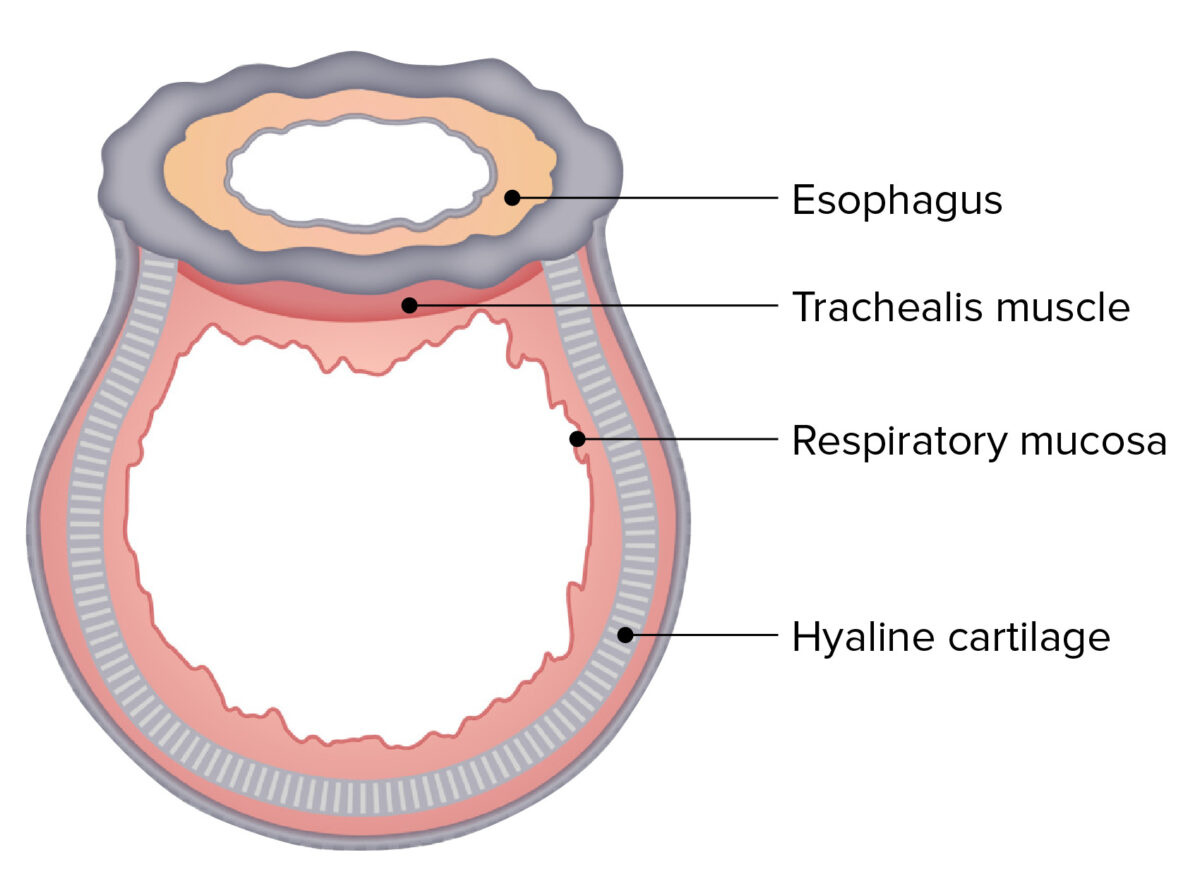
La estructura transversal de la tráquea:
Obsérvese la estructura tubular en forma de D y la proximidad al esófago.
La estructura principal y porciones de la tráquea
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0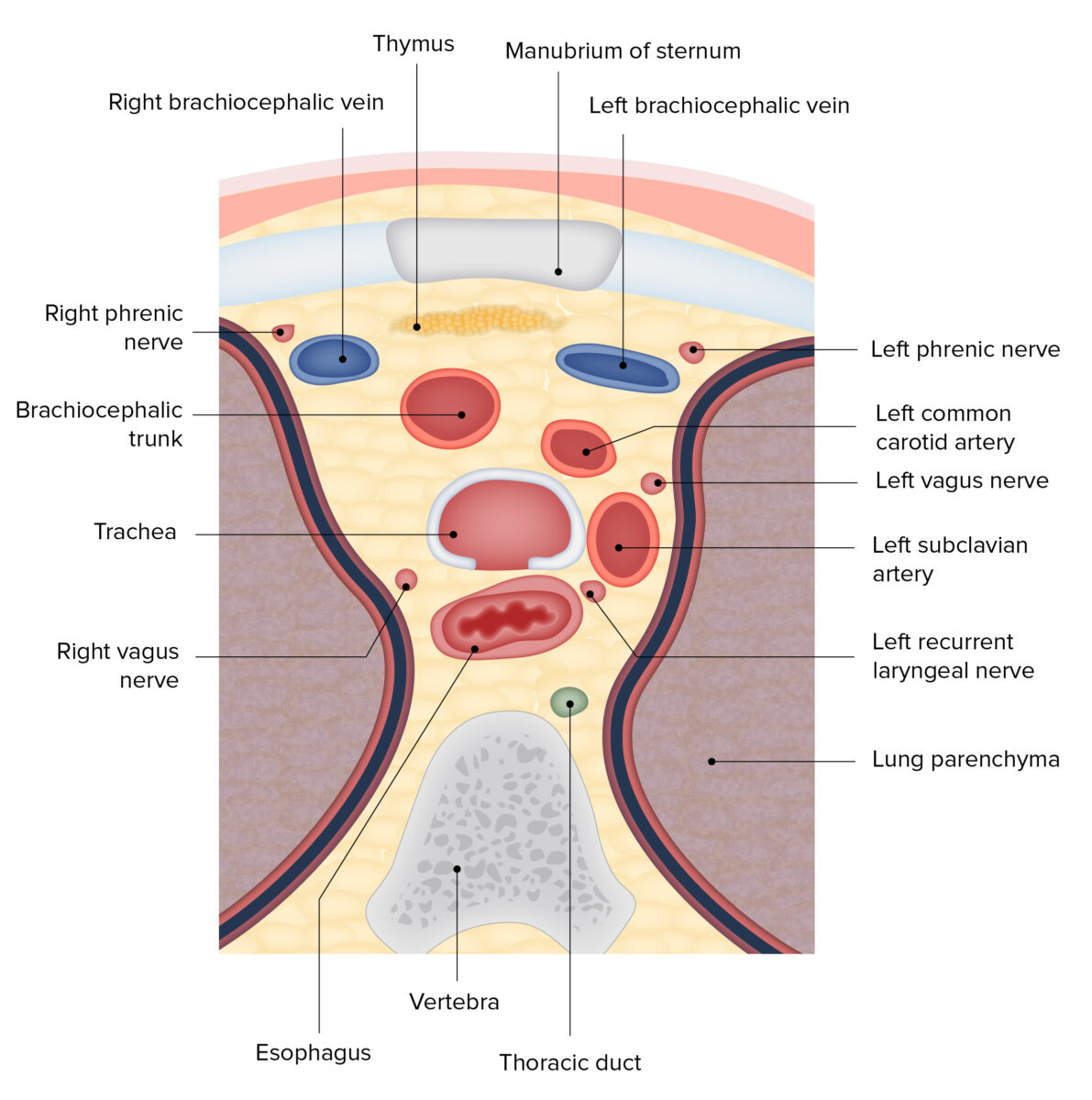
Diagrama de un corte transversal del mediastino superior, con las relaciones anatómicas de la tráquea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio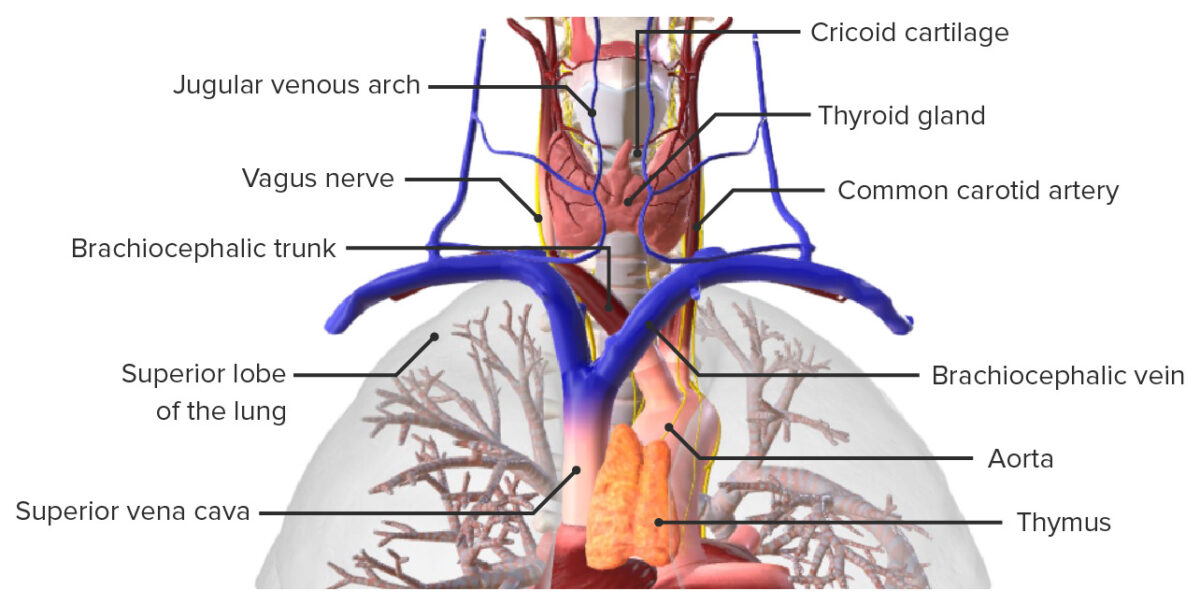
Vista anterior de la tráquea, mostrando sus relaciones anatómicas con las estructuras vecinas
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio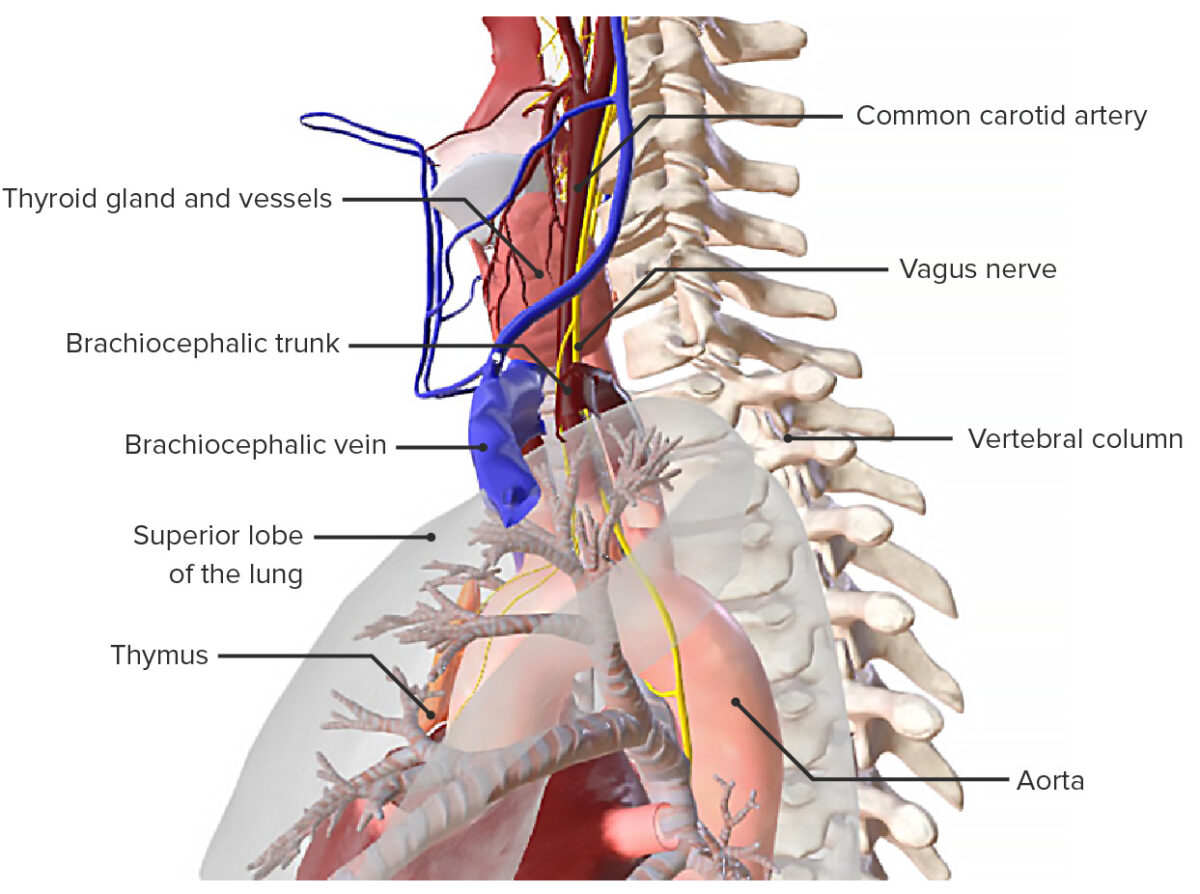
Vista lateral de la tráquea, mostrando sus relaciones anatómicas con las estructuras vecinas
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioLa pared traqueal consta de 4 capas:
Las distintas capas de tejido que componen la tráquea
Imagen: “Layers of tissue: trachea and larynx” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.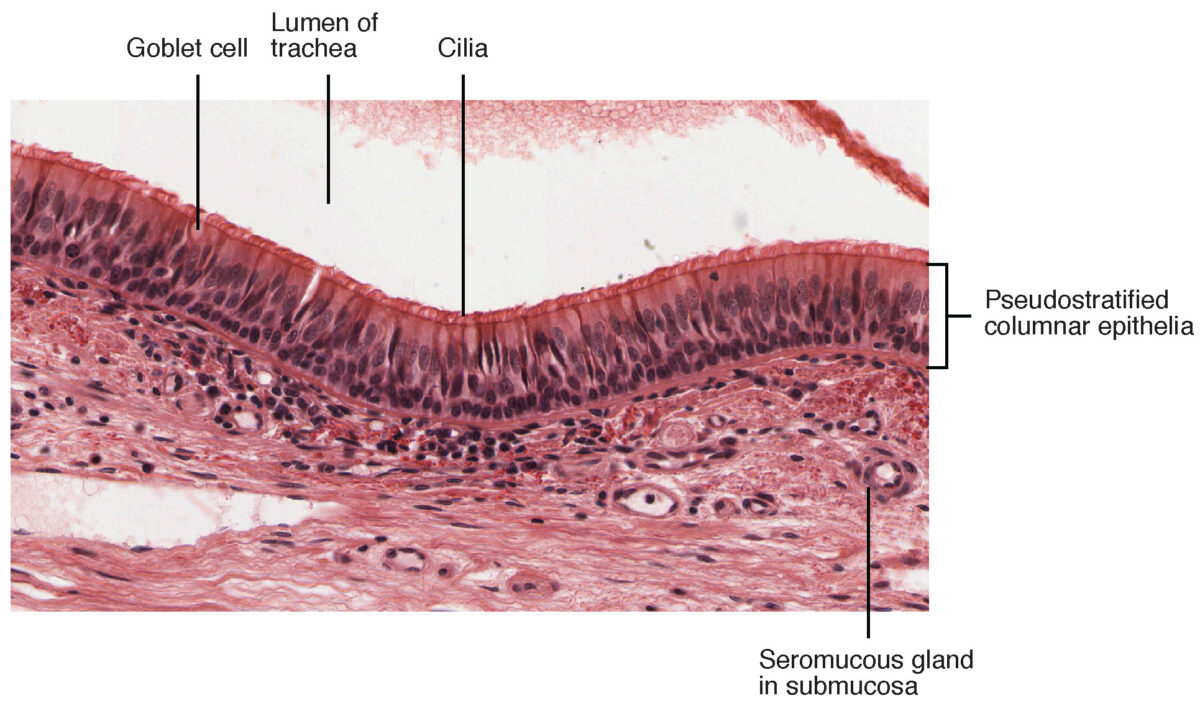
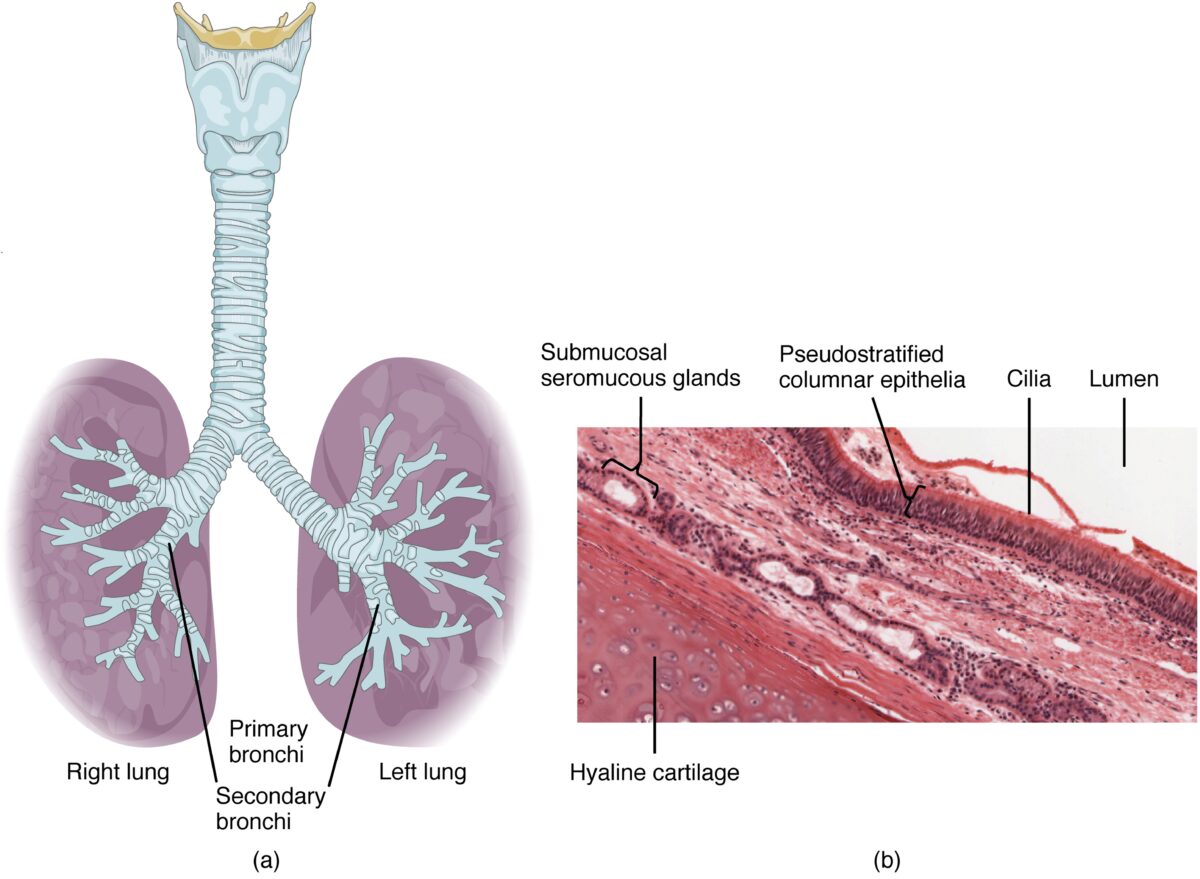
Detalle de las capas histológicas de la luz traqueal
Imagen: “Pseudostratified Epithelium” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Los LOS Neisseria siguientes trastornos de diversas etiologías pueden afectar a la tráquea: