El síndrome hepatorrenal es una causa potencialmente reversible de lesión renal aguda que se desarrolla de forma secundaria a una enfermedad hepática. La principal causa del síndrome hepatorenal es la vasodilatación esplácnica, con la consiguiente disminución del volumen arterial y la subsiguiente vasoconstricción renal, que provoca hipoperfusión de los LOS Neisseria riñonese. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation o anuria Anuria Absence of urine formation. It is usually associated with complete bilateral ureteral (ureter) obstruction, complete lower urinary tract obstruction, or unilateral ureteral obstruction when a solitary kidney is present. Acute Kidney Injury y ascitis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el contexto de una lesión hepática aguda o crónica. El síndrome hepatorrenal se considera un diagnóstico de exclusión. El tratamiento es con agentes que causan vasoconstricción sistémica y, por lo tanto, mejoran la perfusión renal. Esto incluye octreotide Octreotide A potent, long-acting synthetic somatostatin octapeptide analog that inhibits secretion of growth hormone and is used to treat hormone-secreting tumors; diabetes mellitus; hypotension, orthostatic; hyperinsulinism; hypergastrinemia; and small bowel fistula. Antidiarrheal Drugs y midodrina. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de síndrome hepatorrenal tienen un mal pronóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome hepatorrenal se asocia con hipertensión portal debido a:
El sistema de clasificación del síndrome hepatorrenal se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia actualizado recientemente:
Los LOS Neisseria factores desencadenantes son cualquier intervención o condición que ocasione hipovolemia arterial:
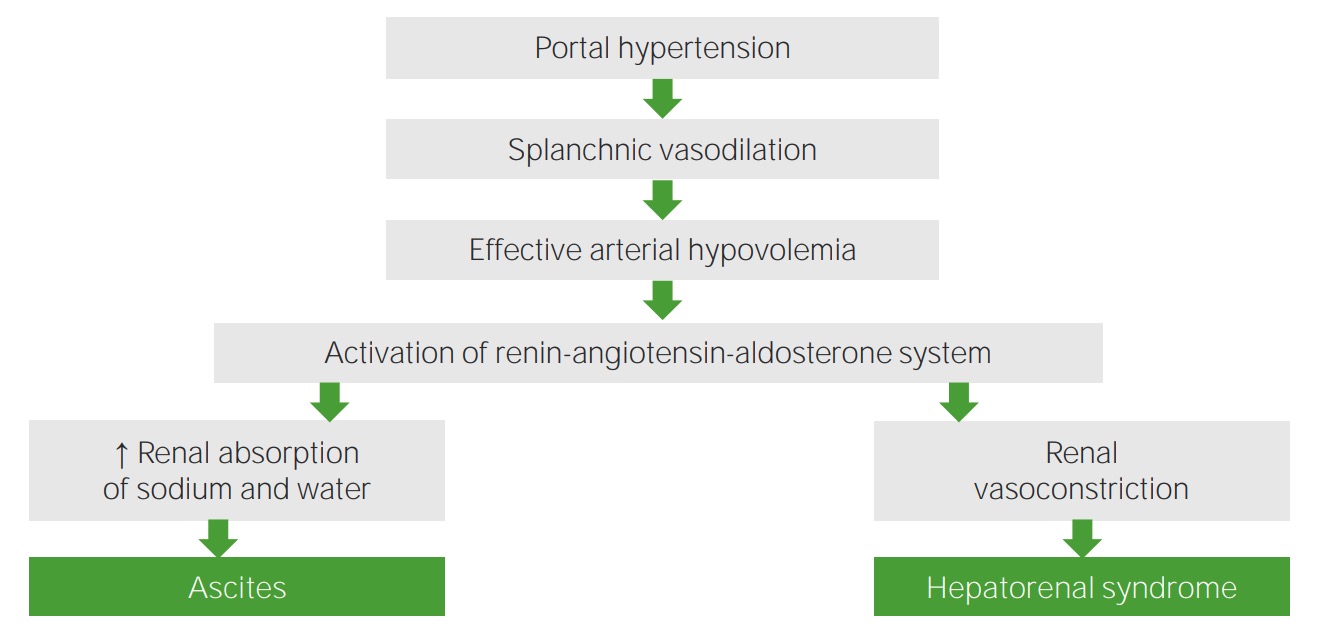
Fisiopatología del síndrome hepatorrenal
Imagen por Lecturio.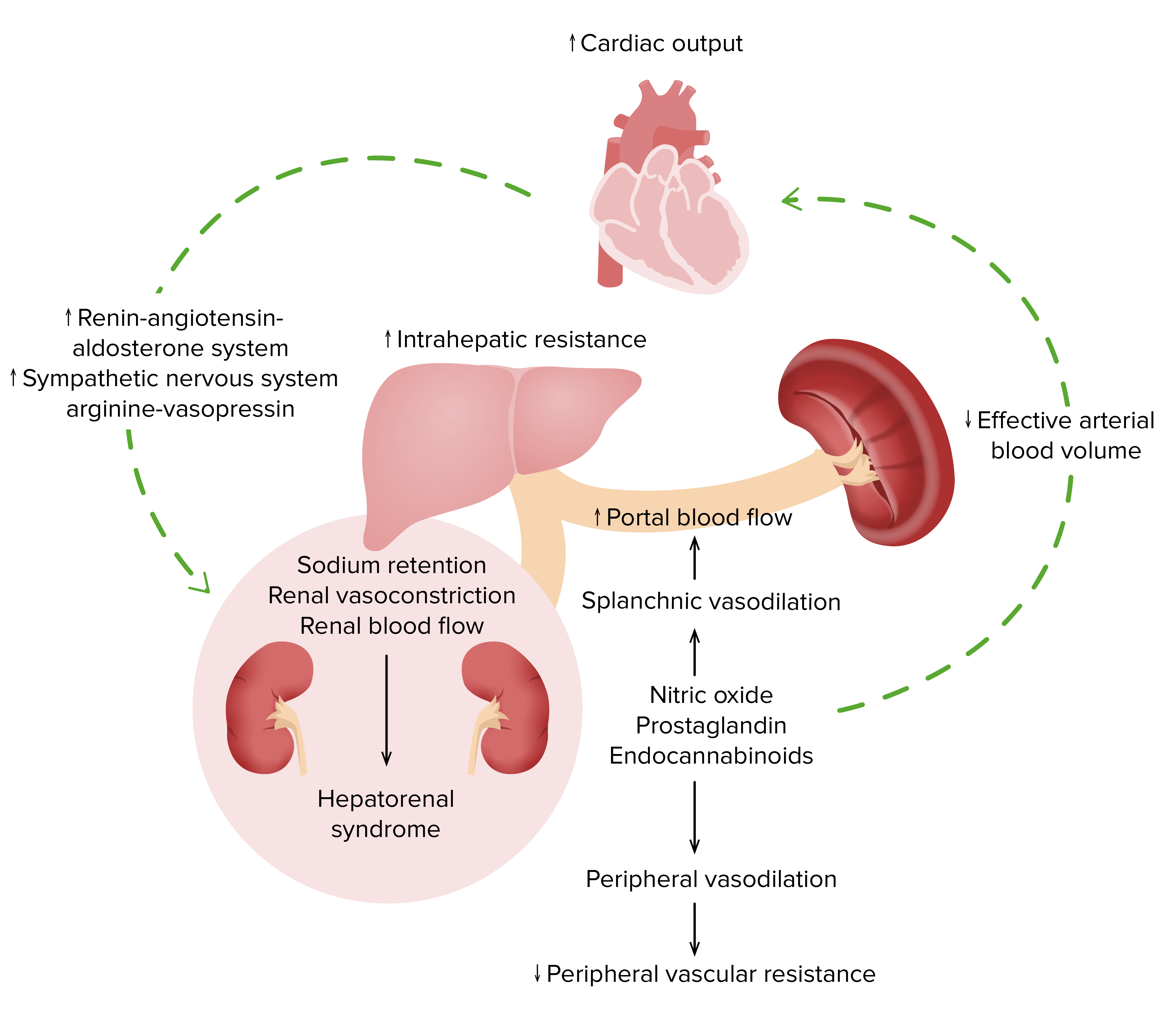
Fisiopatología del síndrome hepatorrenal
Imagen por Lecturio.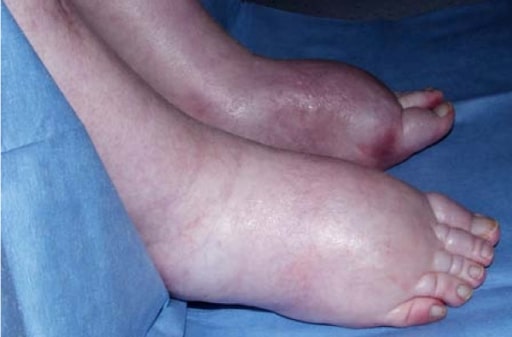
Edema de miembros inferiores por retención de líquidos en paciente con síndrome hepatorrenal
Imagen: “Itraconazole associated quadriparesis and edema” por National Aspergillosis Centre, Education and Research Centre, University Hospital of South Manchester (Wythenshawe Hospital), Southmoor Road, Manchester M23 9LT, UK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El objetivo de la terapia es mejorar la función hepática.
Enfermedad prerrenal: se presenta con hallazgos de laboratorio similares (↑ creatinina sérica y ↑ cociente BUN:Cr) y hallazgos urinarios similares (baja excreción de sodio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la orina). El síndrome hepatorrenal se puede diferenciar de la enfermedad prerrenal a través de una prueba de líquidos por vía intravenosa. La administración de líquidos mejora la enfermedad prerrenal pero no el síndrome hepatorrenal.