Los LOS Neisseria Proteus Proteus Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacilli. Different types of infection result from Proteus, but the urinary tract is the most common site. The majority of cases are caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The bacteria are part of the normal intestinal flora and are also found in the environment. Proteus spp. son bacilos gram-negativos, anaerobios facultativos. Diferentes tipos de infecciones son el resultado de Proteus Proteus Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacilli. Different types of infection result from Proteus, but the urinary tract is the most common site. The majority of cases are caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The bacteria are part of the normal intestinal flora and are also found in the environment. Proteus, pero el tracto urinario es el sitio más común. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son causados por Proteus mirabilis Proteus mirabilis A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that is frequently isolated from clinical specimens. Its most common site of infection is the urinary tract. Proteus ( P. mirabilis P. mirabilis A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that is frequently isolated from clinical specimens. Its most common site of infection is the urinary tract. Proteus). Las bacterias son parte de la flora intestinal normal y también se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el medio ambiente. Proteus Proteus Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacilli. Different types of infection result from Proteus, but the urinary tract is the most common site. The majority of cases are caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The bacteria are part of the normal intestinal flora and are also found in the environment. Proteus spp. exhiben una motilidad de enjambre característica y una fuerte actividad de ureasa, que permiten el inicio de la infección. La hidrólisis de la urea Urea A compound formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end product of protein catabolism and constitutes about one half of the total urinary solids. Urea Cycle por la ureasa conduce a una orina alcalina con un olor a amoníaco. Con el pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance elevado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la orina, se forman cálculos renales de estruvita, que eventualmente pueden causar obstrucción e insuficiencia renal. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum antibióticos (e.g., trimetoprim-sulfametoxazol) para la infección y extirpación quirúrgica de los LOS Neisseria cálculos, si los LOS Neisseria hubiera.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
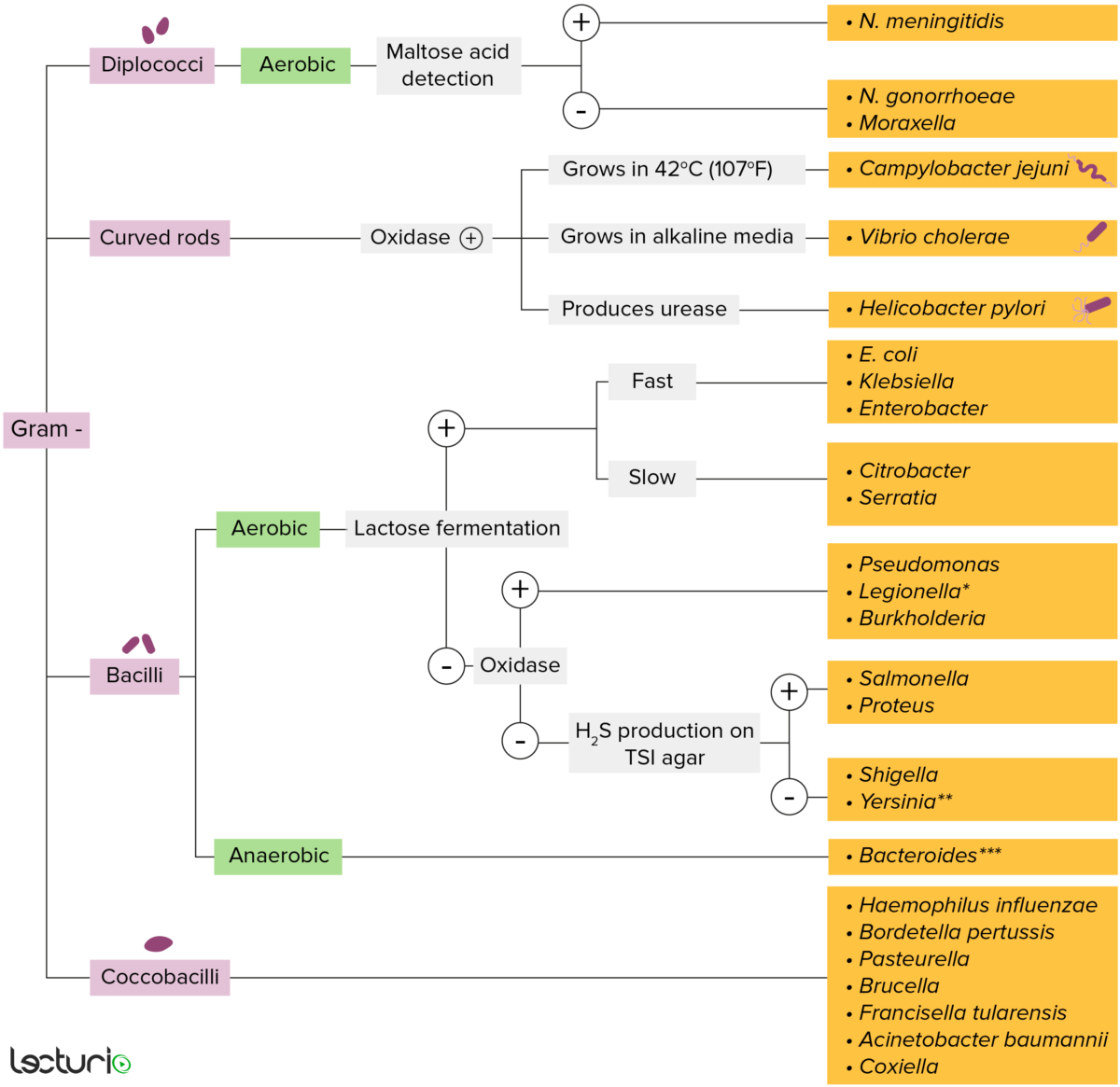
Bacterias gram-negativas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano que no retiene la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, se tiñen de color rojo rosado, lo que las convierte en gram-negativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bacilos curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicas vs. anaeróbicas). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más estrecha cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar hierro- triple azúcar (agar TSI, por sus siglas en inglés)) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe mal en la tinción de Gram
** Bacilo pleomórfico/cocobacilo
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
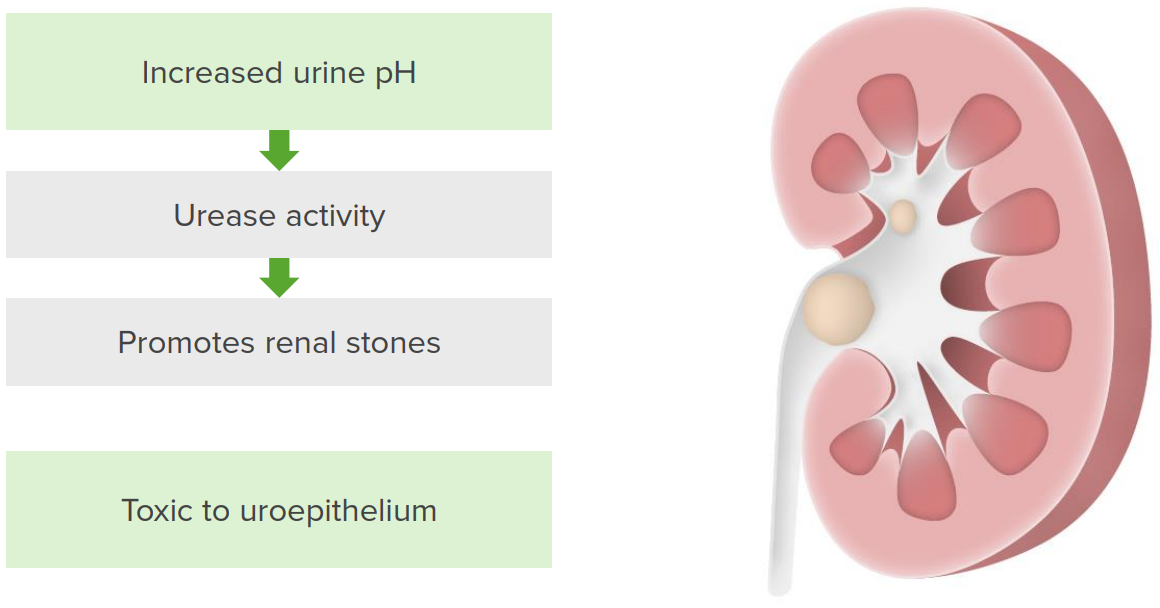
Patogenia de la infección por Proteus
Las bacterias aumentan el pH de la orina al activar la actividad de la ureasa. La ureasa metaboliza la urea en amoníaco y dióxido de carbono. Estos subproductos aumentan el pH de la orina, predisponiendo al paciente a la formación de cálculos de estruvita. Los cálculos y la infección bacteriana conducen al daño uroepitelial.
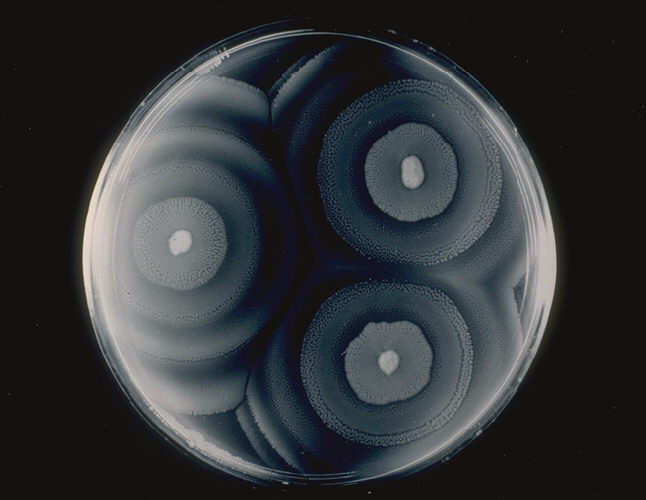
Proteus mirabilis: cultivo que ilustra el fenómeno del enjambre
Imagen: “ProteusMirabilis Schwärmen” por the CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.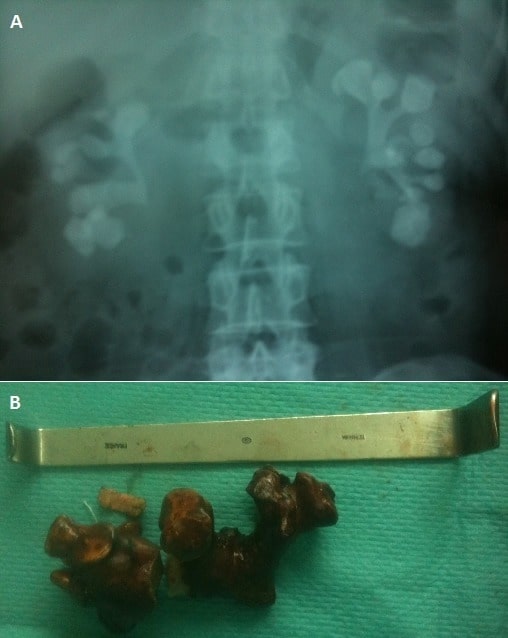
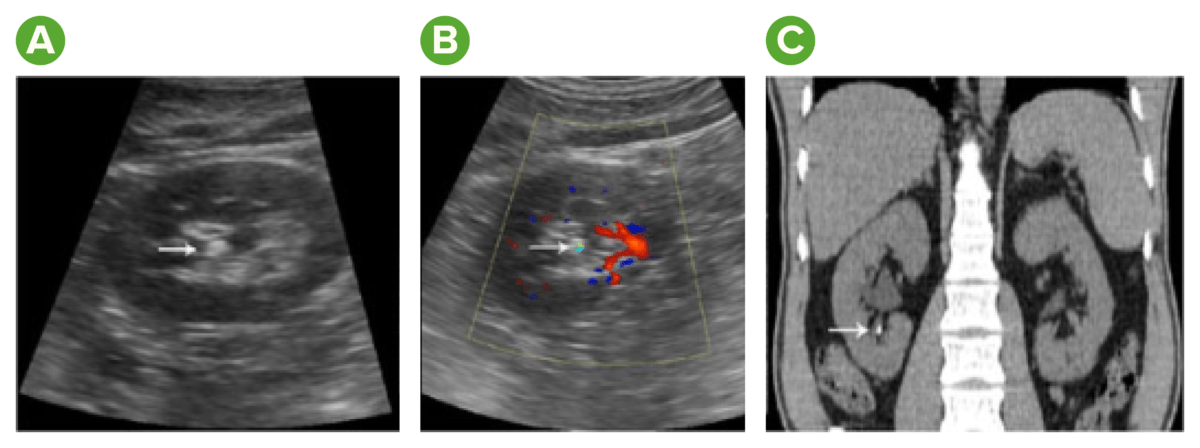
Cálculos coralinos de una infección por Proteus
A: radiografía de abdomen que muestra cálculos coraliformes completos bilaterales
B: parte de los cálculos coraliformes extraídos mediante cirugía abierta
Escherichia coli Escherichia coli The gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli is a key component of the human gut microbiota. Most strains of E. coli are avirulent, but occasionally they escape the GI tract, infecting the urinary tract and other sites. Less common strains of E. coli are able to cause disease within the GI tract, most commonly presenting as abdominal pain and diarrhea. Escherichia coli (E. coli) y Proteus Proteus Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacilli. Different types of infection result from Proteus, but the urinary tract is the most common site. The majority of cases are caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The bacteria are part of the normal intestinal flora and are also found in the environment. Proteus spp. son etiologías comunes de infección del tracto urinario.
| Proteus Proteus Proteus spp. are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacilli. Different types of infection result from Proteus, but the urinary tract is the most common site. The majority of cases are caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The bacteria are part of the normal intestinal flora and are also found in the environment. Proteus spp. | E. coli | |
|---|---|---|
| Características | Bacilos gram-negativos | Bacilos gram-negativos |
| Hábitat | Tracto intestinal | Tracto intestinal |
| Fermentación de lactosa | No fermentan la lactosa | Fermentan la lactosa |
| Indol | P. mirabilis P. mirabilis A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that is frequently isolated from clinical specimens. Its most common site of infection is the urinary tract. Proteus: negativo P. vulgaris P. vulgaris A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that occurs in soil, fecal matter, and sewage. It is an opportunistic pathogen and causes cystitis and pyelonephritis. Proteus: positivo | Positivo |
| Agar hierro triple azúcar | Productores de H2S | No produce H2S |
| Infección | ITU | La causa más común de ITU |