La poliquistosis renal es un trastorno genético hereditario que conduce al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de numerosos quistes llenos de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria riñones. Los LOS Neisseria 2 tipos principales de poliquistosis renal son la poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva, que suele diagnosticarse antes del nacimiento o poco después, y la poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante, que suele diagnosticarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la adultez. La poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva se caracteriza principalmente por dilataciones quísticas de los LOS Neisseria conductos colectores renales y de los LOS Neisseria conductos biliares intrahepáticos con fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans hepática. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante el examen físico y el ultrasonido. El tratamiento requiere un enfoque multidisciplinario para frenar la progresión de la enfermedad renal mediante el control de la hipertensión, la proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children y los LOS Neisseria síntomas. El pronóstico de la poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva depende de la edad de presentación, junto con el grado de afectación hepática y renal. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes que evolucionan hacia la enfermedad renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estadio terminal necesitarán terapia de reemplazo renal.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2022
La poliquistosis renal afecta a unas 500 000 personas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos. La poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva (antes conocida como poliquistosis renal infantil), es 1 de los LOS Neisseria 2 tipos principales de poliquistosis renal.
Las manifestaciones varían según la edad y afectan las siguientes estructuras:
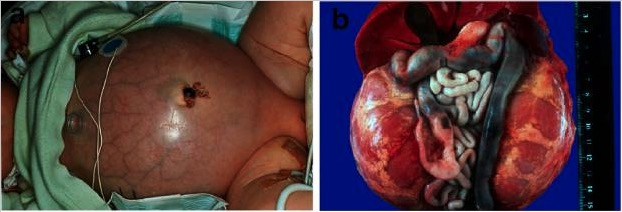
Poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva:
a) Bebé con el abdomen distendido debido a riñones voluminosos, lo que provoca problemas respiratorios y fallecimiento prematuro
b) Situación abdominal de un paciente fallecido perinatalmente con poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva con riñones simétricamente agrandados en su configuración reniforme
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria 3 primeros años, los LOS Neisseria supervivientes del periodo neonatal experimentan una mejora temporal de la función renal, seguida de un declive.
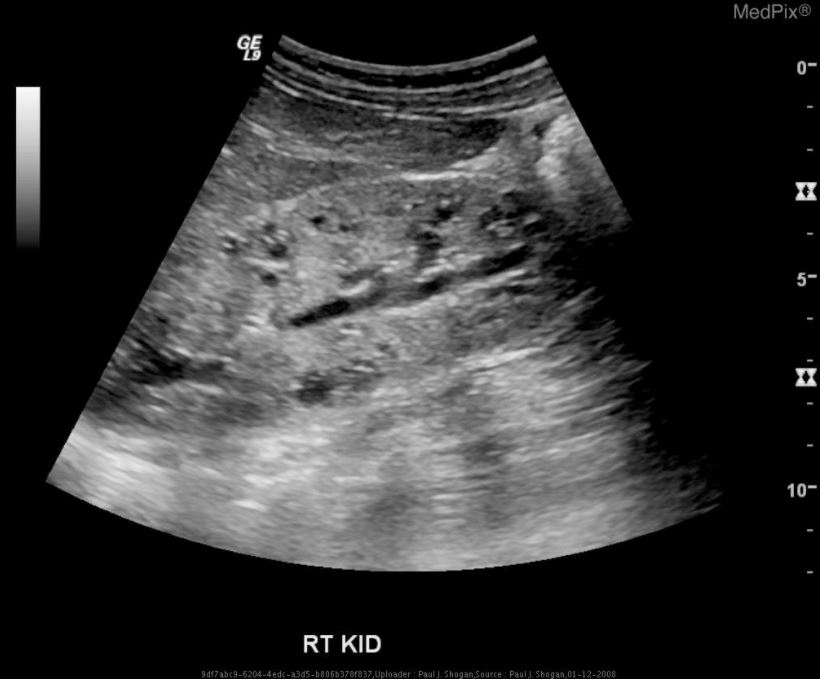
Ultrasonido del riñón derecho que muestra una poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva:
aumento difuso de la ecogenicidad, pérdida de la diferenciación corticomedular y múltiples microquistes dentro del parénquima renal
Tratamiento prenatal (si se detecta a tempranamente):
Tratamiento neonatal:
Tratamiento durante la infancia y la niñez:
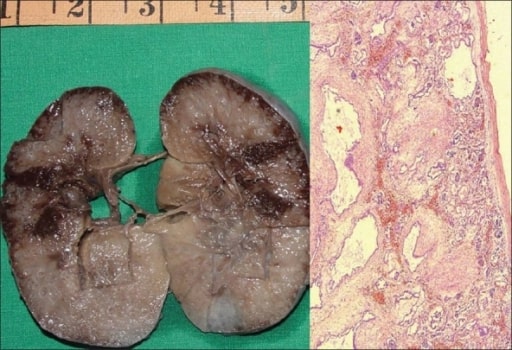
Poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva en un feto:
A la izquierda, se muestra un espécimen macroscópico de un riñón derecho que mide 10 × 7 × 4 cm. La superficie del corte es esponjosa con escasa diferenciación corticomedular. Hay múltiples quistes diminutos, algunos en ángulo recto a la superficie cortical.
A la derecha, una microfotografía muestra numerosos quistes revestidos por una sola capa de células epiteliales cuboidales bajas con un mesénquima peritubular grueso. Los glomérulos son normales (H&E, 40x).
Los LOS Neisseria 2 tipos principales de poliquistosis renal son la poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante y la poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva.
| Poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante | Poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva | |
|---|---|---|
| Herencia | Autosómica dominante | Autosómica recesiva |
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure implicados | PKD1, PKD2 PKD1, PKD2 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | PKHD1 PKHD1 Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) |
| Proteínas asociadas | Policistina-1, policistina-2 | Fibrocistina |
| Edad de presentación | Adultez | Prenatal, neonatal, infantil |
| Hallazgos clínicos |
|
|
| Morfología macroscópica y patológica |
|
|
| Resultados del ultrasonido | Múltiples quistes (según la edad):
|
|