La poliquistosis renal (PQR) es un trastorno genético hereditario que conduce al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de numerosos quistes llenos de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria riñones. Los LOS Neisseria 2 tipos principales de PQR son la poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante (PQRAD), que suele diagnosticarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la edad adulta, y la poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva (PQRAR), que suele diagnosticarse prenatalmente o poco después del nacimiento. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con PQRAD suelen presentar hipertensión, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma y dolor Dolor Inflammation de costado. Las manifestaciones extrarrenales incluyen aneurisma intracerebral, quistes hepáticos y pancreáticos, y anomalías valvulares cardíacas. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, el examen físico y el ultrasonido. El tratamiento requiere un enfoque multidisciplinario y muchos pacientes necesitan terapia de reemplazo renal. El objetivo final es frenar la progresión de la enfermedad renal mediante el control de la hipertensión, la proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children y los LOS Neisseria síntomas. El pronóstico de la PQRAD depende de varios factores. Un aneurisma cerebral es una complicación asociada a un pronóstico especialmente malo.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2022
La poliquistosis renal (PQR) afecta a aproximadamente 500 000 personas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos. Uno de los LOS Neisseria 2 tipos principales de PQR es la poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante (PQRAD).
La edad de inicio de los LOS Neisseria síntomas es variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, pero normalmente ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la adultez. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con la mutación de PKD1 presentan síntomas antes que los LOS Neisseria pacientes con PKD2.
El diagnóstico se realiza con la combinación de antecedentes familiares positivos y la presencia de múltiples quistes renales bilaterales.
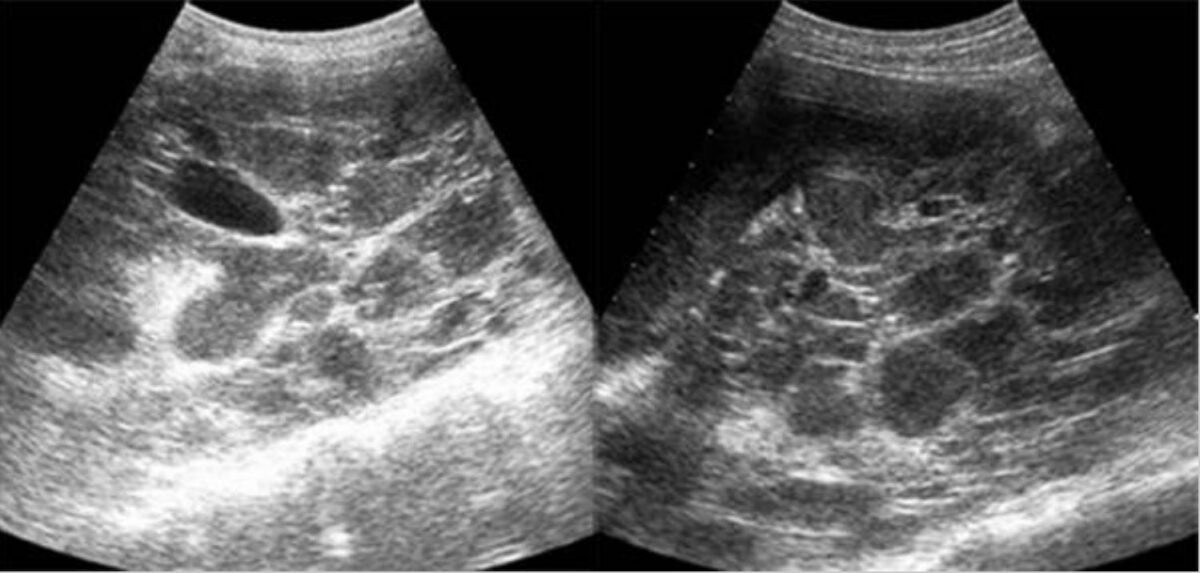
Ultrasonido de la poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante (PQRAD): El ultrasonido sagital en escala de grises de ambos riñones muestra numerosas lesiones quísticas ocupantes espacio con marcados restos ecogénicos internos y septos gruesos, que representan los numerosos quistes infectados
Imagen: “Value of ultrasound-guided irrigation and drainage of refractory pyocysts in ADPKD” por Saedi D, Varedi P, Varedi P, Mahmoodi S, Gashti HN, Darabi M. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Objetivos:
Medidas de tratamiento:
Para la enfermedad renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estadio terminal:
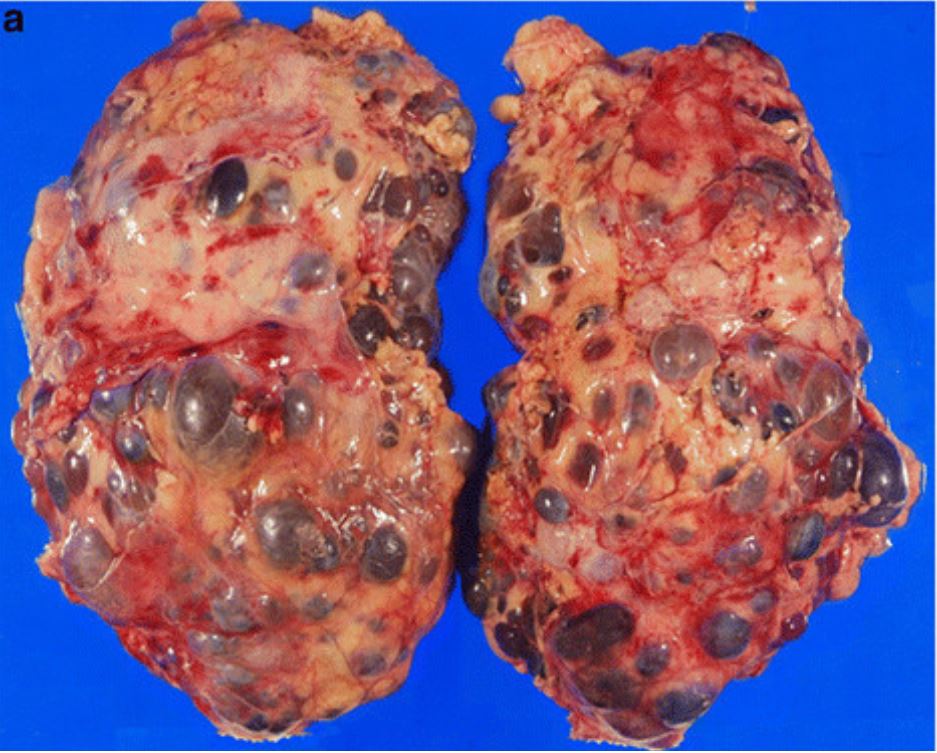
Patología macroscópica de nefrectomía en un paciente con poliquistosis renal autosómica dominante (PQRAD)
Imagen: “Incidental renal cell carcinoma presenting in a renal transplant recipient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease” por Misumi T, Ide K, Onoe T, Banshodani M, Tazawa H, Teraoka Y, Hotta R, Yamashita M, Tashiro H, Ohdan H. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editada por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria dos tipos principales de poliquistosis renal son la PQRAD y la poliquistosis renal autosómica recesiva (PQRAR).
| PQRAD | PQRAR | |
|---|---|---|
| Herencia | Autosómica dominante | Autosómica recesiva |
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure implicados | PKD1, PKD2 PKD1, PKD2 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | PKHD1 PKHD1 Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) |
| Proteínas asociadas | Policistina-1, policistina-2 | Fibrocistina |
| Edad de presentación | Adultez | Prenatal, neonatal, infantil |
| Hallazgos clínicos |
|
|
| Morfología macroscópica y patológica |
|
|
| Resultados del ultrasonido | Múltiples quistes (según la edad):
|
|