El ojo humano es un órgano sensorial cuya función principal es la visión. El ojo tiene una forma esferoidal y está estructurado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 capas: una capa fibrosa externa de soporte, una capa vascular media y una capa neural interna. El ojo también se puede subdividir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 compartimentos: las cámaras anterior, posterior y vítrea. Alrededor del globo ocular se encuentran los LOS Neisseria músculos extraoculares, el aparato lagrimal, varios nervios y vasos, y la estructura ósea de la órbita. La luz viaja a través de los LOS Neisseria compartimentos del ojo para enfocarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy, que es el lugar donde los LOS Neisseria fotorreceptores convierten el estímulo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un impulso neural que es transportado por el nervio óptico al AL Amyloidosis cerebro.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
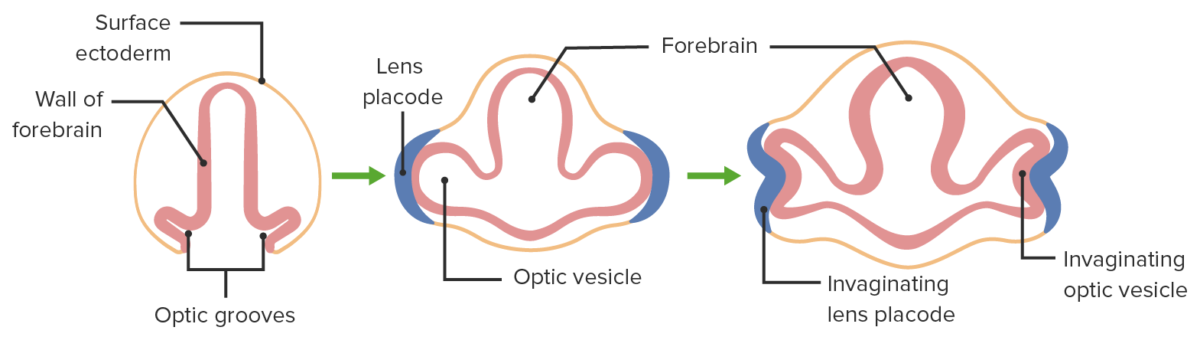
Desarrollo embrionario del ojo
Imagen por Lecturio.El ojo adulto es un órgano complejo contenido dentro de la cavidad orbitaria (compuesta por 7 huesos). Cada ojo tiene múltiples capas y cámaras y está rodeado por 7 músculos extraoculares.
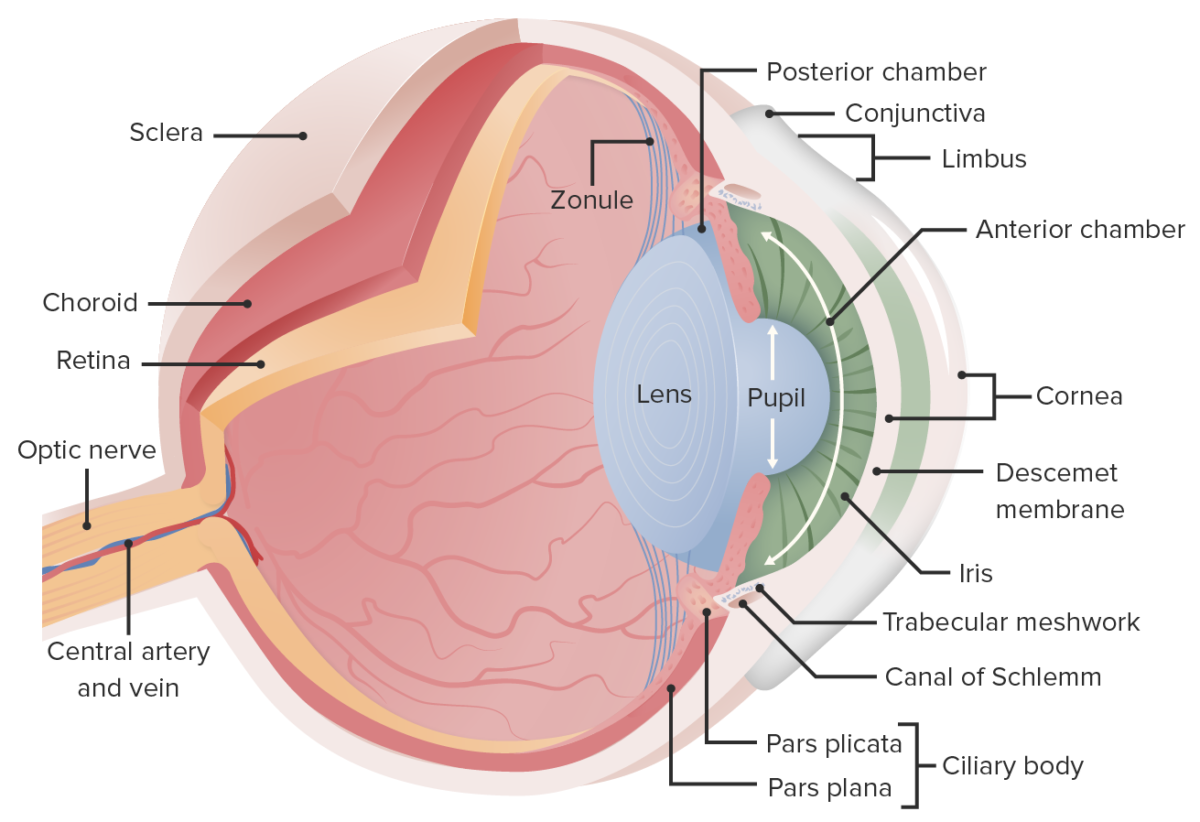
Anatomía del ojo
Imagen por Lecturio.El ojo está compuesto por 3 capas (fibrosa, vascular, neural) y una cubierta de tejido conectivo transparente (conjuntiva).
Conjuntiva :
Capa fibrosa:
Capa vascular:
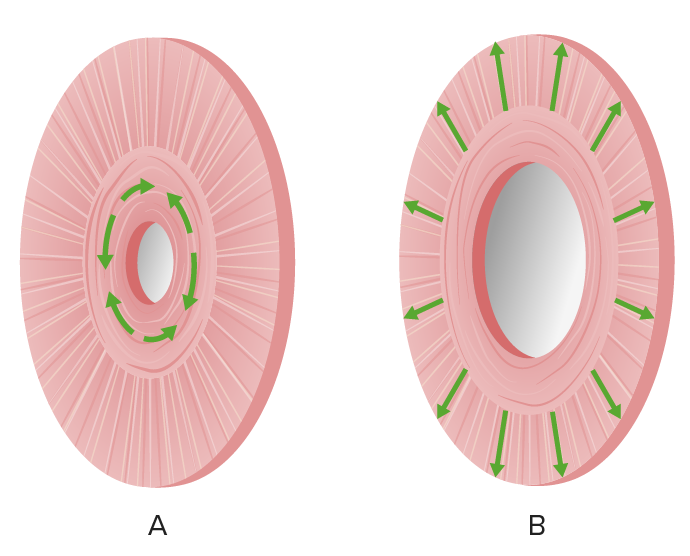
Los músculos del esfínter del iris son responsables de contraer (A) y dilatar (B) la pupila.
Imagen por Lecturio.Capa neural:
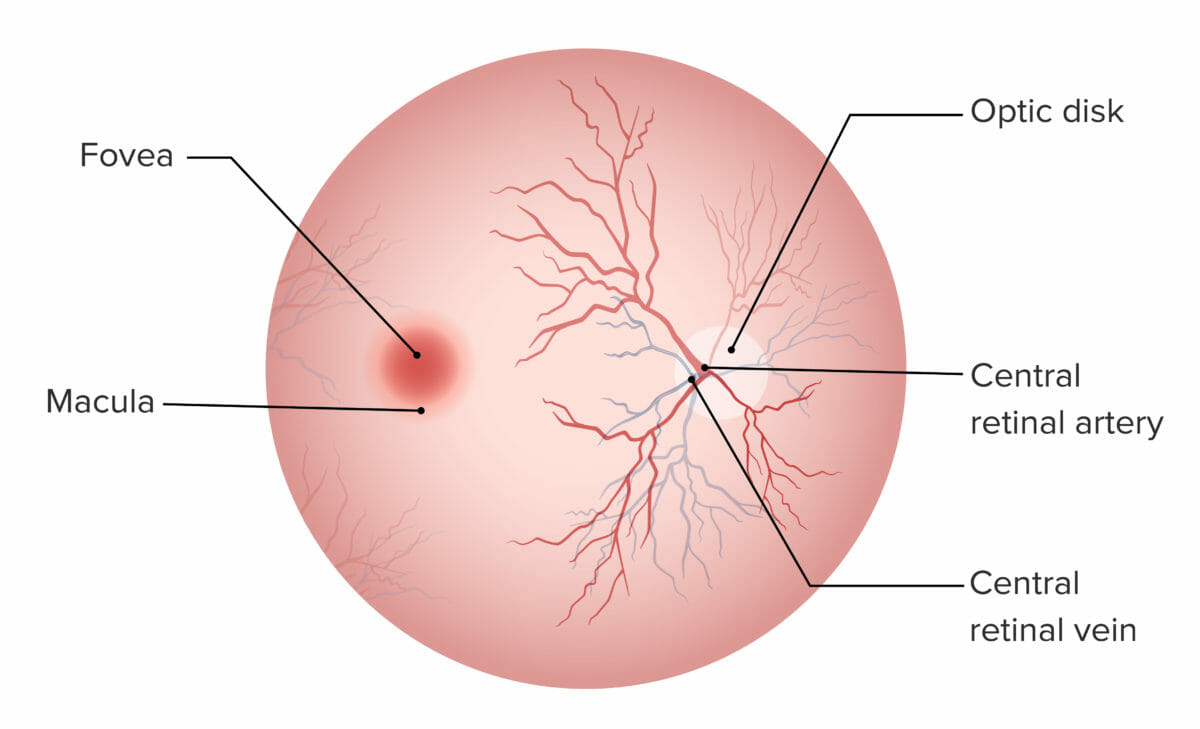
Retina:
La fóvea y la mácula carecen de vasos sanguíneos y son responsables de la visión de alta agudeza. El disco óptico es el punto de entrada para la irrigación del ojo y no contiene fotorreceptores.
Características de la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy y sus capas:
| Capa de la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy (externa a interna) | Características |
|---|---|
| Epitelio pigmentario | |
| Capa de bastones y conos |
|
| Membrana limitante externa | Da soporte a las células fotorreceptoras |
| Membrana nuclear exterior | Núcleos de células fotorreceptoras (neurona de 1er orden) |
| Capa plexiforme externa | 1ra sinapsis, entre conos y bastones y células bipolares |
| Membrana limitante media | Membrana de soporte |
| Capa nuclear interna | Los LOS Neisseria cuerpos celulares y los LOS Neisseria núcleos de las células bipolares (neurona de 2do orden) transmiten información a las células ganglionares |
| Capa plexiforme interna | Segunda sinapsis, entre células bipolares y células ganglionares |
| Capa de células ganglionares |
|
| Fibras del nervio óptico | Axones de células ganglionares |
| Membrana limitante interna | Capa más interna, más cercana al AL Amyloidosis humor Humor Defense Mechanisms vítreo |
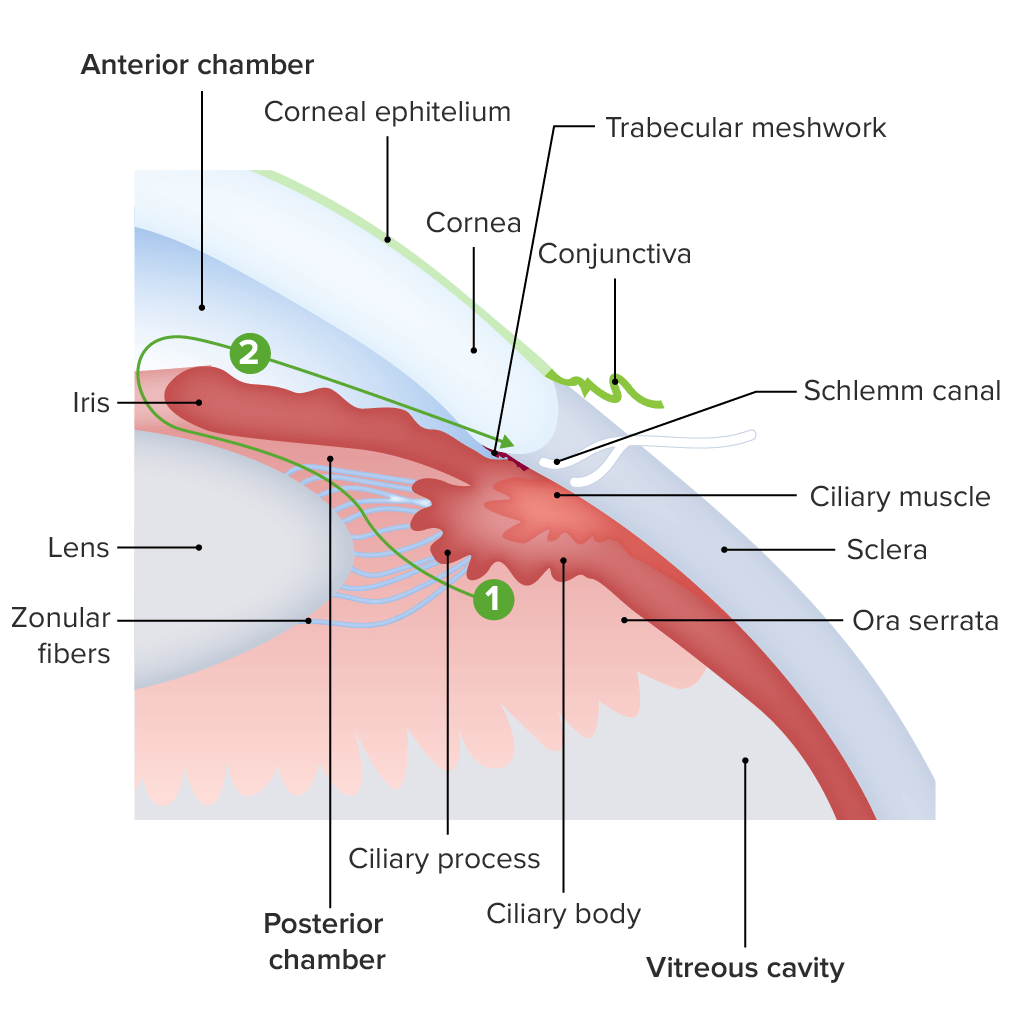
Diagrama de la estructura de la región del limbo:
El humor acuoso es producido por los procesos ciliares (1), circula a través de la pupila del iris hacia la cámara anterior (2) y finalmente a través del canal de Schlemm hacia el seno venoso escleral.
Toda la irrigación arterial del ojo proviene de ramas de la arteria oftálmica y es drenado por un sistema de venas que se unen para formar la vena central de la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy.
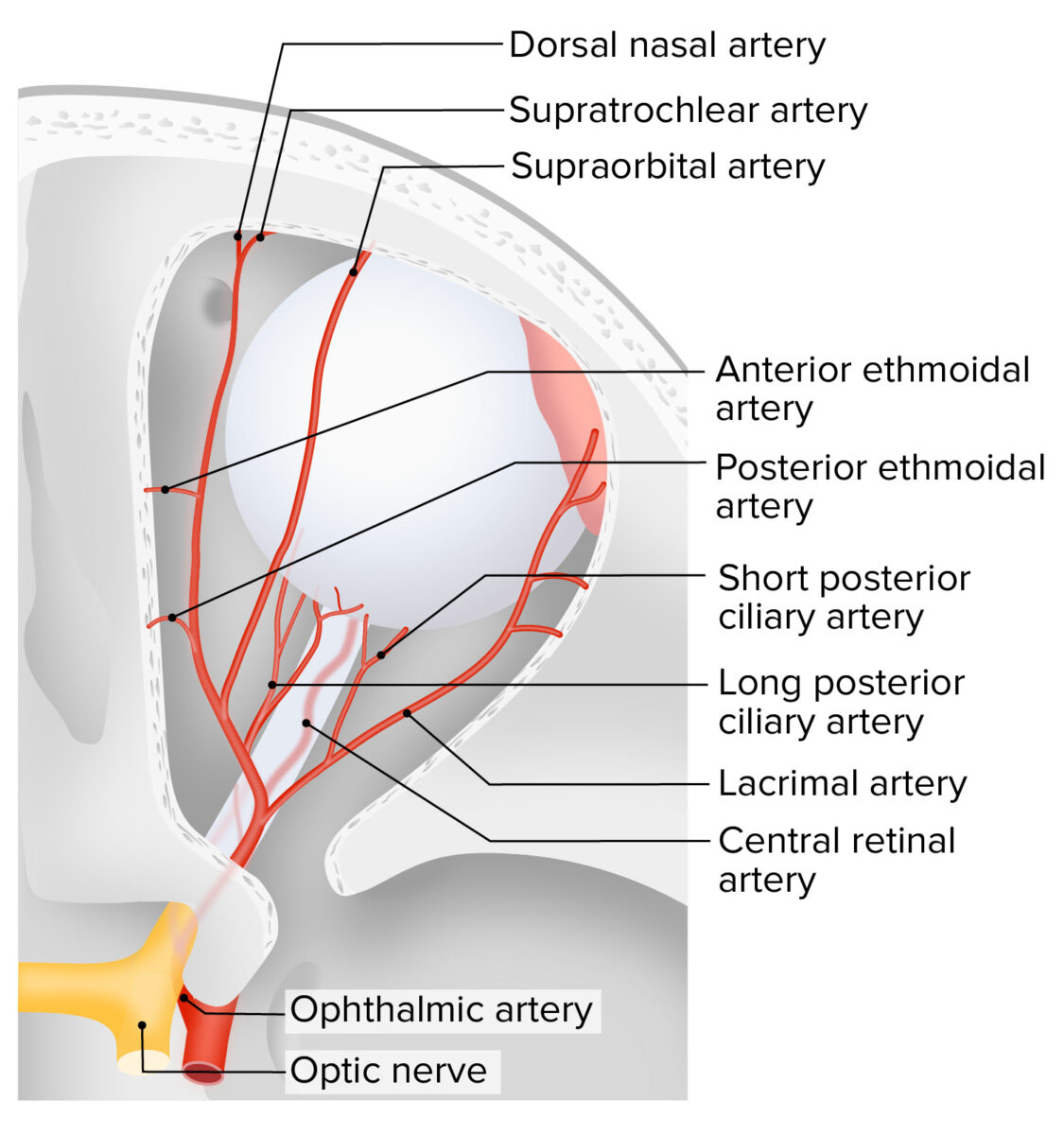
Irrigación del ojo
Imagen por Lecturio.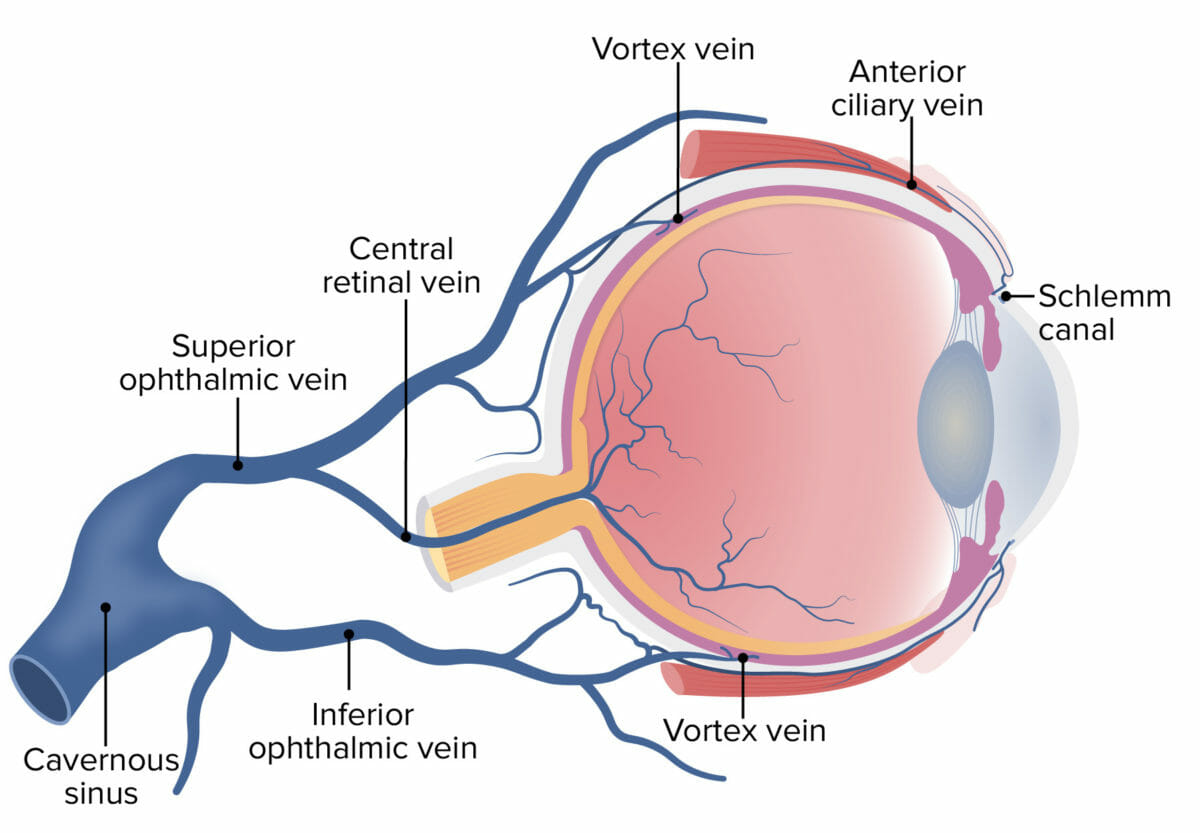
Drenaje venoso del ojo
Imagen por Lecturio.