Los LOS Neisseria nevos, también conocidos como “lunares”, son neoplasias benignas de la piel. El término nevo es inespecífico porque abarca tanto lesiones congénitas como adquiridas, lesiones hiperpigmentadas e hipopigmentadas y lesiones elevadas o planas. Además, los LOS Neisseria nevos se pueden encontrar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum diferentes profundidades de las capas de la piel y se originan a partir de varios tipos de células (e.g., melanocíticas, tejido conectivo, vascular). Los LOS Neisseria nevos también tienen una amplia variedad de formas características, que deben entenderse bien para diferenciar los LOS Neisseria nevos del melanoma Melanoma Melanoma is a malignant tumor arising from melanocytes, the melanin-producing cells of the epidermis. These tumors are most common in fair-skinned individuals with a history of excessive sun exposure and sunburns. Melanoma maligno. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esta página, cubriremos las clasificaciones básicas y los LOS Neisseria tipos más comunes de nevos, así como los LOS Neisseria criterios clínicos utilizados para evaluarlos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un nevo es una neoplasia benigna de la piel:
Los LOS Neisseria nevos se pueden clasificar de varias formas, según varios factores que no son mutuamente excluyentes:
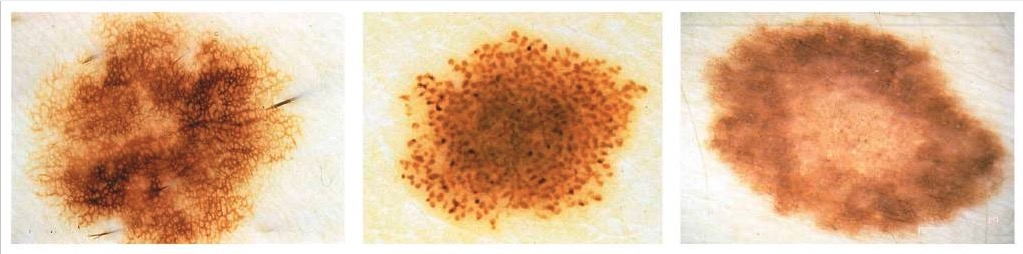
De izquierda a derecha: tipos de nevos reticular, estallido de estrellas y globular
Imagen : “Clark nevus” por the Department of Automatics and Biomedical Engineering, AGH University of Science and Technology, Aleja Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Krakow, Poland. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.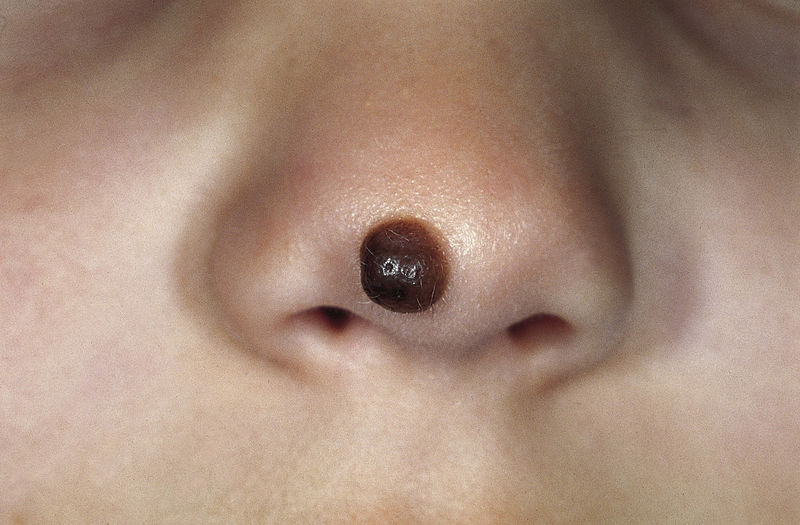
Nevo melanocítico congénito: una pápula marrón bien delimitada en la nariz que se desarrolló poco después del nacimiento
Imagen: “Congenital melanocytic nevus” por M. Sand et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.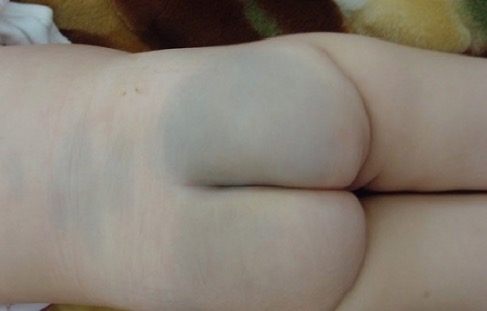
Mancha mongólica o melanocitosis dérmica congénita sobre las regiones lumbar y glútea
Imagen: “Enorme tache mongoloïde” por Service de Pédiatrie, Hôpital Militaire d’Instruction Mohamed V, Université Med V, Souissi, Maroc. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.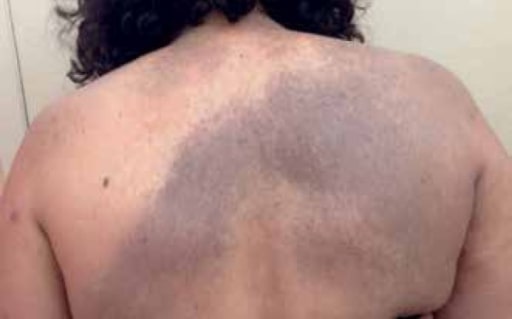
Nevo de Ito congénito: mácula gris-azulada, que representa una melanocitosis dérmica benigna que afecta preferentemente las áreas inervadas por los nervios supraclaviculares posteriores
Imagen: “Nevus of Ito” por the U.S. National Library of Medicine Licencia: CC BY 4.0.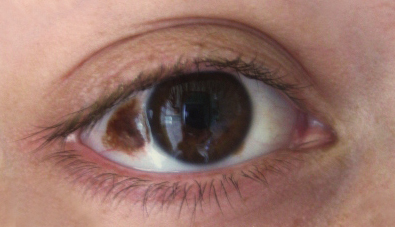
Nevo de Ota congénito: melanocitosis dérmica benigna que afecta preferentemente a zonas inervadas por la 1ra y 2da división del nervio trigémino. Un nevo de Ota congénito a menudo afecta las escleróticas.
Imagen: “Nevus” por Luninsky. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.| Tipo | Descripción | Presentación |
|---|---|---|
| Nevos de unión |
|
|
| Nevos compuestos | Células del nevo encontradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la unión dermoepidérmica e intradérmicamente, células más pequeñas que producen menos melanina |
|
| Nevos intradérmicos | Células del nevo encontradas intradérmicamente, células pequeñas que producen poca o ninguna melanina |
|
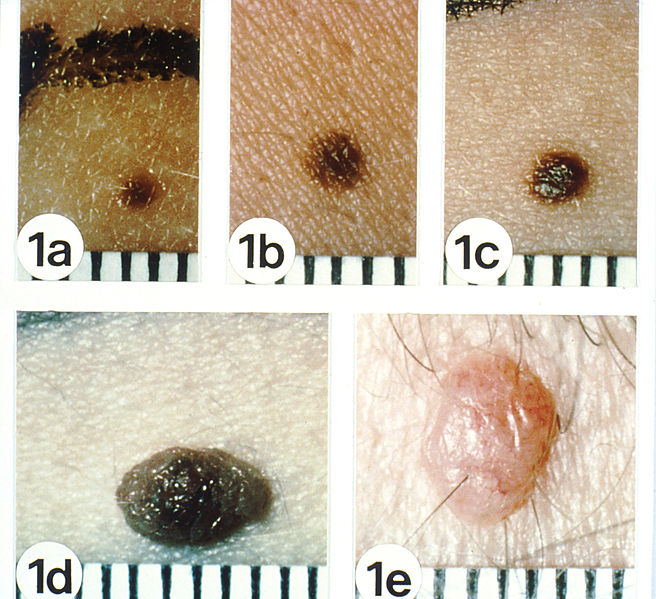
Historia natural de los nevos melanocíticos adquiridos
Los nevos comunes (“lunares”) comienzan como máculas uniformemente marrón claro a oscuro, de 1 a 2 mm de diámetro (a) se expanden a una mácula más grande (b), progresan a una pápula pigmentada que puede ser mínima (c) u obviamente (d) elevada por encima de la superficie de la piel y termina como una pápula rosada o de color piel (e).
Los nevos melanocíticos adquiridos son de unión (a, b), compuestos (c, d), y dérmicos (e), respectivamente. Tenga en cuenta sus bordes lisos, coloración uniforme y una clara demarcación de la piel circundante con bordes lisos.
Los nevos melanocíticos adquiridos suelen ser < 5 mm de diámetro.
Según la apariencia clínica, un nevo benigno típico debe tener las siguientes características:
Un nevo displásico o atípico es un nevo melanocítico benigno con una apariencia que difiere de los nevos comunes o “lunares” según los LOS Neisseria criterios ABCDE (asimetría, irregularidad de los LOS Neisseria bordes, variedad de colores, diámetro ≥ 6 mm y evolución):
| Nevos comunes (benignos) | Nevos atípicos | Melanomas (m.) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asimetría (A) | Simetría (una línea recta trazada a través del centro de la lesión da 2 imágenes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum espejo) |
|
|
| Borde (B) | Borde liso y bien definido | Margen irregular con borde mal definido | Margen irregular con borde mal definido |
| Color (C) | Color uniforme o patrón de color regular Regular Insulin (e.g., moteado o estallido de estrellas) | Color abigarrado o diferentes tonos de color. | Color abigarrado o diferentes tonos de color. |
| Diámetro (D) | < 5 mm | Por lo general ≥ 5 mm | > 6 mm |
| Evolución (E) | Crecimiento estable o lento |
|
|
| Ubicación (no es parte de los LOS Neisseria criterios, pero es un factor importante) | Concentrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sitios expuestos al AL Amyloidosis sol. |
|
Depende del tipo:
|
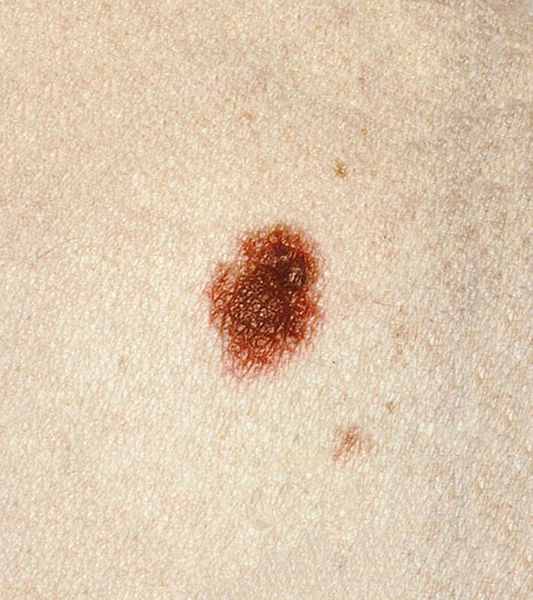
Un nevo displásico que se presenta como una lesión maculopapular. La porción central es el área papular, apenas perceptible en esta fotografía. Tenga en cuenta el borde irregular e indistinto y el patrón de color abigarrado de marrón y rosa.
Imagen: Dysplastic nevi” por the National Cancer Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público.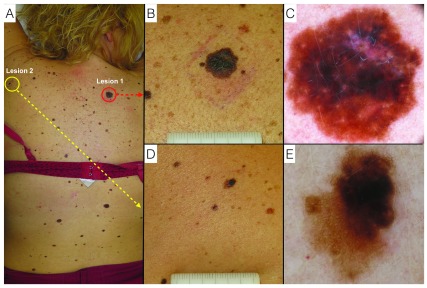
Melanoma y nevo displásico.
A: descripción clínica del paciente;
B: lesión 1: melanoma, primer plano clínico a simple vista;
C: lesión 1: melanoma, vista de dermatoscopia digital;
D: lesión 2: nevo displásico, primer plano clínico a simple vista;
E: lesión 2: nevus displásico, visión dermatoscópica digital.