Las modificaciones postranscripcionales son procesos que facilitan la generación de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) maduro y funcional. Estos mecanismos reguladores de rápida respuesta permiten que se produzcan diferentes proteínas a partir de un mismo gen y actúan como reguladores del fenotipo y de la tasa de proliferación. Estas modificaciones también desempeñan un papel en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunas formas de cáncer y enfermedades neurodegenerativas. El ARN pre-mensajero (ARNm), llamado ARN heterogéneo nuclear (ARNhn), se modifica añadiendo una caperuza de 7-metilguanosina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 5' y una cola de poli-A (poliadenilato) 3' para su estabilidad y protección. Además, los LOS Neisseria ARNhn que contienen intrones (secuencias no codificantes) entre las secuencias expresadas o los LOS Neisseria exones se someten a empalme. Este proceso elimina los LOS Neisseria intrones para producir un ARNm maduro que lleva la secuencia codificante para la traducción. El empalme alternativo, por su parte, también excluye los LOS Neisseria intrones, pero se enlazan combinaciones variables de exones, produciendo proteínas diferentes del ARNm original. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la edición del ARN, la secuencia del ARNm se altera y difiere de la plantilla de ADN transcrita. El ARN de transferencia y el ARN ribosómico parten de moléculas precursoras más largas y pasan por etapas que incluyen la metilación, el recorte y la adición de nucleótidos.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
La información genética del ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) se copia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ARN mensajero (ARNm).
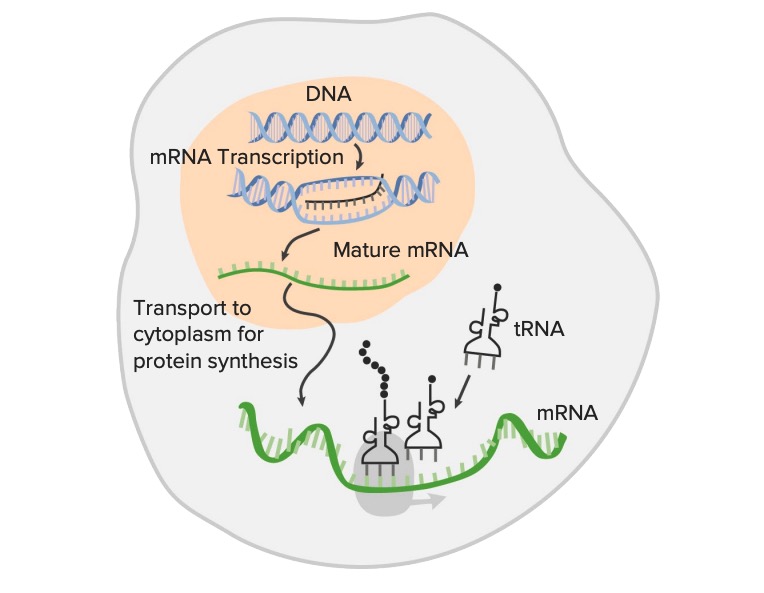
La expresión de los genes a partir del ADN, la secuencia genética, se transcribe en el ARN (transcripción):
La transcripción de la información genética es el primer paso en la expresión de los genes y es el proceso mediante el cual una región codificante del ADN (estructura de doble cadena) se utiliza como plantilla para la síntesis del ARN mensajero (ARNm). El ARNm maduro se traduce en aminoácidos, formando proteínas (traducción) con la ayuda del ARN ribosomal y el ARN de transferencia (ARNt). Esta imagen muestra la transcripción sin modificaciones post-transcripcionales del ARN.
Los LOS Neisseria transcritos primarios, o productos inmediatos de la transcripción, sufren alteraciones para convertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum biológicamente funcionales.
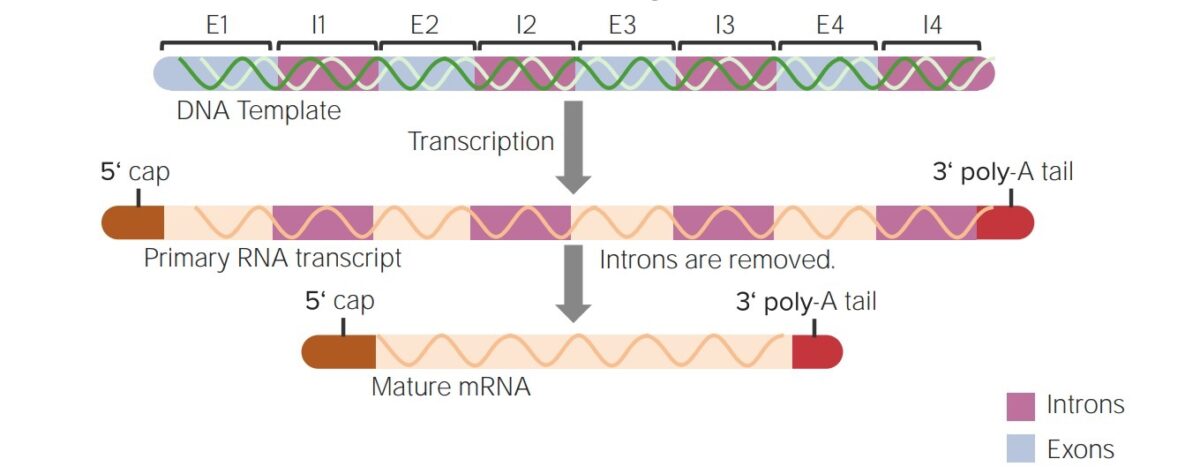
Resumen de las modificaciones post-transcripcionales del ARNhn en un ARNm maduro:
La adición de la caperuza 5′ y la cola de poli-A 3′ y el empalme (eliminación de las secuencias intermedias o intrones)
La 7-metilguanosina (residuo de guanilo metilado) se añade al AL Amyloidosis extremo 5′ del ARNhn a través de:
Funciones:
De 50 a 250 residuos de adenilo adenosin monofosfato (AMP, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) se añaden al AL Amyloidosis extremo 3′ del ARNhn a través de:
Función:
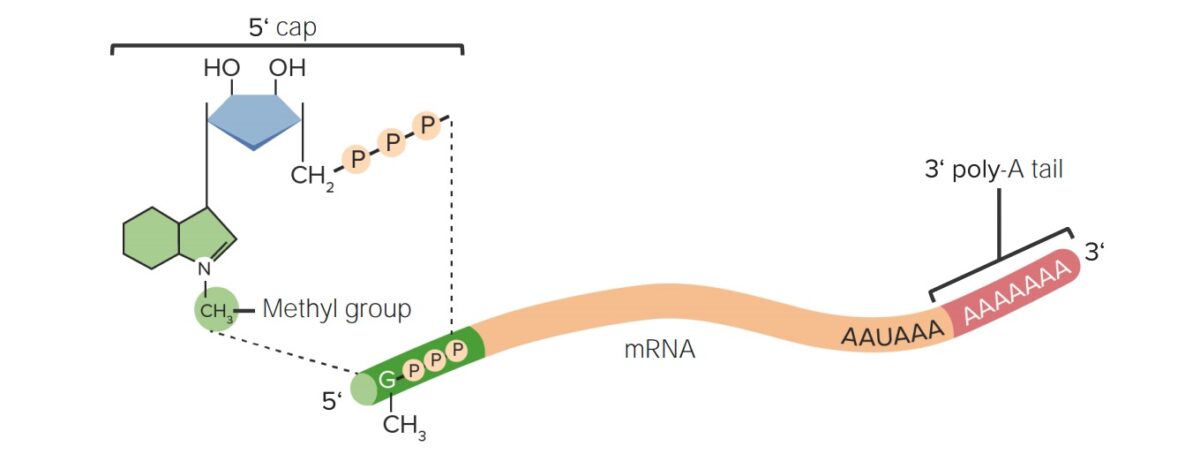
Modificaciones post-transcripcionales del ARN:
Las modificaciones de la caperuza 5′ (7-metilguanosina) y la cola de poli-A 3′ impiden la degradación del ARNm en el citosol.
El heterogéneo nuclear (pre-ARNm) contiene:
Procesamiento:
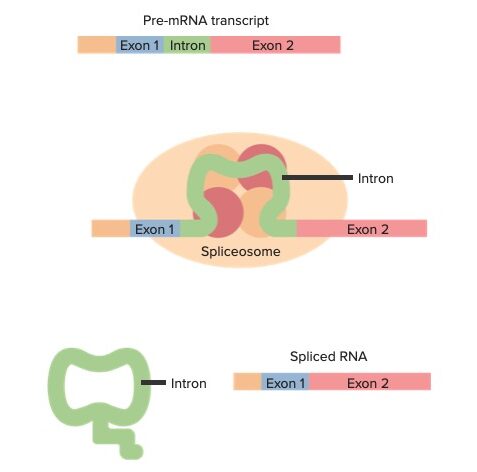
Exones e intrones del pre-ARNm con una visión general del empalme (de arriba a abajo):
El transcrito del pre-ARNm contiene exones e intrones. Las interacciones del transcrito con las ribonucleoproteínas nucleares pequeñas y otras proteínas forman un espliceosoma en determinadas uniones del transcrito. Se realizan cortes en los sitios de empalme y se libera el intrón. El ARN empalmado ahora solo tiene exones, que contienen la secuencia codificante.
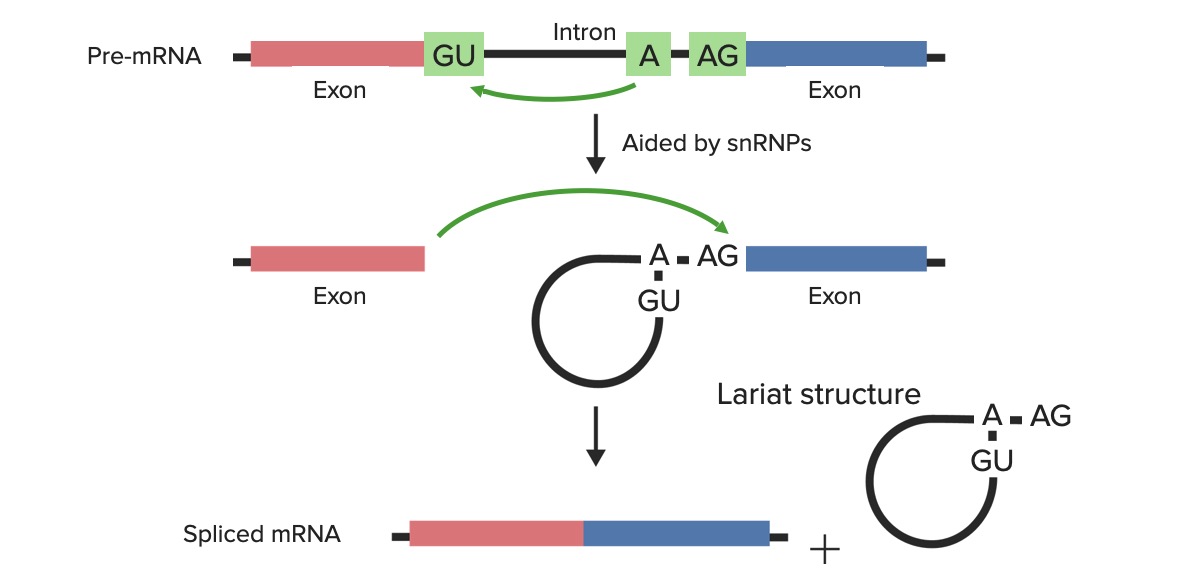
Aspectos técnicos del empalme:
El pre-ARNm/ARNhn está formado por exones e intrones. Las ribonucleoproteínas nucleares pequeñas + otras proteínas reconocen el sitio de ramificación y las uniones exón–intrón donde cortar: el sitio donador 5′ (que contiene la secuencia invariable GU) y el sitio aceptor 3′ (que contiene la secuencia invariable AG). El transcrito del ARNhn + las ribonucleoproteínas nucleares pequeñas + otras proteínas se combinan en estos sitios y forman el espliceosoma.
Imagen superior: Con la ayuda de las ribonucleoproteínas nucleares pequeñas (snRNPs), el primer corte lo realiza el residuo adenil (en el sitio de ramificación) mediante un ataque nucleofílico en el sitio donador 5′.
Imagen central: El extremo 5′ libre forma entonces un enlace con el sitio de ramificación (formando la estructura de lazo).
Imagen inferior: El segundo corte se realiza en el sitio 3′ del intrón y los exones se unen.
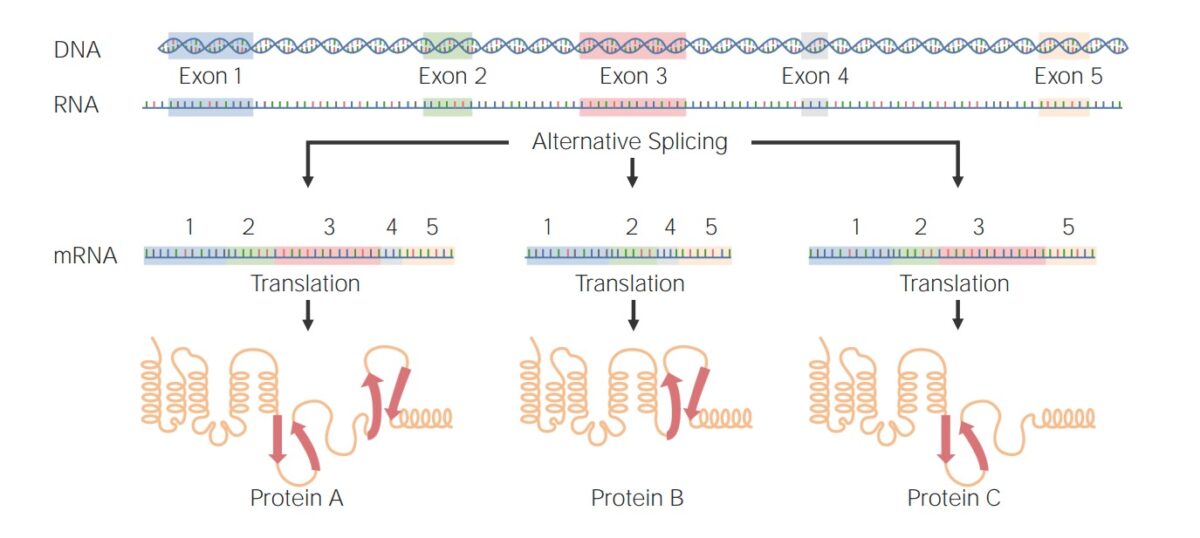
Ejemplos de empalmes alternativos:
Proteína A: Los exones 1–5 se unieron tras el empalme de los intrones.
Proteínas B y C: Se excluyó selectivamente un exón para formar una proteína diferente.
Generalmente, la secuencia de ADN se refleja en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ARNm maduro. La alteración de la secuencia o la edición del ARN es una excepción.
Edición de “C a U”:
Edición de “A a I”:
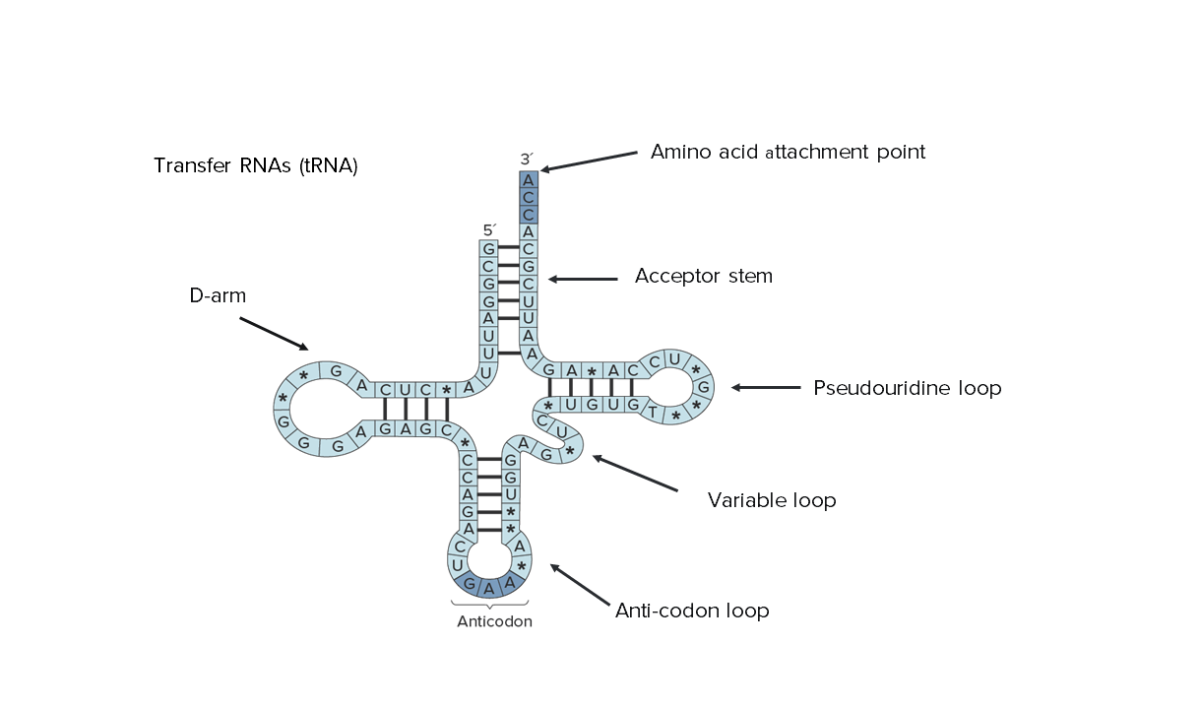
Estructura secundaria del ARN de transferencia (ARNt). Observe que toda la secuencia puede ser vista, lo que indica su tamaño reducido.
Imagen por Lecturio.