Las miopatías mitocondriales son afecciones que surgen de la disfunción de las mitocondrias ( los LOS Neisseria organelos productores de energía) y se caracterizan por síntomas musculares prominentes y se acompañan de varios síntomas causados por órganos con altos requerimientos de energía. Los LOS Neisseria órganos desproporcionadamente afectados incluyen los LOS Neisseria músculos esqueléticos, el cerebro y el corazón. Las miopatías mitocondriales son causadas por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN nuclear o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN mitocondrial, que generalmente resultan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una producción reducida de la energía que necesitan las células. La presentación puede ser una miopatía aislada, encefalomiopatía, oftalmoplejías o una enfermedad multisistémica. El diagnóstico implica antecedentes médicos y familiares detallados, junto con estudios genéticos y de laboratorio. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la biopsia, existe proliferación subsarcolémica e intermiofibrilar de mitocondrias que se observan como “fibras rojas rasgadas”. Esta afección indica una respuesta compensatoria a la falta de energía. No existe un tratamiento definitivo. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fisioterapia y un enfoque multidisciplinario para abordar los LOS Neisseria síntomas acompañantes.
Last updated: Apr 24, 2025
Las miopatías mitocondriales son enfermedades que surgen de la disfunción mitocondrial ( los LOS Neisseria organelos productores de energía). Estas enfermedades se caracterizan por síntomas musculares prominentes (como debilidad muscular) y se acompañan de varios síntomas causados por órganos con altos requerimientos de energía.
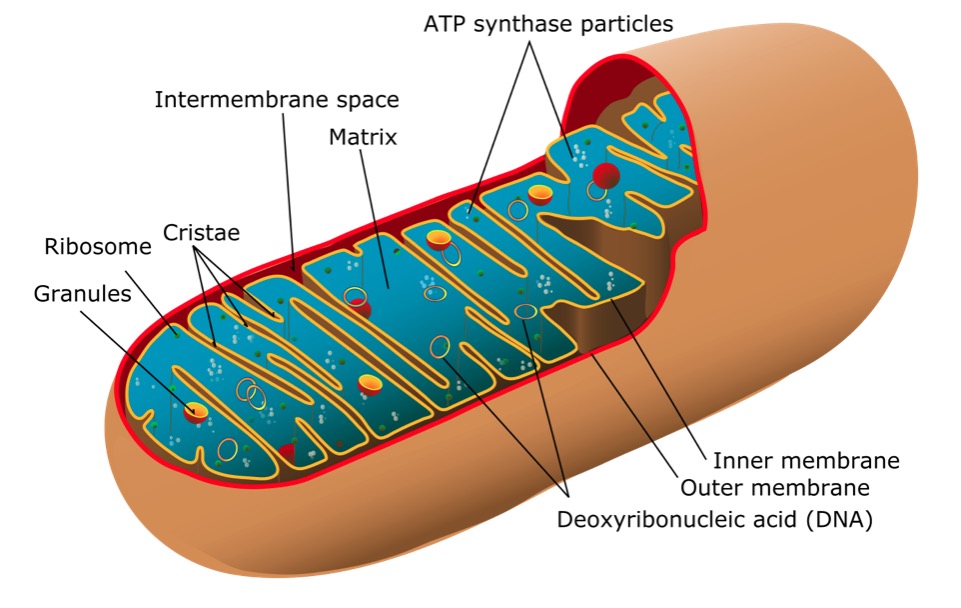
Estructura de una mitocondria
Imagen: “Mitochondrion of the eukaryotic cell” por Mariana Ruiz Villarreal. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas se correlacionan con los LOS Neisseria órganos o tejidos afectados:

Síndrome de Kearns-Sayre:
Paciente con ptosis bilateral
Biopsia muscular en un paciente con características típicas de encefalomiopatía mitocondrial, acidosis láctica y episodios similares a accidentes cerebrovasculares (MELAS):
Tinción tricrómica de Gomori modificada que muestra varias fibras rojas rasgadas (flechas)
Biopsia muscular de un paciente con mioclonías y deterioro cognitivo progresivo:
Fibras azules rasgadas observadas en la preparación de succinato deshidrogenasa