El monóxido de carbono (CO) es un gas inodoro, incoloro, insípido y no irritante que se forma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la combustión de hidrocarburos (e.g., incendios, gases de escape de automóviles, calentadores de gas). El monóxido de carbono tiene mayor afinidad con la hemoglobina que el oxígeno, formando carboxihemoglobina. El aumento de los LOS Neisseria niveles de carboxihemoglobina provoca hipoxia tisular y daño cerebral. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas de la intoxicación por CO incluyen cefalea, náuseas, debilidad, dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico, dificultad para respirar, convulsiones, coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma e incluso la muerte. La oxigenoterapia es clave en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la intoxicación por CO.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas de la intoxicación por CO son variados e inespecíficos.
La gravedad de la presentación clínica de la intoxicación por CO depende de la cantidad de CO en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el aire inhalado, la duración de la exposición y el estado general de salud del individuo afectado.
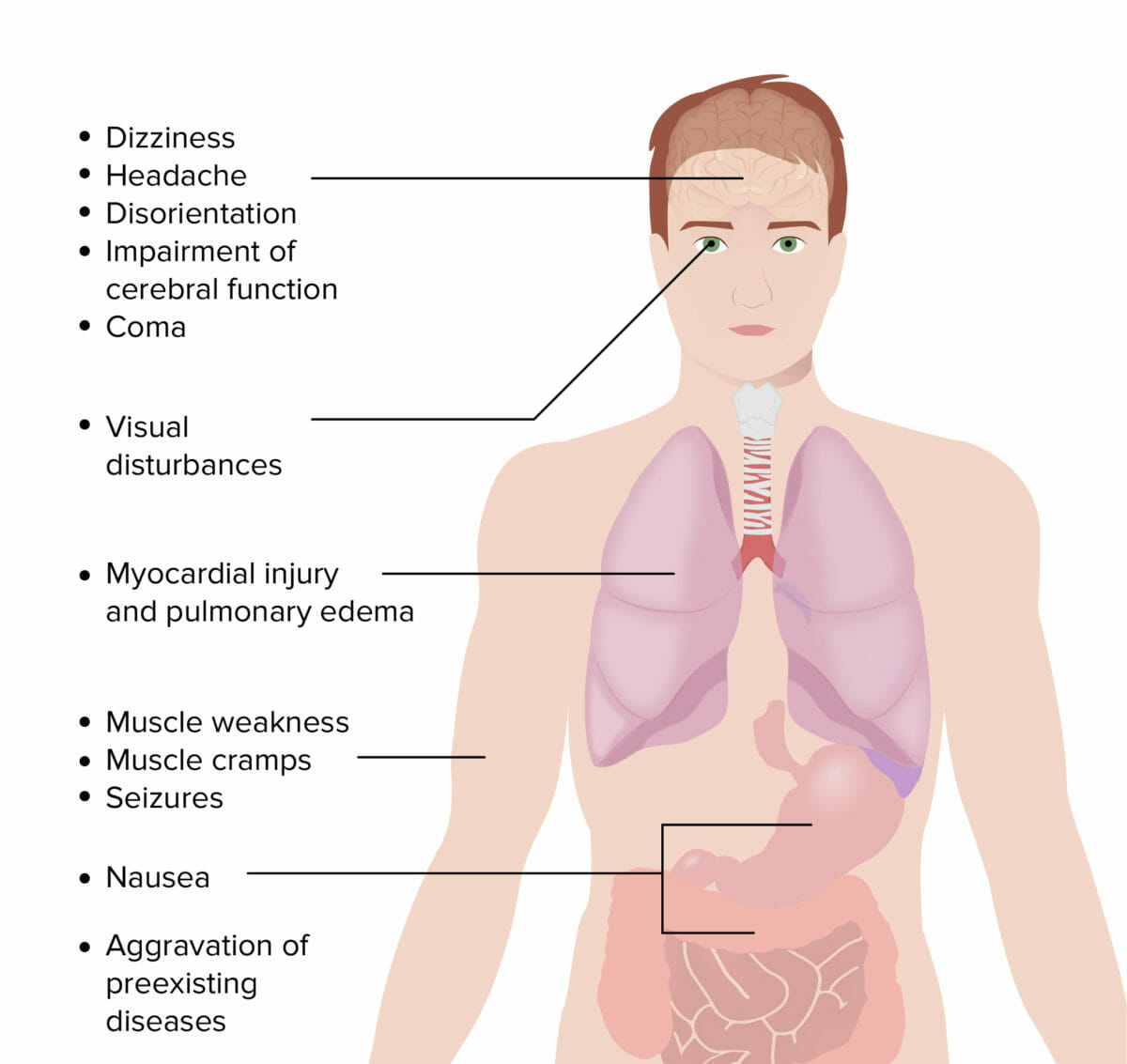
Síntomas de intoxicación por monóxido de carbono
Imagen por Lecturio.