La hemorragia epidural es un evento caracterizado por sangrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio epidural entre la duramadre y el cráneo. El mecanismo principal que desencadena la hemorragia es el traumático (i.e., traumatismo craneoencefálico cerrado), que causa una lesión arterial, más comúnmente una lesión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la arteria meníngea media. La hemorragia epidural se presenta de forma aguda, generalmente inmediatamente (segundos a horas) después del traumatismo craneoencefálico, con un nivel alterado de conciencia que puede abarcar desde una pérdida momentánea de conciencia hasta coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha clínica posterior a un traumatismo craneoencefálico y se confirma mediante la neuroimagenología (i.e., tomografía computarizada (TC) de cabeza sin contraste). El tratamiento incluye la estabilización del paciente, la interrupción (posiblemente la reversión) de todos los LOS Neisseria anticoagulantes, monitorización en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI) neurológica y la intervención neuroquirúrgica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La hemorragia epidural ( hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception epidural) es un evento caracterizado por sangrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio epidural entre la duramadre y el cráneo. La hemorragia epidural suele ser consecuencia de un traumatismo.
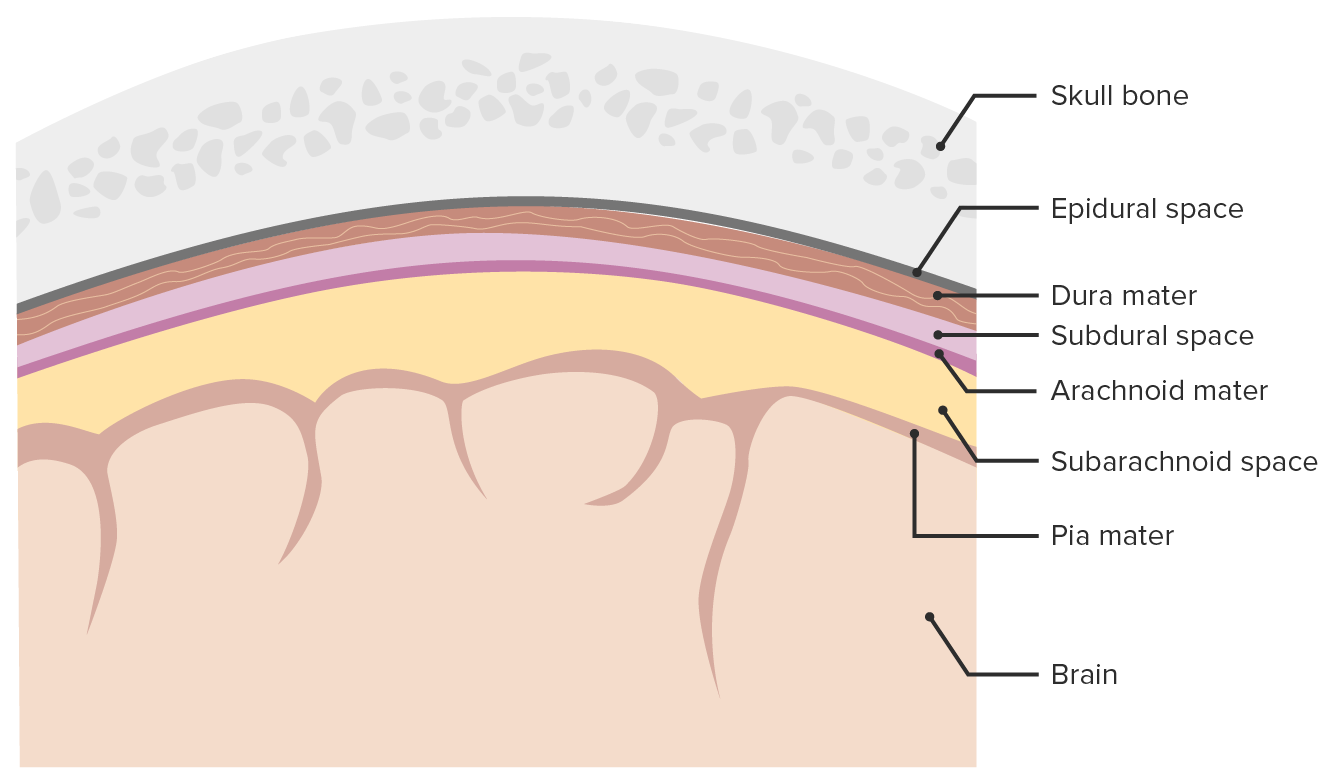
Meninges y espacios meníngeos:
Imagen que muestra las 3 capas (duramadre, aracnoides, piamadre) que rodean el cerebro y la médula espinal. Las meninges sirven como protección mecánica del sistema nervioso central (SNC), sostienen los vasos sanguíneos cerebrales y espinales y permiten el paso del líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR). Solo el espacio subaracnoideo es un verdadero espacio presente en condiciones fisiológicas, mientras que los espacios epidurales y subdurales se forman solamente durante procesos patológicos. El espacio epidural puede abrirse como resultado de un traumatismo craneoencefálico o en raras ocasiones debido a otros procesos patológicos.
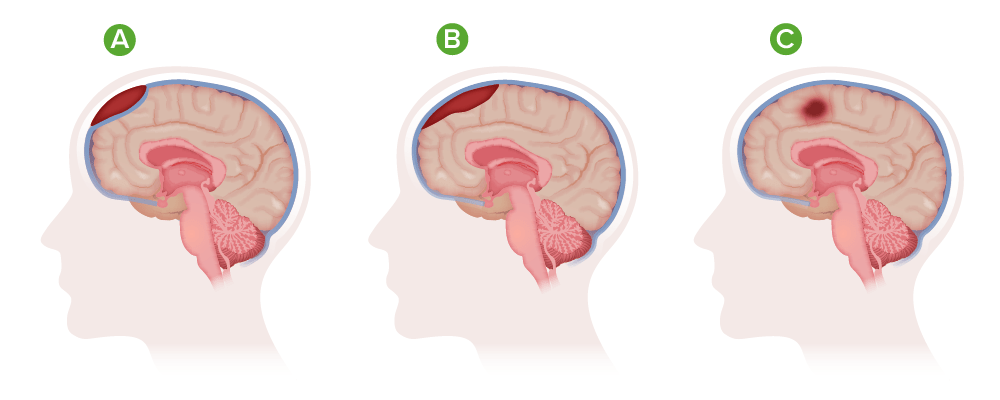
Tipos de hematomas
A) Hematoma epidural;
B) Hematoma subdural;
C)Hematoma intracraneal
Traumatismo de la cabeza:
Hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception epidural no traumático:
El traumatismo craneoencefálico es la etiología más común del hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception epidural. Es común un “intervalo lúcido” seguido de un rápido deterioro neurológico.
TC de cabeza sin contraste:
RM de cabeza:
Angiografía:
Punción lumbar:
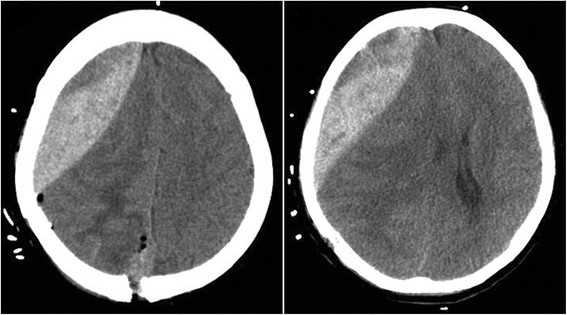
Hematoma epidural:
TC que muestra un hematoma epidural frente al campo quirúrgico después de la resección del tumor
El hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception epidural, especialmente si se presenta con compromiso neurológico o coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma, es una situación neurológica emergente que a menudo requiere intervención quirúrgica. La falta de estabilización del paciente, diagnóstico, evaluación e intervención oportuna podría resultar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una expansión hemorrágica, lesión cerebral parenquimatosa, aumento de la PIC, hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias cerebral y muerte.
Las herramientas de toma de decisiones que se utilizan clínicamente para determinar el manejo operatorio o no operatorio incluyen: