El estómago es un saco muscular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la parte superior izquierda del abdomen que juega un papel fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la digestión. El estómago se desarrolla a partir del intestino anterior y conecta el esófago con el duodeno. Estructuralmente, el estómago tiene forma de J y forma una curvatura mayor y menor y se divide a grandes rasgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum regiones: cardias, fundus Fundus The superior portion of the body of the stomach above the level of the cardiac notch. Stomach: Anatomy, cuerpo y píloro. A nivel microscópico, la pared del estómago tiene varias capas, que incluyen mucosa, submucosa, muscular y serosa. El estómago está lleno de glándulas que secretan una variedad de sustancias involucradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el proceso digestivo. La irrigación arterial al AL Amyloidosis estómago proviene principalmente de los LOS Neisseria vasos que se originan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tronco celíaco.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El estómago es un saco muscular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la parte superior del abdomen que juega un papel fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la digestión.
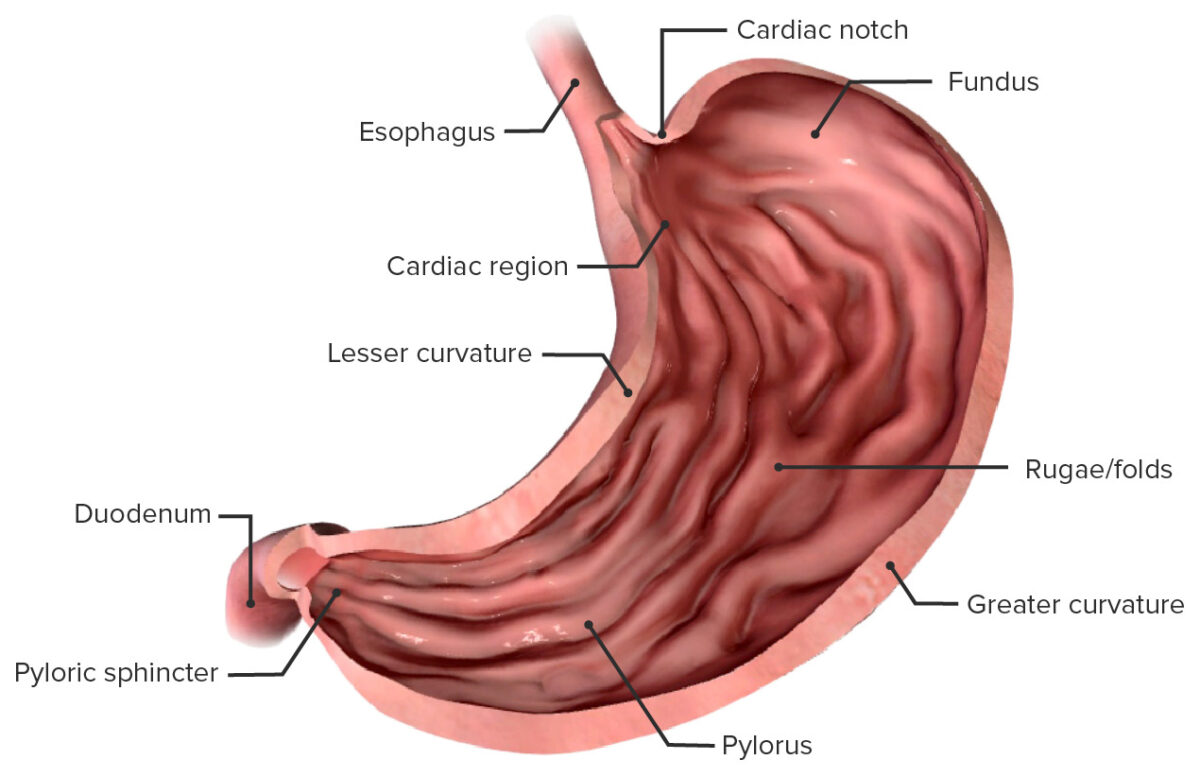
Componentes anatómicos del estómago
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioEl estómago está en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum contacto directo con una serie de otros órganos, que incluyen:
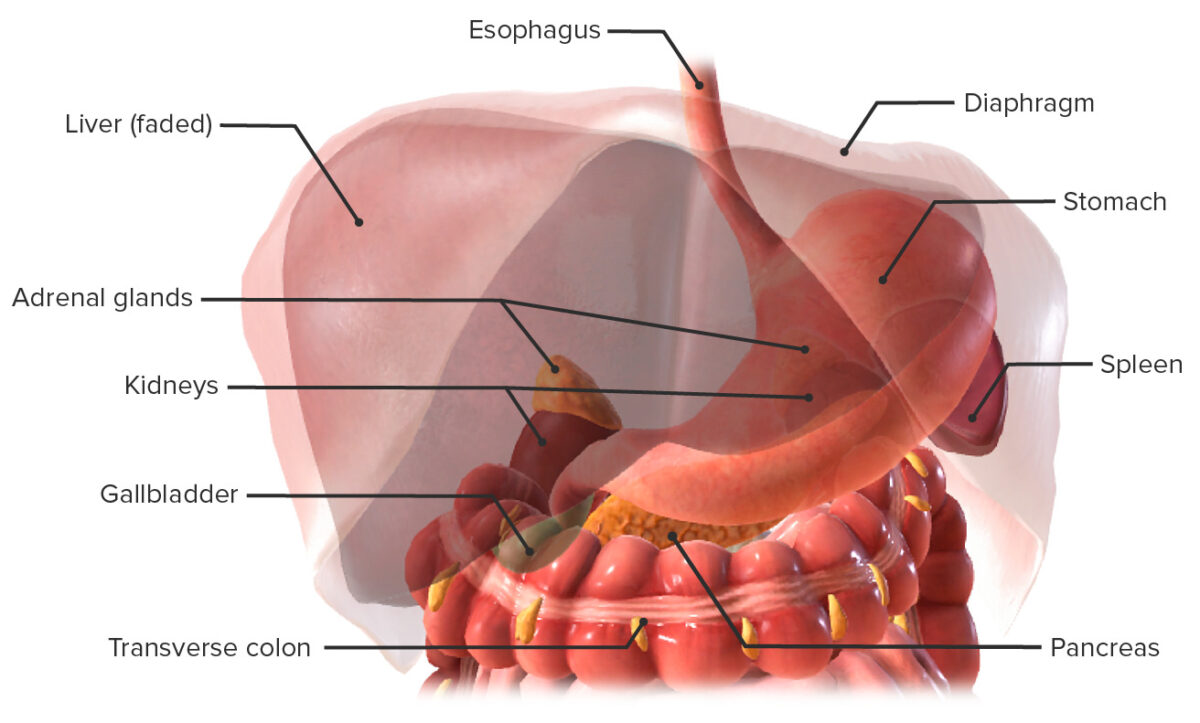
Estómago in situ y las relaciones con sus estructuras vecinas
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio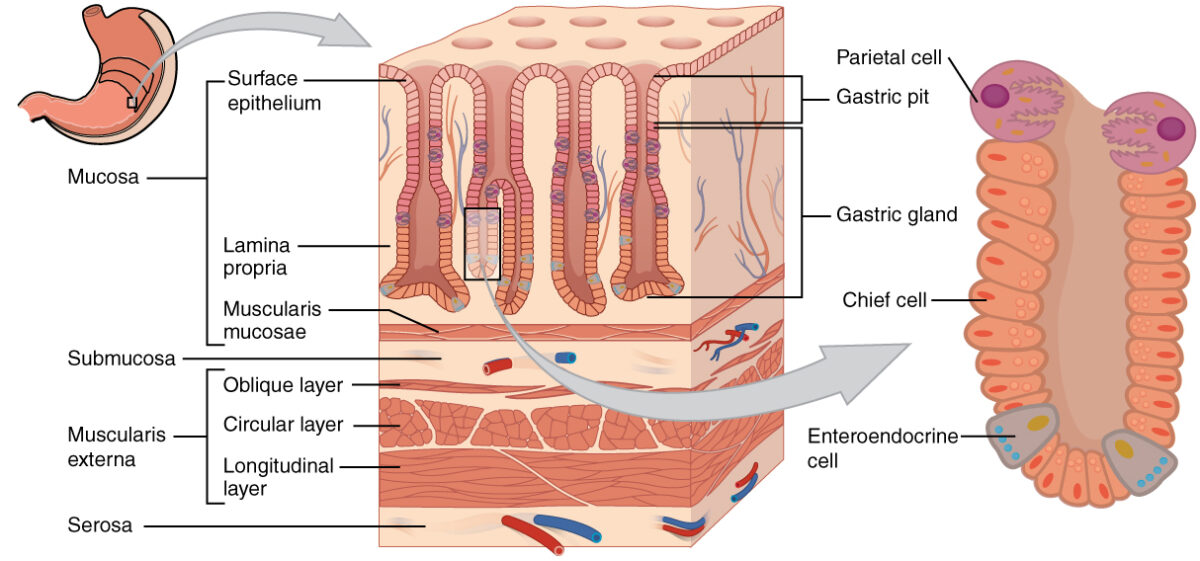
Capas de la pared del estómago:
En el epitelio, las fosas gástricas conducen a glándulas gástricas que secretan una variedad de sustancias para ayudar en la digestión.
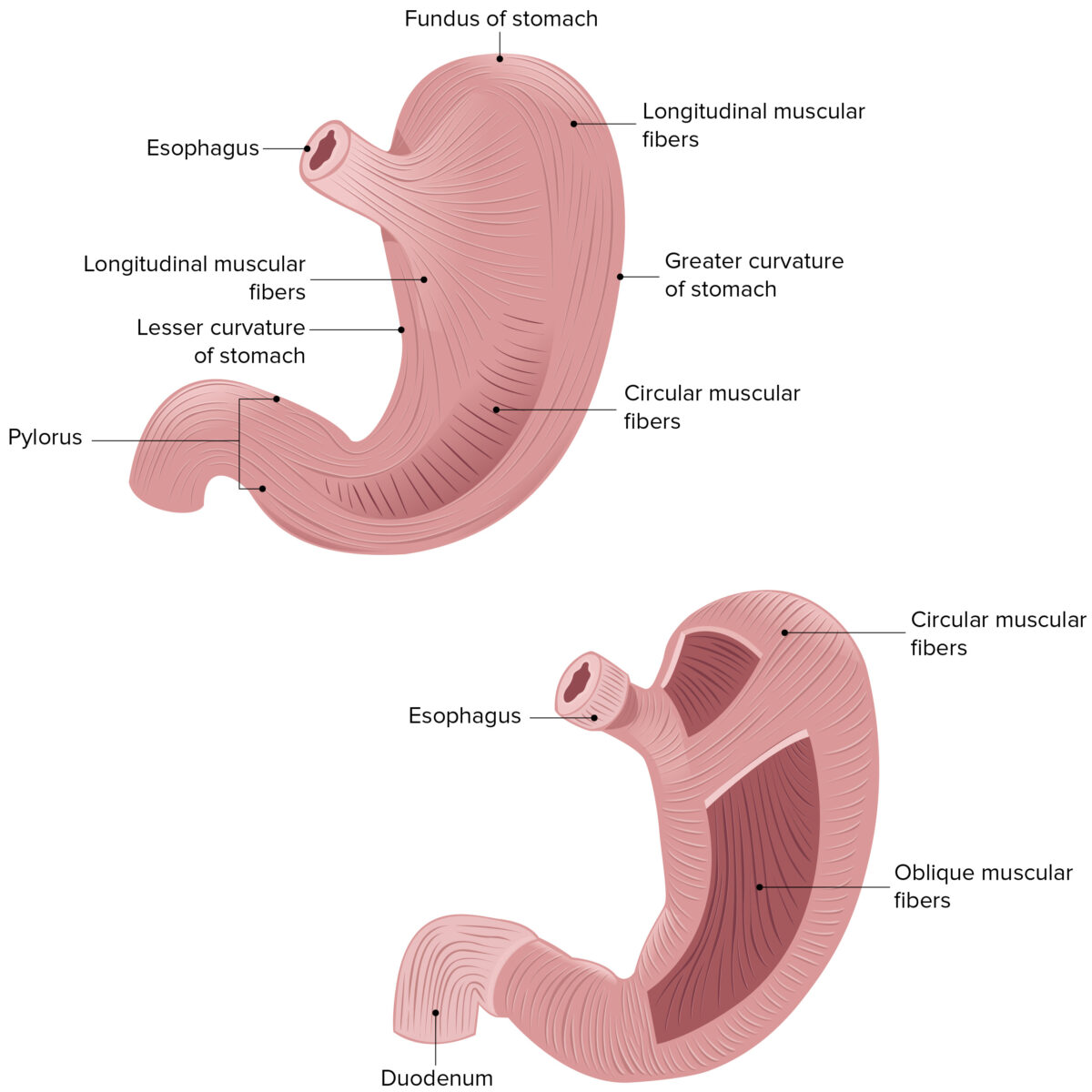
Imagen que muestra las 3 capas musculares de la pared del estómago
Imagen por Lecturio.Características generales:
Tipos de glándulas:
Tipos de células dentro de las glándulas:
Comprende (de superficie a profundidad):
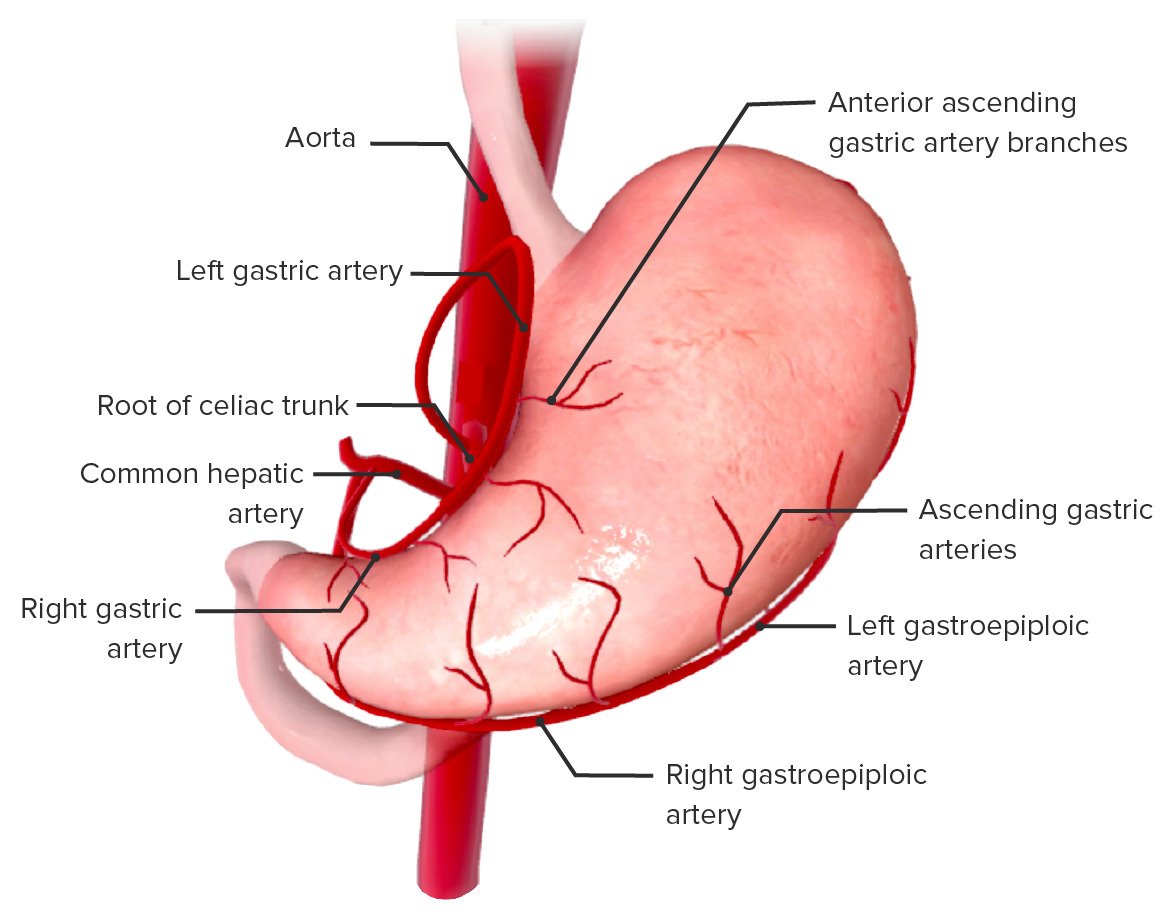
Imagen que muestra la irrigación del estómago
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio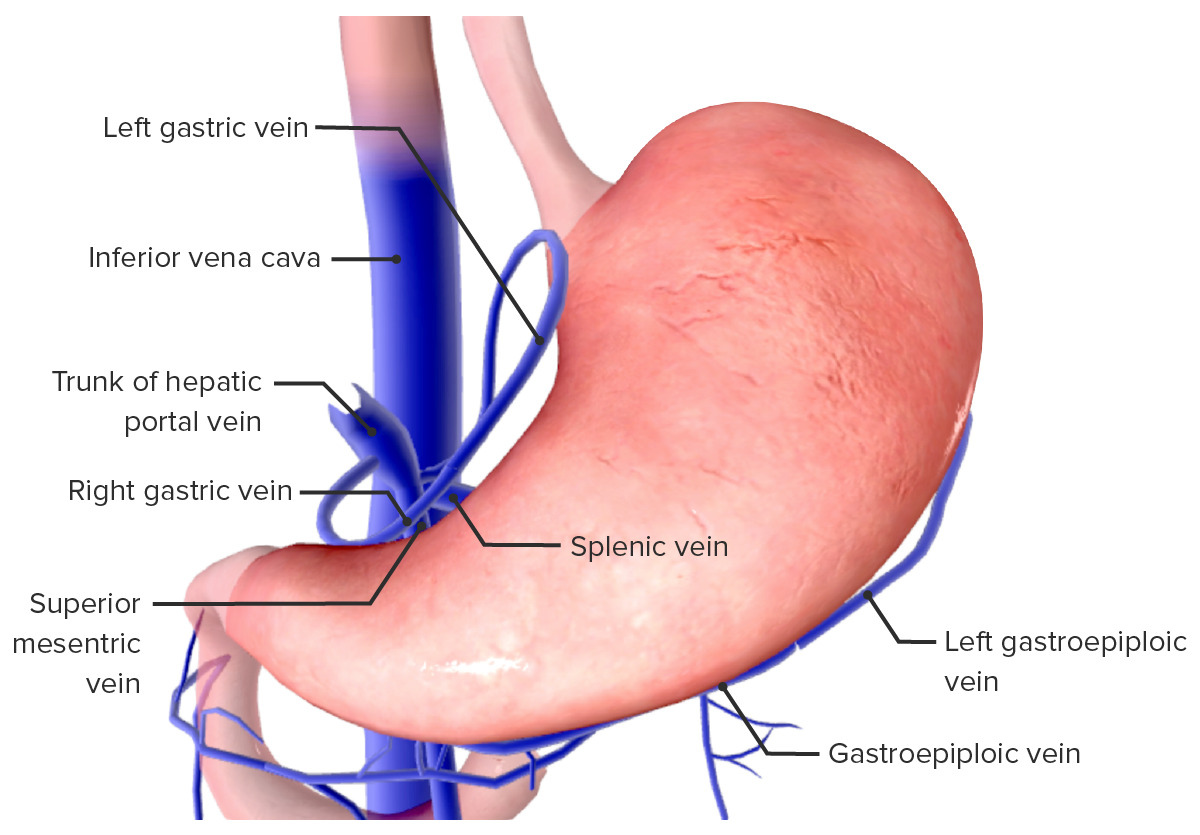
Drenaje venoso del estómago
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioLos LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos que drenan el estómago están dispuestos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una red compleja.
El estómago está inervado por el sistema nervioso autónomo.
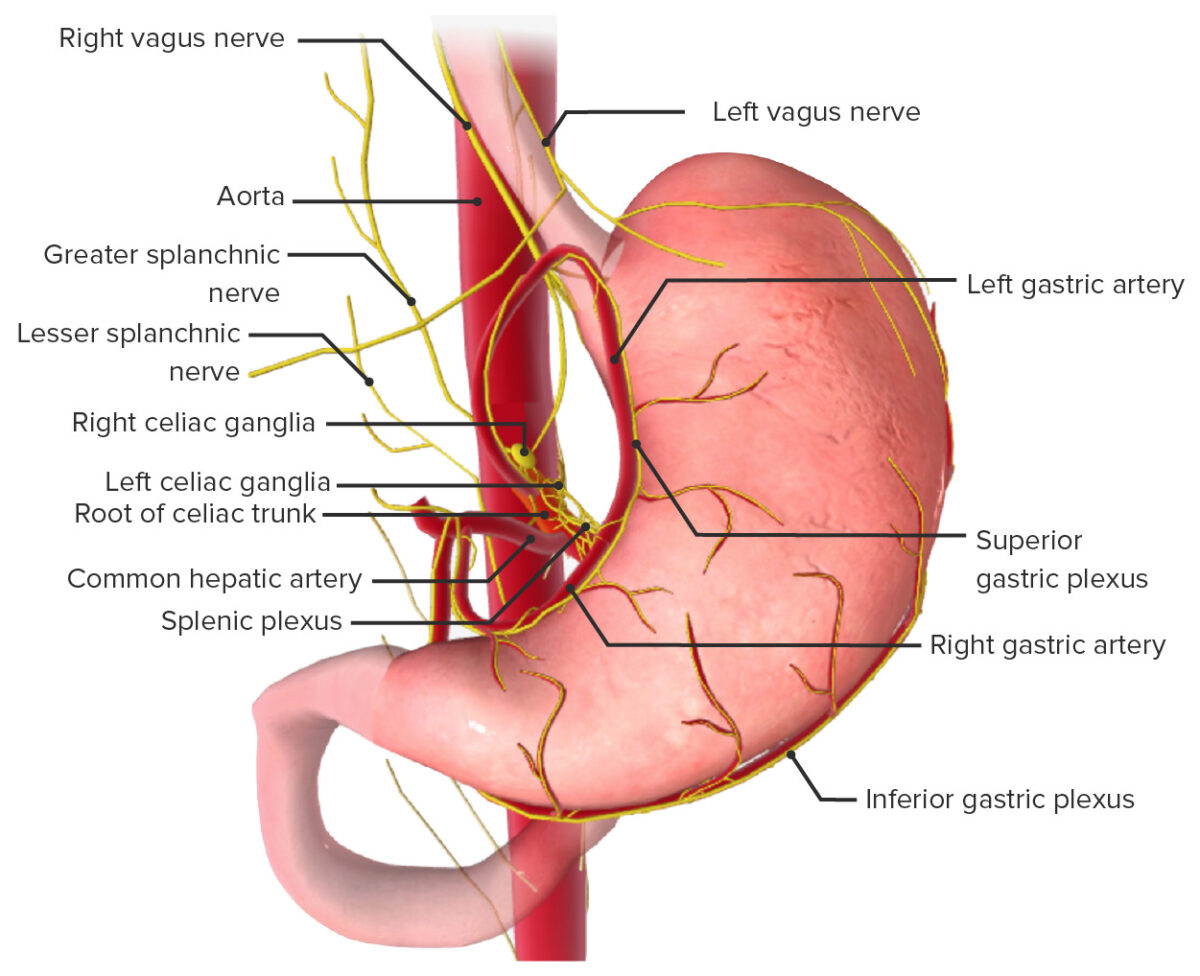
Inervación del estómago
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio