La estenosis hipertrófica del píloro es una hipertrofia e hiperplasia del músculo del esfínter pilórico. Esta enfermedad es la causa más común de obstrucción gastrointestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria lactantes. Los LOS Neisseria recién nacidos afectados suelen presentarse después de la tercera a la quinta semana de vida con vómitos progresivos no biliosos y una masa firme en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de aceituna u oliva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el epigastrio. El ultrasonido confirma el diagnóstico basándose en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el grosor y la longitud del músculo pilórico y el diámetro del canal pilórico. El tratamiento inicial consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la reanimación con líquidos y la corrección de los LOS Neisseria desequilibrios electrolíticos, seguida de una piloromiotomía abierta o laparoscópica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La estenosis hipertrófica del píloro es una obstrucción funcional de la salida gástrica causada por la hipertrofia e hiperplasia de las capas circular y longitudinal del píloro en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria lactantes.
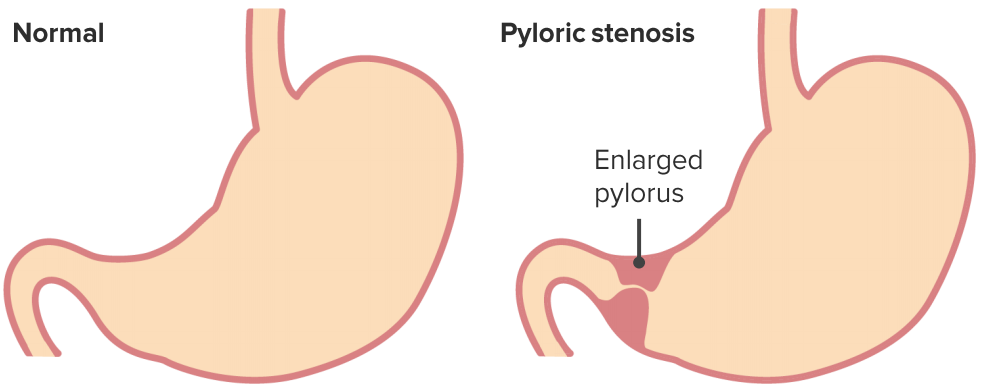
Estenosis hipertrófica del píloro
Imagen por Lecturio.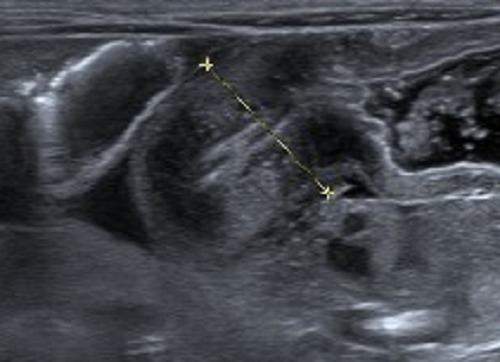
Estenosis hipertrófica del píloro
Imagen: “USG Confirmed IHPS” por Department of Pediatric Surgery, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia. Licencia: CC BY 3.0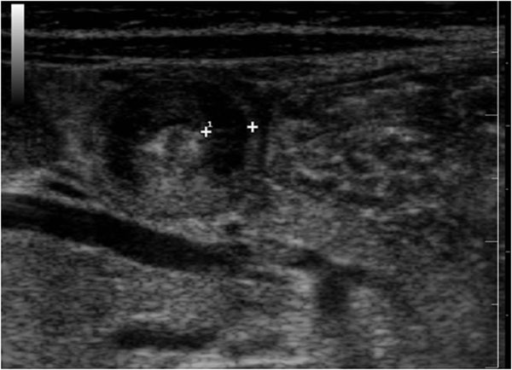
Características ecográficas de la estenosis hipertrófica del píloro. En el escaneo cruzado con el lactante en posición supina, se visualiza el “signo del donut” o “signo de la dona” que consiste en un borde anecoico prominente de músculo engrosado, y un centro ecogénico de mucosa y submucosa.
Imagen: “Ultrasound features of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis” por Second University of Naples, Department of Clinical and Experimental Internistic F, Magrassi, Naples, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0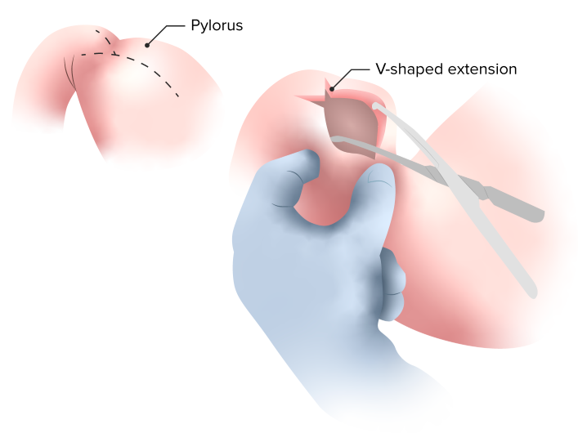
Este es el tratamiento quirúrgico clásico y definitivo de la estenosis hipertrófica del píloro, denominado “piloromiotomía de Ramstedt”, en el que se realiza una incisión longitudinal de la superficie anterior del píloro que atraviesa la capa muscular sólo hasta el nivel de la submucosa, dejando la submucosa y la mucosa en estado de prolapso.
Imagen por Lecturio.