El epitelio es un complejo de organizaciones celulares especializadas dispuestas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum láminas y que recubren las cavidades y cubren las superficies del cuerpo. Las células exhiben polaridad, teniendo un polo apical y uno basal. Las estructuras importantes para la integridad y función del epitelio involucran la membrana basal, la lámina semipermeable sobre la que descansan las células y las interdigitaciones, así como las uniones celulares. El epitelio se clasifica según las células (escamosas, cúbicas, columnares), el número de capas y otras características únicas, ya sea por función (epitelio de transición que permite la distensión) o apariencia (epitelio pseudoestratificado que da una falsa impresión de múltiples capas). El epitelio de superficie tiene múltiples funciones, que incluyen protección, secreción, filtración y recepción sensorial.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un complejo de organizaciones celulares especializadas dispuestas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum láminas y que recubren las cavidades y cubren las superficies del cuerpo:
Estas células exhiben polaridad:
El epitelio de superficie no posee vasos sanguíneos; por lo tanto, los LOS Neisseria nutrientes y el oxígeno se reciben del tejido conectivo adyacente.
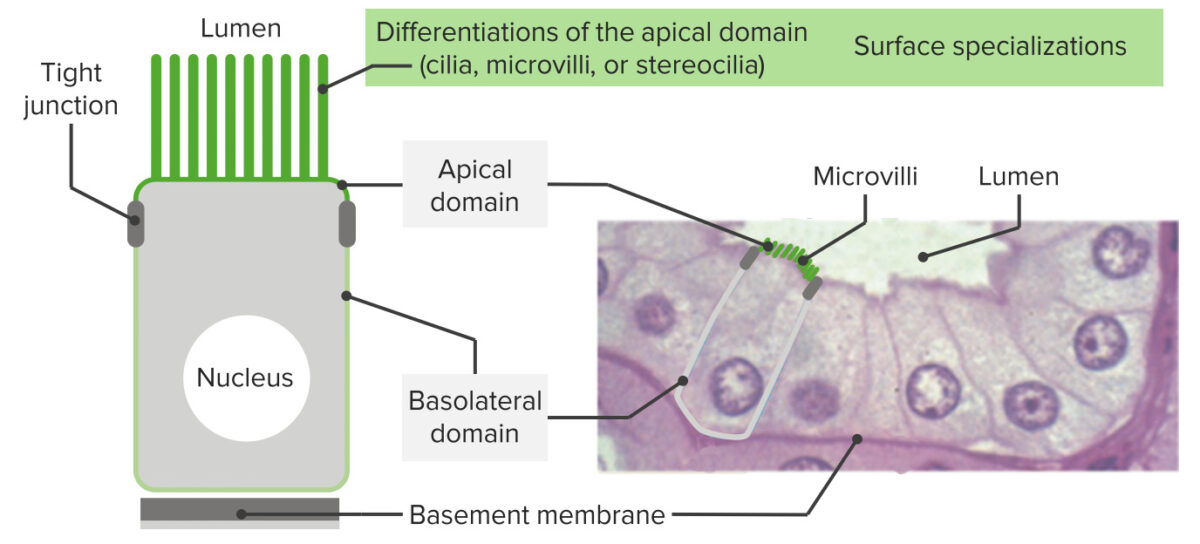
Los epitelios tienen un ápice, bordes laterales y una superficie asentada sobre una membrana basal: Como se ve en la imagen, estas células exhiben polaridad (tienen dominios apicales y dominios basal/basolateral). En el extremo apical, las estructuras rodean el área (como una banda alrededor de la célula) facilitando la adhesión de célula a célula (uniones estrechas y uniones adherentes). Cerca de la membrana basal, los hemidesmosomas anclan el epitelio a la lámina basal. A la derecha se muestra la histología del revestimiento epitelial intestinal con las estructuras correspondientes. En el dominio apical, se ven microvellosidades.
Imagen por Lecturio.Tenga en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuenta que hay tejidos que tienen ambas:
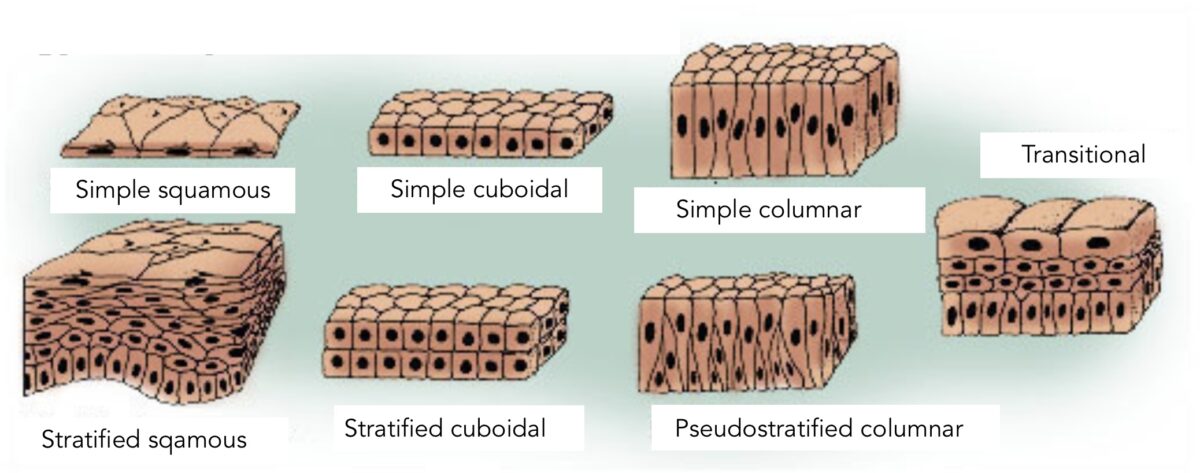
Los tipos de epitelio:
La diferenciación y clasificación de los tipos se basan en la forma de la célula y las capas. El epitelio simple indica 1 capa de células. El epitelio estratificado indica múltiples capas. El epitelio pseudoestratificado da una falsa impresión de > 1 capa debido a los núcleos en diferentes niveles. El epitelio de transición es un tipo en el que la forma de las células “transiciona” dependiendo de la función del órgano (distensión versus relajación, como ocurre en la vejiga urinaria).
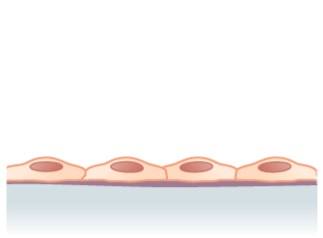
Estructura observada en un epitelio escamoso simple (capa única de células aplanadas)
Imagen: “Simple squamous epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0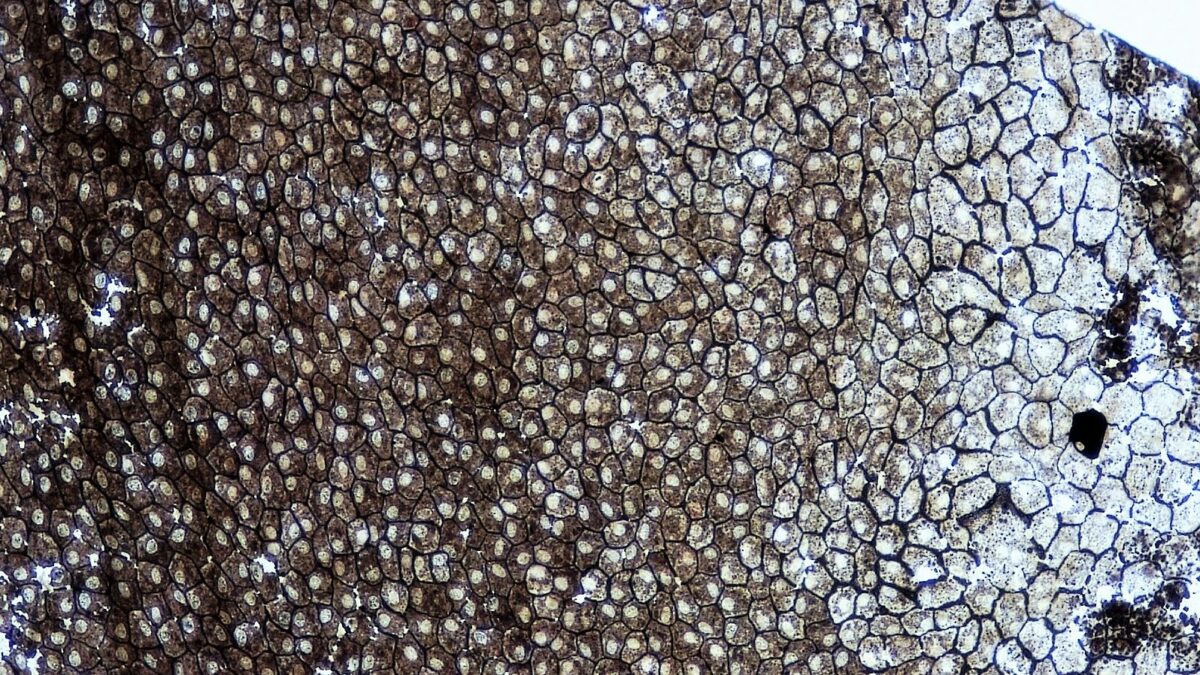
Un montaje completo de epitelio escamoso simple.
Imagen: “Epithelial Tissues Simple Squamous Epithelium” por Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. Licencia: CC0 1.0
Epitelio cúbico simple: 1 capa de células cúbicas
Imagen: “Simple cuboidal epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0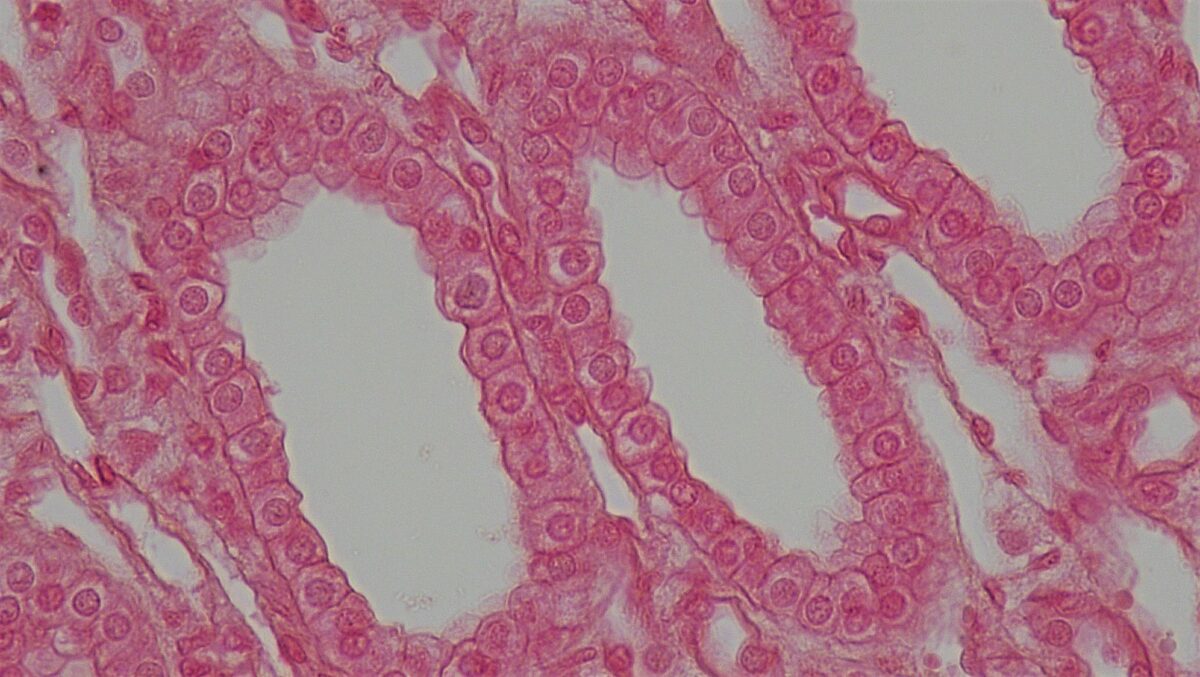
Sección transversal de un túbulo renal que muestra una capa de células cúbicas
Imagen: “Epithelial Tissues Simple Cuboidal Epithelium” por Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. Licencia: CC0 1.0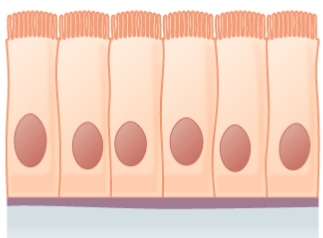
Epitelio columnar simple:
Se muestra una capa de células columnares con cilios
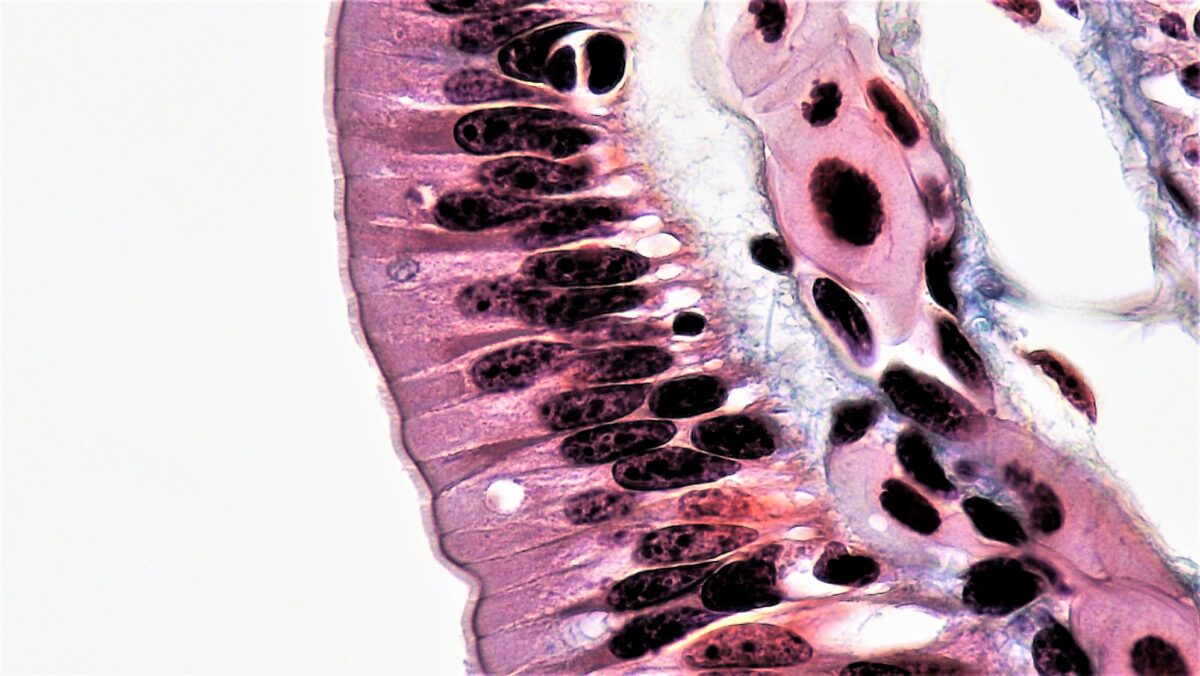
Epitelio columnar simple que recubre el tracto intestinal
Imagen: “Epithelial Tissues Simple Columnar Epithelium” por Epithelial Tissues: Simple Columnar Epithelium. Licencia: CC0 1.0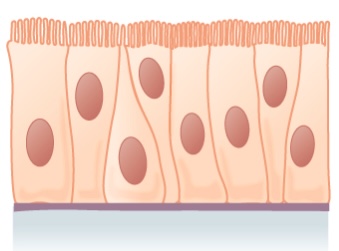
Epitelio pseudoestratificado:
Se muestra una capa única de células columnares, con núcleos en diferentes niveles
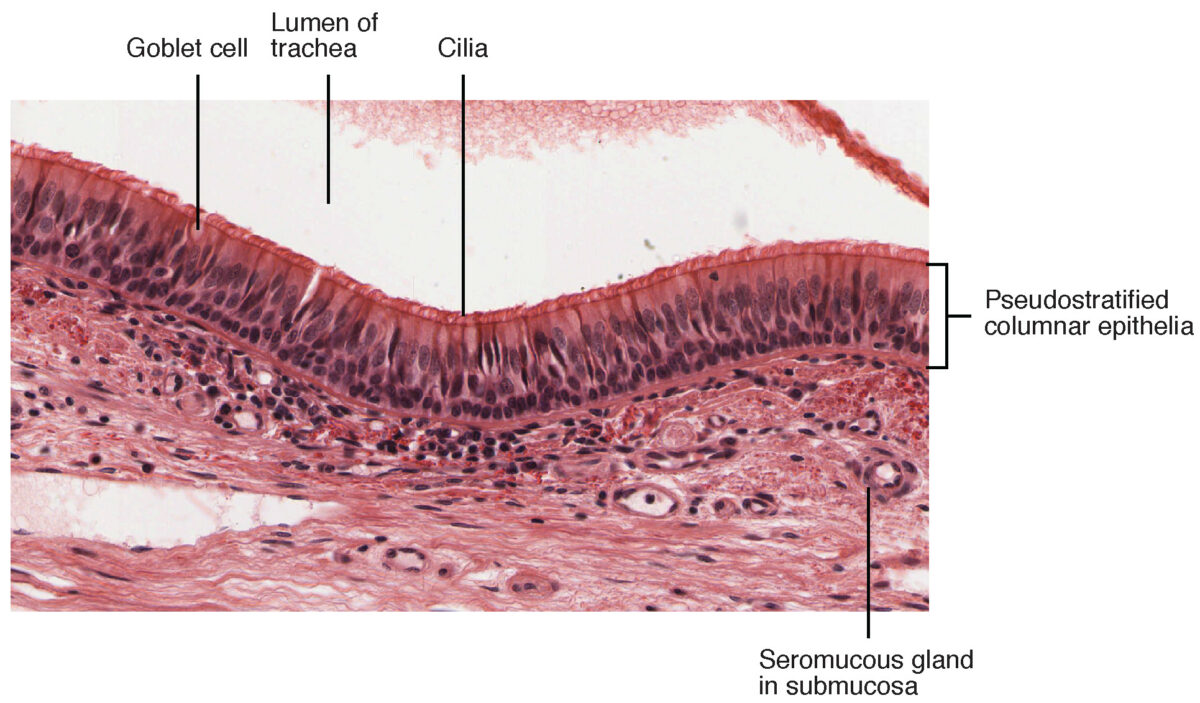
Epitelio columnar pseudoestratificado encontrado en la tráquea
Imagen: “Cross-section of pseudostratified columnar epithelium” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Ilustración del epitelio escamoso estratificado (múltiples capas)
Imagen: “Stratified squamous epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0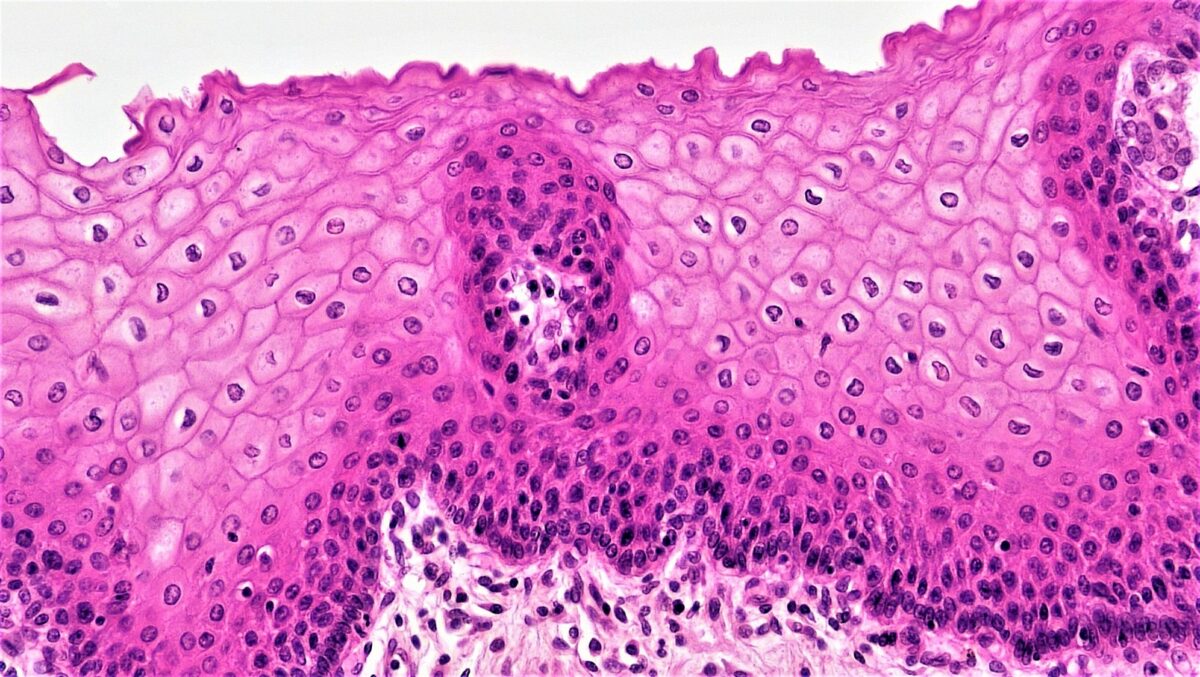
Imagen histológica del epitelio escamoso estratificado
Imagen: “Epithelial Tissues Stratified Squamous Epithelium” por Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. Licencia: CC0 1.0
Epitelio columnar estratificado
Imagen: “Stratified columnar epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0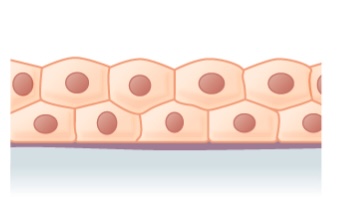
Epitelio cúbico estratificado
Imagen: “Stratified cuboidal epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0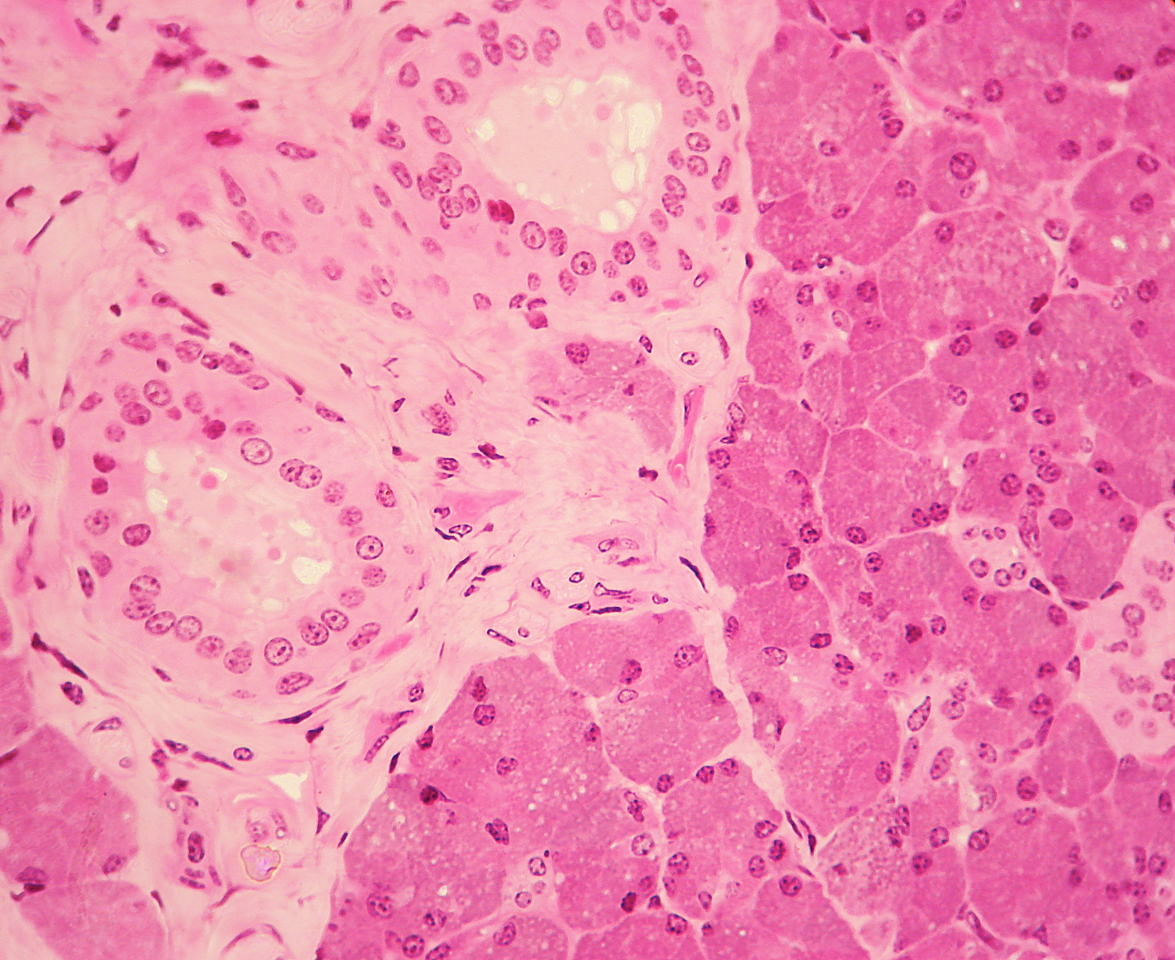
El epitelio cúbico estratificado (visto a la izquierda) es visible en un conducto rodeado por tejido conectivo en la glándula parótida.
Imagen: “WVSOM Parotid Gland1” por Wbensmith. Licencia: CC BY 3.0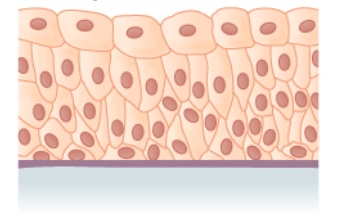
Epitelio transicional
Imagen: “Transitional epithelium” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0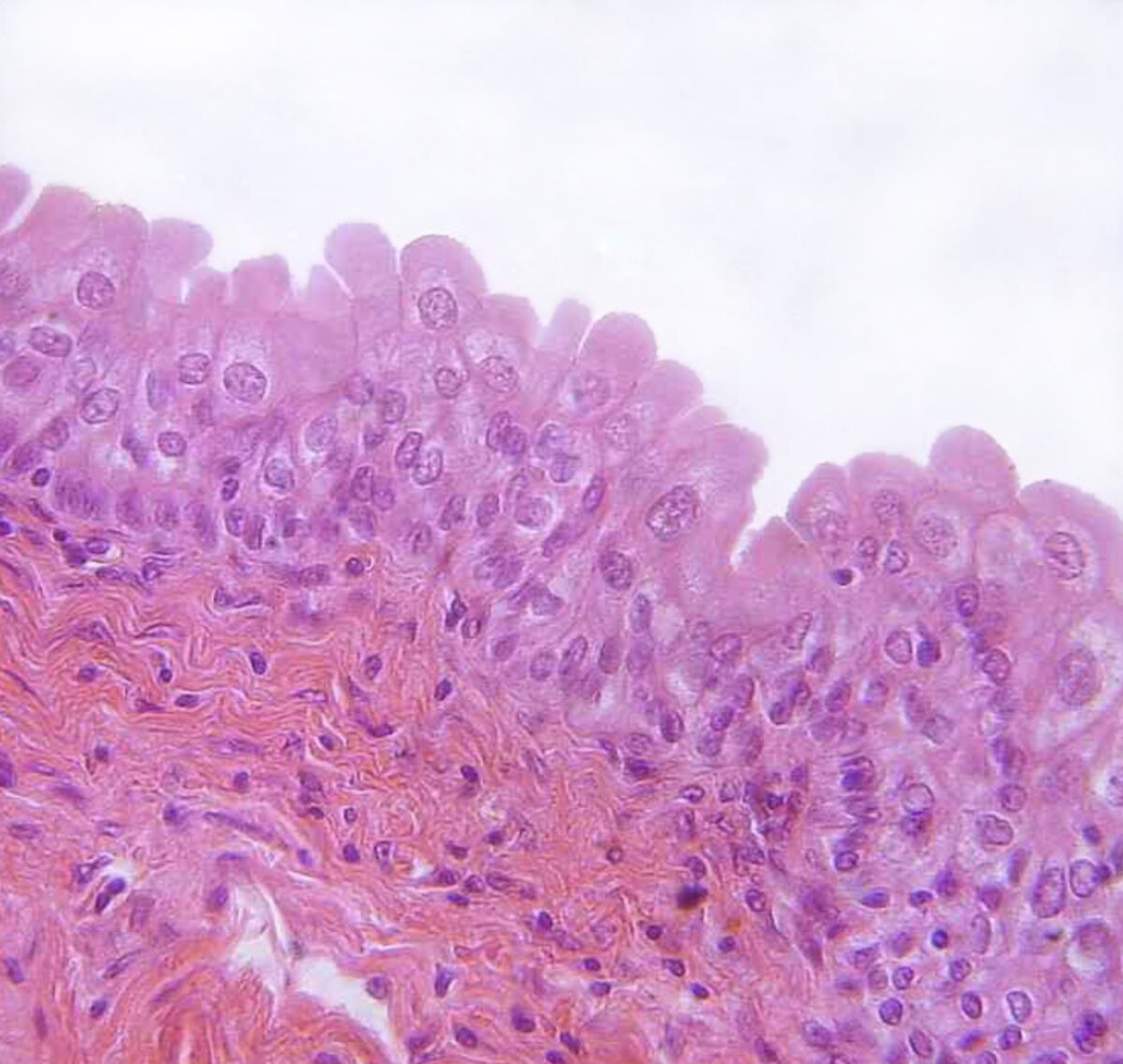
Epitelio de transición encontrado en la vejiga urinaria
Imagen: “urinary bladder, urothelium, haemalum-eosin stain” por Polarlys. Licencia: CC BY 2.5