Las enfermedades pulmonares intersticiales son un grupo heterogéneo de trastornos caracterizados por inflamación y fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans del parénquima pulmonar, especialmente del tejido conectivo pulmonar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las paredes alveolares. Puede ser idiopática (e.g., fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans pulmonar idiopática) o secundaria a enfermedades del tejido conectivo, medicamentos, malignidad, exposición laboral o alérgenos. Las enfermedades pulmonares intersticiales suelen presentarse con disnea de esfuerzo progresiva y tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome seca. Las pruebas de función pulmonar muestran un patrón de enfermedad pulmonar restrictiva. La tomografía computarizada de alta resolución de pulmón y la biopsia suelen establecer el diagnóstico. El tratamiento incluye esteroides e inmunosupresores.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans pulmonar idiopática, la sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly. Sarcoidosis y la enfermedad pulmonar intersticial asociada a enfermedades del tejido conectivo son los LOS Neisseria tipos más comunes de enfermedad pulmonar intersticial.
Es útil clasificar las enfermedades pulmonares intersticiales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aquellas con y sin causa conocida.
| Causa desconocida | Causa conocida |
|---|---|
Neumonías intersticiales idiopáticas:
|
Enfermedades sistémicas
|
| Edad |
|
|---|---|
| Sexo |
|
| Presentación clínica |
|
| Síntomas |
|
| Antecedentes médicos |
|
| Antecedentes de medicamentos | Metotrexato, azatioprina, rituximab Rituximab A murine-derived monoclonal antibody and antineoplastic agent that binds specifically to the cd20 antigen and is used in the treatment of leukemia; lymphoma and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunosuppressants, bloqueadores del factor de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tumoral, amiodarona, nitrofurantoína, quimioterapia |
| Antecedentes familiares | Tener un pariente cercano con neumonitis intersticial idiopática es un fuerte factor de riesgo de padecer enfermedad pulmonar intersticial, especialmente fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans pulmonar idiopática. |
| Antecedentes sociales |
|
La detección de autoanticuerpos puede ayudar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico de algunas enfermedades del tejido conectivo.
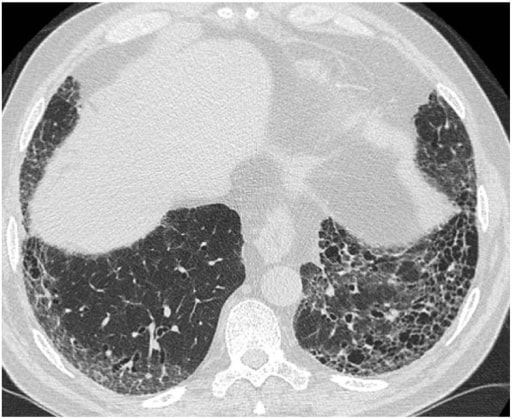
Patrón típico de la neumonía intersticial usual en la TC de alta resolución. La imagen muestra un predominio subpleural y basal de opacidades reticulares asociadas a bronquiectasias por tracción y cambios en forma de panal de abeja (espacios aéreos quísticos agrupados con paredes gruesas bien definidas y un diámetro de 0,3-1,0 cm).
Imagen: “(HRCT) pattern” por Interstitial Lung Disease Unit, Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK. Licencia: CC BY 4.0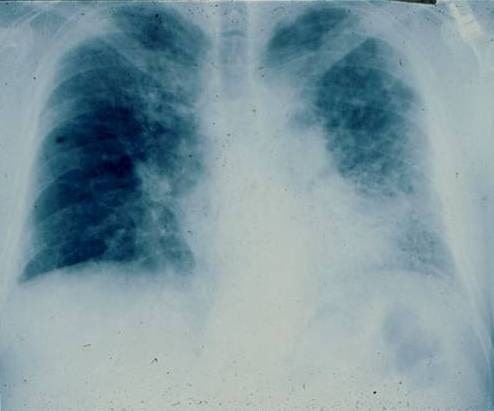
Radiografía de tórax posteroanterior de un hombre de 67 años con disnea progresiva que revela infiltrados reticulares bilaterales con predominio en el lóbulo inferior
Imagen: “PA chest radiograph of a 67-year old man” por Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27710, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0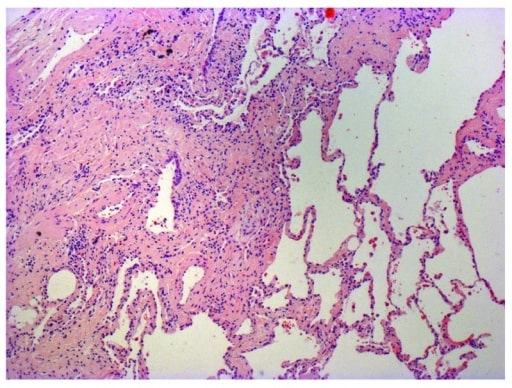
Microfotografía de la biopsia de un hombre de 63 años con un diagnóstico multidisciplinario de fibrosis pulmonar idiopática. El paciente presenta los rasgos histopatológicos típicos de la neumonía intersticial usual, caracterizados por una heterogeneidad espacial con áreas de fibrosis subpleural y paraseptal y cambios en forma de panal de abeja (espacios aéreos quísticos revestidos por epitelio bronquiolar) que alternan con áreas de parénquima pulmonar relativamente indemne, heterogeneidad temporal con zonas mezcladas de fibrosis activa con focos de fibroblastos, deposición de matriz extracelular (principalmente colágeno) y un infiltrado celular inflamatorio relativamente leve o ausente junto con regiones de tejido pulmonar histológicamente normal.
Imagen: “Photomicrograph of biopsy from a 63-year-old man with a multi-disciplinary diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis” por Interstitial Lung Disease Unit, Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK. Licencia: CC BY 4.0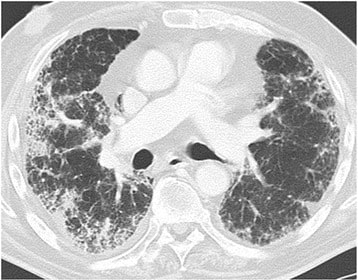
Enfermedad pulmonar inducida por medicamentos con patrón de neumonía intersticial inespecífica. El paciente se ha sometido a quimioterapia para cáncer de vejiga. TC de tórax a nivel de la arteria pulmonar derecha en ventana pulmonar. Patrón reticular periférico bilateral difuso, vidrio esmerilado y cierta consolidación.
Imagen: “Drug-induced lung disease” por Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Marien Hospital, Academic Teaching Hospital, Rochusstr. 2, D- 40479, Düsseldorf, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 4.0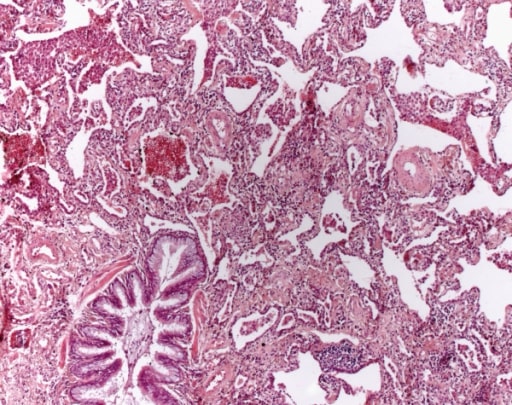
Neumonía intersticial inespecífica. Se observa una fibrosis de los septos alveolares en forma de malla. No se encuentran focos fibroblásticos. A veces se encuentran agregados de linfocitos (HE, aumento original 40x).
Imagen: “Non specific interstitial pneumonia” por Institute of Pathology and Neuropathology, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, Essen 45147, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 2.0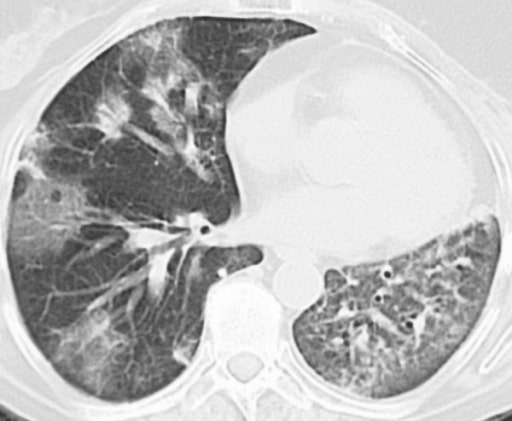
Mujer de 59 años con antecedentes de cáncer de mama izquierda y mastectomía radical. La paciente fue diagnosticada con neumonía organizada criptogénica inducida por radioterapia (antes conocida como neumonía organizada por bronquiolitis obliterante). La tomografía computarizada muestra áreas parcheadas en el pulmón izquierdo y en el lóbulo medio del pulmón derecho.
Imagen: “Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia” por Dept of Pulmonary Diseases, Sint Franciscus Gasthuis, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Licencia: CC BY 2.0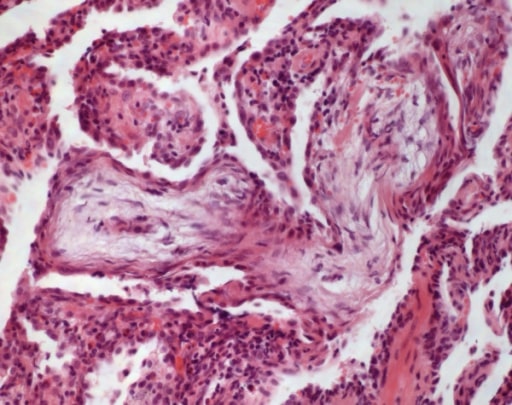
Neumonía organizada criptogénica: En los conductos alveolares y bronquiolos se detectan brotes de tejido de granulación (HE, aumento original 100x).
Imagen: “Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia” por Institute of Pathology and Neuropathology, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, Essen 45147, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| Fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans pulmonar idiopática | Enfermedad pulmonar intersticial asociada a esclerosis sistémica | Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly. Sarcoidosis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Síntomas | Adulto mayor con disnea gradual y tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome seca | Disnea gradual y tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome seca, fatiga, tensión cutánea, fenómeno de Raynaud, reflujo, disfagia | Asintomático o con disnea y tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome gradual, fatiga, palpitaciones, dolor Dolor Inflammation articular, afectación ocular y cutánea |
| Signos | Crepitantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance pulmonares e hipocratismo digital | Crepitantes, engrosamiento de la piel y aumento de volumen articular, telangiectasias Telangiectasias Ataxia-telangiectasia | Ninguno o crepitantes, hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel, aumento de volumen articular, linfadenopatía |
| Exposiciones | Humo de tabaco | Mayormente desconocido | Mayormente desconocido |
| TC de alta resolución |
|
Patrón de neumonía intersticial usual o neumonía intersticial inespecífica, esófago dilatado, dilatación vascular pulmonar | Linfadenopatía mediastínica/hiliar, afectación reticulonodular peribronquiovascular |
| Histopatología | Patrón de neumonía intersticial usual (focos fibroblásticos, patrón en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum panal de abeja, heterogeneidad espacial) | Patrón de neumonía intersticial inespecífica con características ocasionales de neumonía intersticial usual | Granuloma no caseificante |
| Curso clínico | Supervivencia a los LOS Neisseria 3–5 años: 50%. | Supervivencia a los LOS Neisseria 10 años: 70%–80%. | Buena supervivencia general |
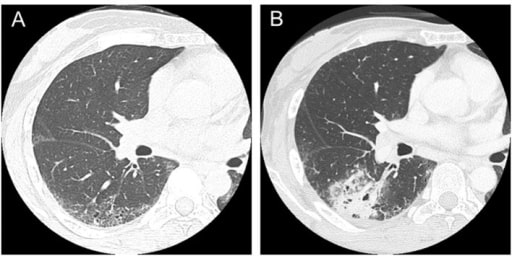
Tomografía computarizada en un paciente con esclerosis sistémica:
(A) Se observó enfermedad pulmonar intersticial en los lóbulos inferiores en un paciente de 47 años.
(B) Cáncer de pulmón de células escamosas desarrollado en el área de enfermedad pulmonar intersticial en un paciente de 50 años.
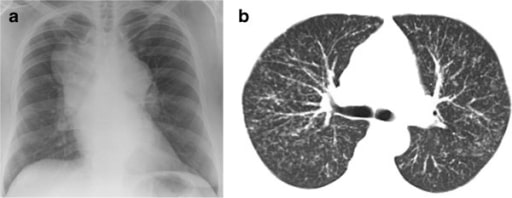
Paciente con sarcoidosis: (a). Radiografía de tórax que muestra una linfadenopatía hiliar y mediastínica masiva; (b) TC de tórax que muestra una infiltración nodular difusa del intersticio pulmonar. Ninguno de estos pacientes presentó tos.
Imagen: “Chest radiograph” por College of Medicine, Swansea University, Swansea, Wales, UK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0