La enfermedad de Parkinson es un trastorno neurodegenerativo crónico y progresivo. Aunque se desconoce la causa, actualmente se están estudiando varios factores de riesgo genéticos y ambientales. Los LOS Neisseria individuos se presentan clínicamente con temblor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo, bradicinesia, rigidez e inestabilidad postural. La enfermedad de Parkinson se diagnostica clínicamente sobre la base de signos y síntomas característicos. El diagnóstico definitivo es patológico (cuerpos de Lewy), aunque cada vez se utilizan más biomarcadores in vivo. El tratamiento incluye atención física y emocional de soporte, además de medicamentos como levodopa Levodopa The naturally occurring form of dihydroxyphenylalanine and the immediate precursor of dopamine. Unlike dopamine itself, it can be taken orally and crosses the blood-brain barrier. It is rapidly taken up by dopaminergic neurons and converted to dopamine. It is used for the treatment of parkinsonian disorders and is usually given with agents that inhibit its conversion to dopamine outside of the central nervous system. Parkinson’s Disease Drugs/carbidopa, inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa tipo B y agonistas de la dopamina.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2026
La enfermedad de Parkinson es un trastorno neurodegenerativo crónico y progresivo que afecta al AL Amyloidosis sistema nervioso central (SNC) con rasgos característicos de temblor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo, rigidez, bradicinesia e inestabilidad postural.
La etiología de la enfermedad de Parkinson no está clara, pero depende de varios factores genéticos y ambientales.
Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos compensatorios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cerebro pueden disminuir temporalmente los LOS Neisseria efectos del agotamiento de la dopamina hasta que estos mecanismos sean superados por la progresión de la enfermedad de Parkinson.
Los LOS Neisseria signos de la enfermedad de Parkinson son progresivos y aparecen gradualmente durante un largo período de tiempo, ya sean años o décadas.
El diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Parkinson se realiza mediante los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos y el examen neurológico.
El diagnóstico requiere de 4 cosas:
El parkinsonismo motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology, un criterio esencial de la enfermedad de Parkinson, requiere bradicinesia y al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
Criterios de exclusión absolutos (incompatibles con un diagnóstico de enfermedad de Parkinson):
Criterios de soporte:
Banderas rojas (signos de una patología alterna que apuntan hacia otro diagnóstico):
No existen análisis fisiológicos, radiológicos o de sangre para confirmar el diagnóstico clínico de la enfermedad de Parkinson:
La enfermedad de Parkinson se confirma mediante el hallazgo de cuerpos de Lewy en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el análisis post mortem.
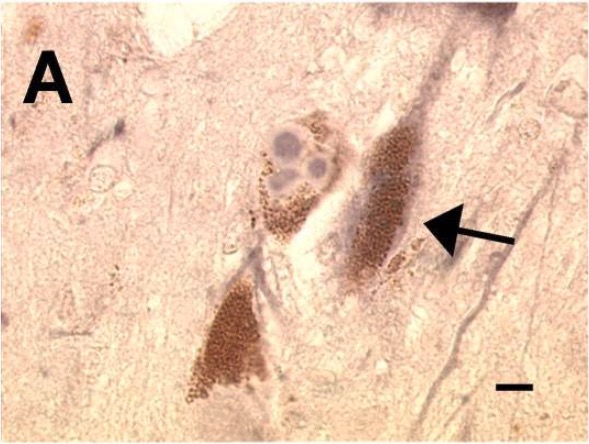
Cuerpos de Lewy observados en una muestra de la enfermedad de Parkinson
Imagen: “Staining of multiple Lewy bodies” por Division of Neurology, William Beaumont Hospital Research Institute, Royal Oak, MI 48073, USA Licencia: CC BY 2.0El objetivo del tratamiento es tratar las características motoras y no motoras sintomáticas del trastorno para mejorar la calidad de vida.
Medidas generales:
Tratamiento médico:
Estimulación cerebral profunda:
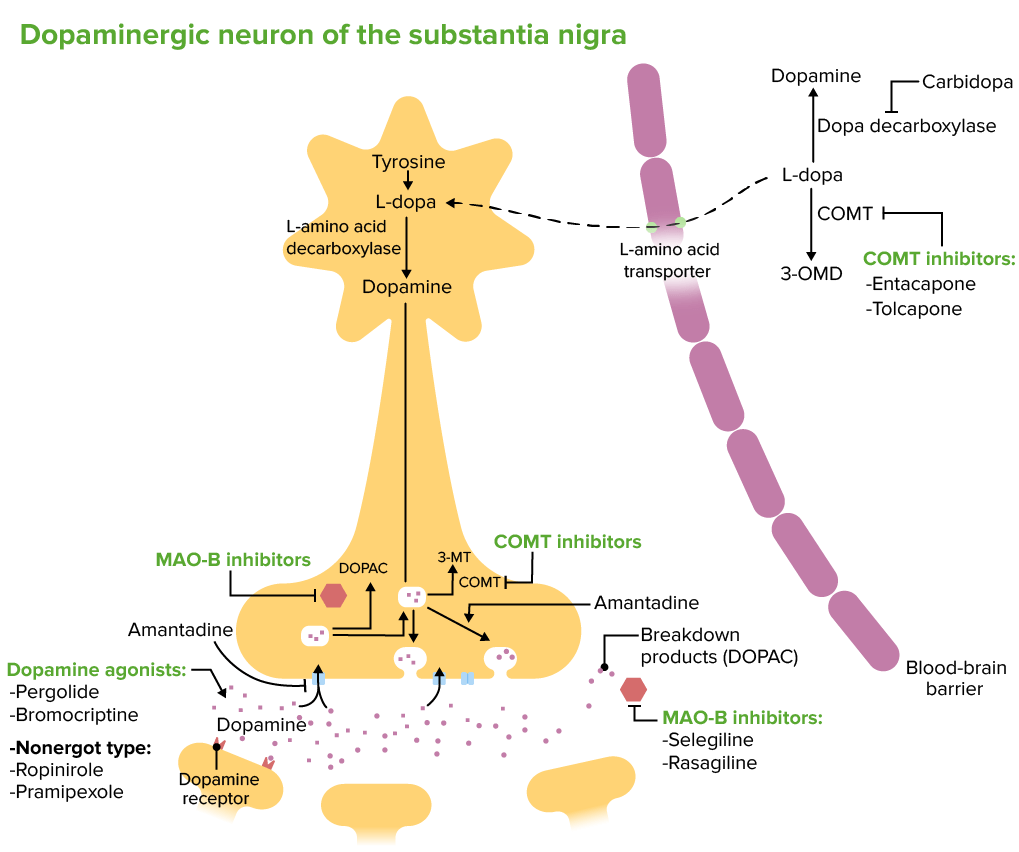
Efectos de los tratamientos de la enfermedad de Parkinson en las neuronas dopaminérgicas de la sustancia negra
3-OMD: 3-O-metildopa (un metabolito de la l-dopa)
3-MT: 3-metoxitiramina (un metabolito de la dopamina)
COMT: catecol O-metiltransferasa (un metabolito de la dopamina)
DOPAC: ácido 3,4-dihidroxifenilacético
MAO-B: monoamino oxidasa tipo B