Los LOS Neisseria meniscos son estructuras fibrocartilaginosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de cuña entre el fémur distal y la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy proximal que estabilizan y disipan las fuerzas que soportan peso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la articulación de la rodilla. Un desgarro de menisco es una lesión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el menisco causada por fuerzas de rotación o cizallamiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la articulación tibiofemoral. La presentación clínica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente joven con un desgarro traumático incluye antecedentes de una lesión por torsión o rotación seguida de dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la línea articular con un pequeño derrame. La presentación clínica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente mayor incluye dolor Dolor Inflammation al AL Amyloidosis soportar peso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la línea articular que imita y acompaña al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation progresivo debido a los LOS Neisseria cambios degenerativos de la osteoartritis. Las quejas mecánicas (e.g., bloqueo, enganche o chasquido de las articulaciones) también son comunes. El diagnóstico puede ser un desafío clínico y, a menudo, se confirma mediante imagenología diagnóstica o visualización directa (artroscopia). El tratamiento puede ser conservador o quirúrgico, dependiendo de la situación individual.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
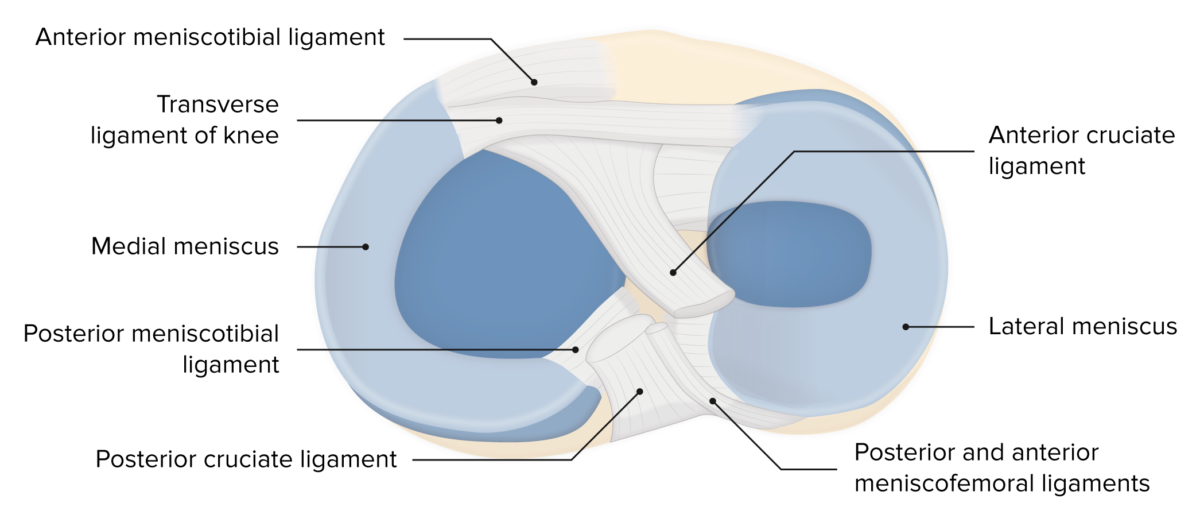
Meniscos de la rodilla
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Hay varios tipos de patrones de ruptura en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria desgarros de menisco:
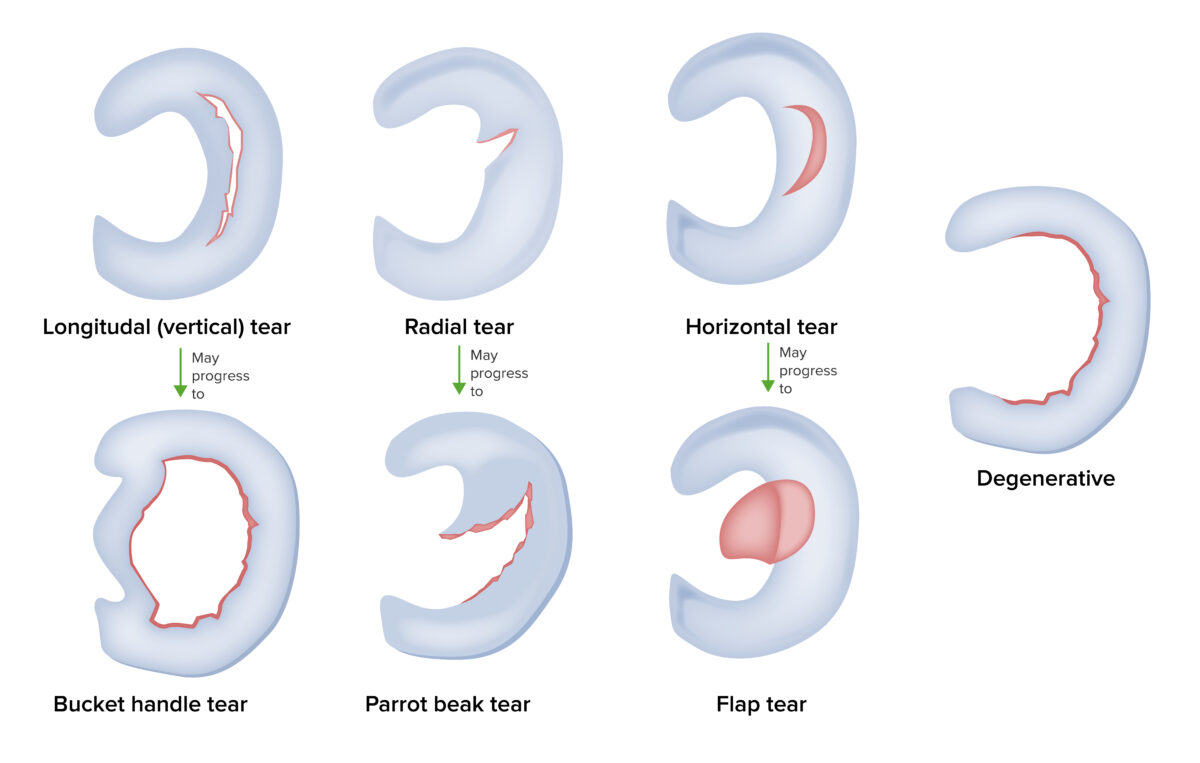
Tipos de desgarro de menisco
Imagen por Lecturio.Anatomía clínica:
Mecanismos traumáticos de los LOS Neisseria desgarros:
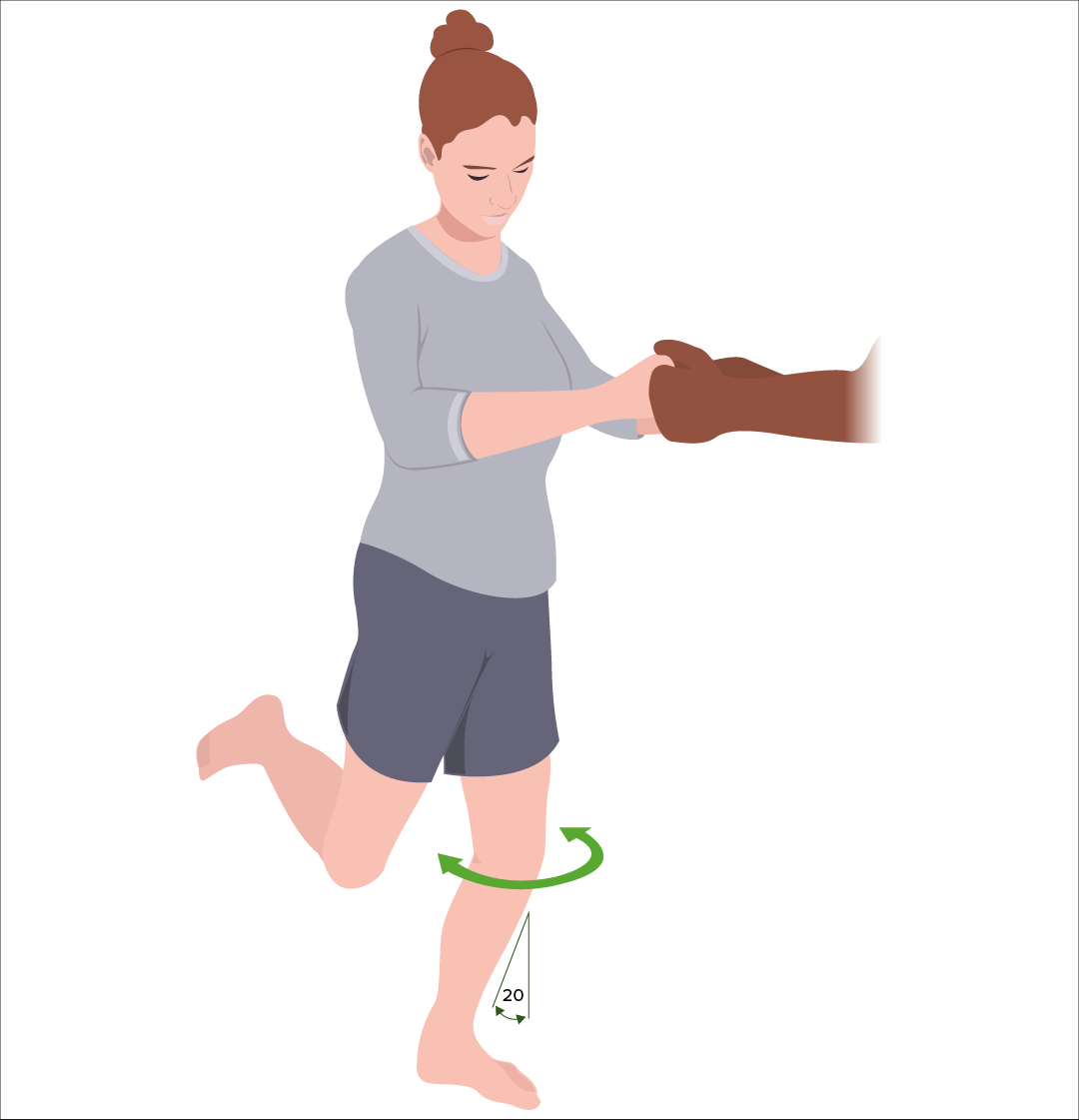
Prueba de Tesalia
Imagen por Lecturio.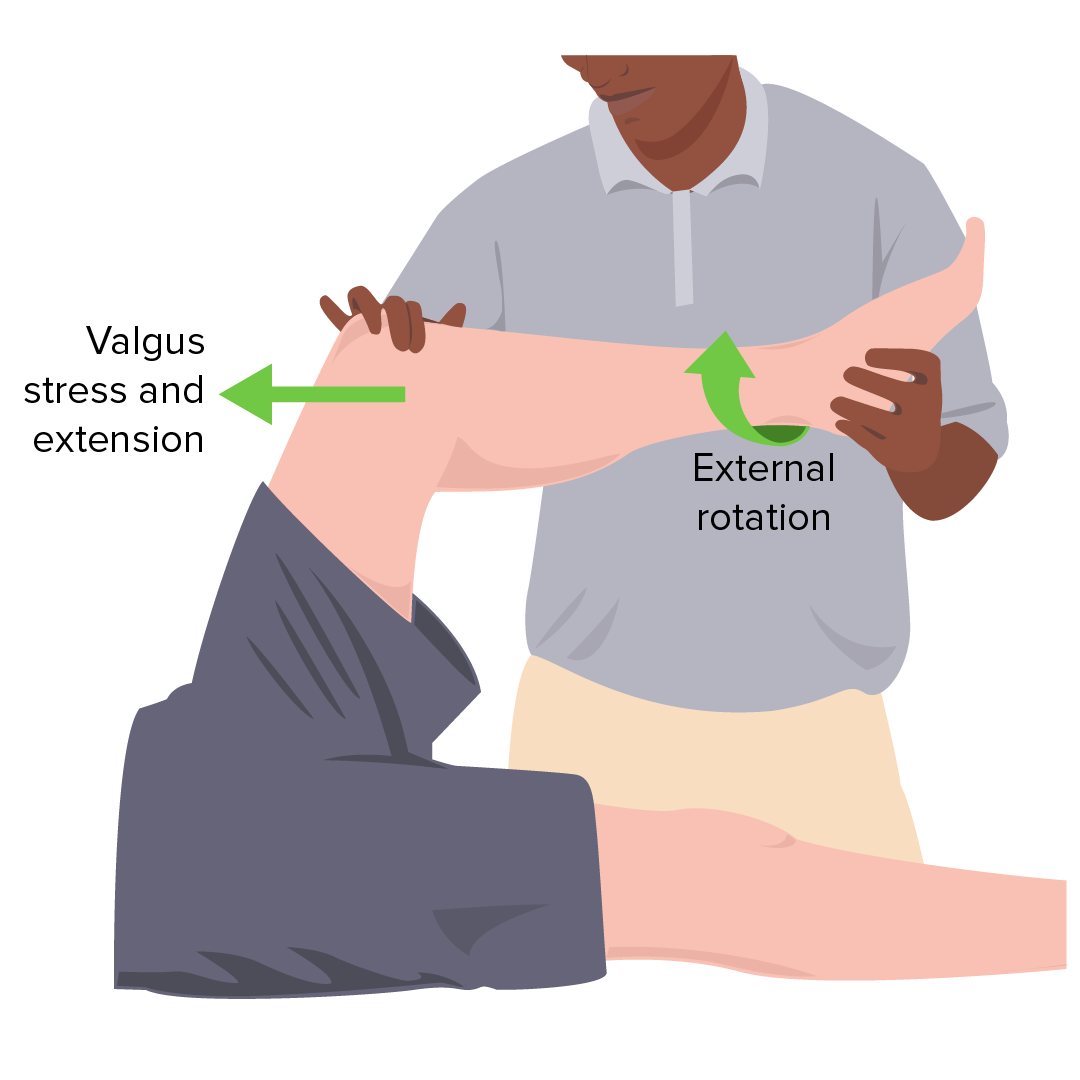
Prueba de McMurray
Imagen por Lecturio.Por lo general, el diagnóstico se sospecha con los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y un examen físico completo y, a menudo, se confirma con imagenología (e.g., RM) o mediante visualización directa (e.g., artroscopia).
Radiografía:
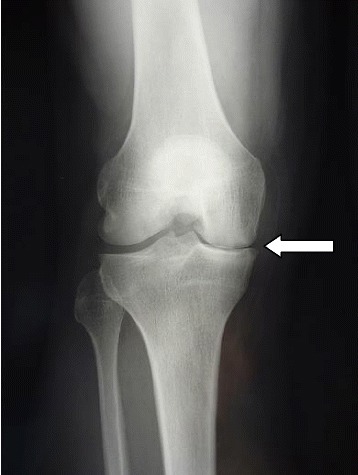
Radiografía que demuestra el estrechamiento del espacio articular medial
Imagen: “Postoperative radiography at 3 month follow-up” por Steinmetz S, Bonnomet F, Rahme M, Adam P, Ehlinger M. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Ultrasonido:
RM:
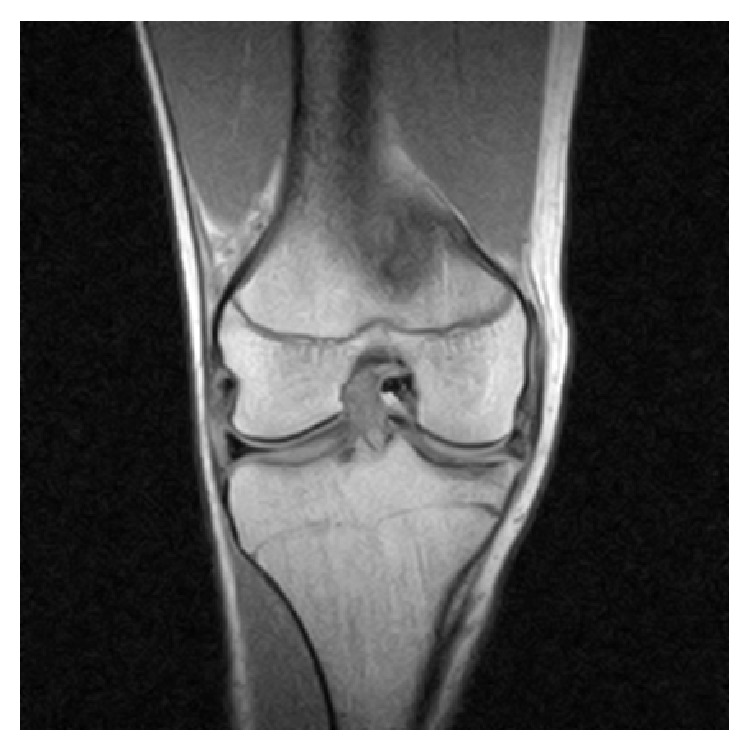
RM de la rodilla derecha que revela un desgarro del menisco interno intraarticular y en asa de cubo con el fragmento desplazado ubicado en la escotadura intercondílea
Imagen: “Coronal MRI of the right knee” por Ahmed Ali R, McKay S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0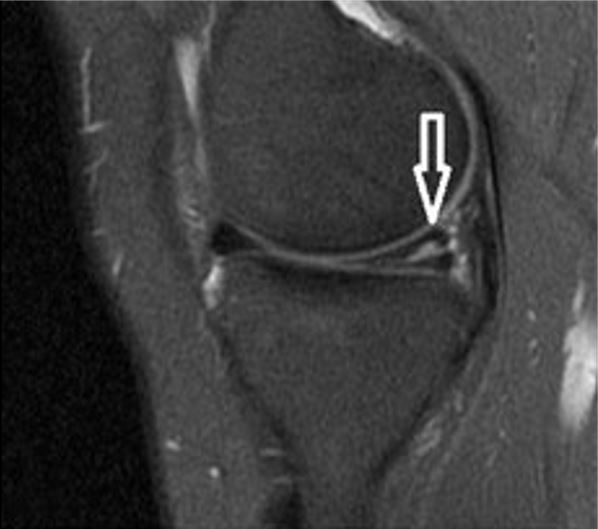
RM de la rodilla que muestra un desgarro horizontal (flecha blanca) en el cuerno posterior del menisco medial
Imagen: “A sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows horizontal tear” por Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Artroscopia:
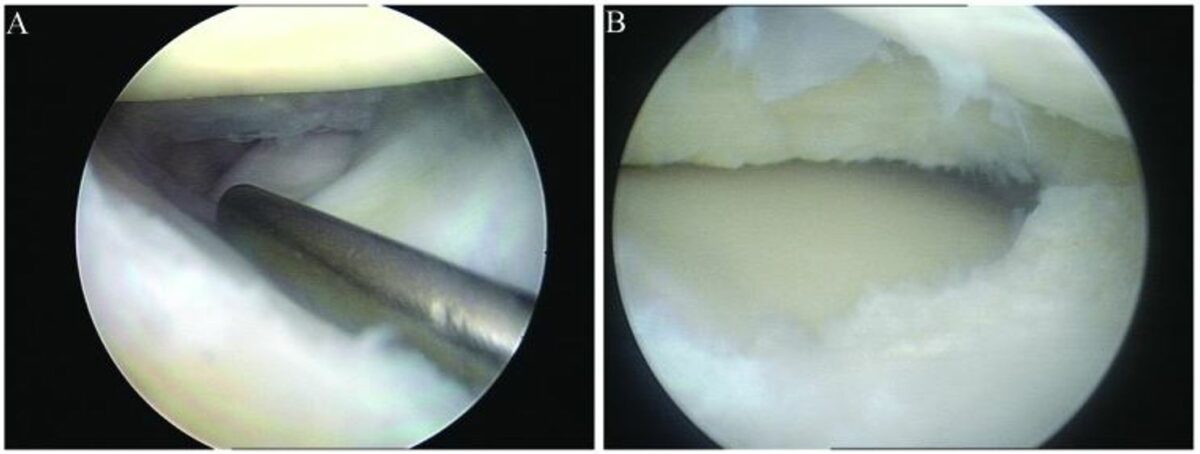
Artroscopia con reparación artroscópica de menisco:
A: menisco lateral discoideo con desgarro longitudinal
B: menisco lateral discoideo tras resección parcial
El tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria desgarros de menisco depende del tipo de desgarro, la edad del paciente, la ocupación del paciente, los LOS Neisseria síntomas mecánicos asociados y otras lesiones asociadas (e.g., desgarro del ligamento cruzado anterior).
Tratamiento conservador indicado como tratamiento inicial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum desgarros degenerativos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes mayores o previo a la artroscopia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes más jóvenes:
Posicionamiento quirúrgico para artroscopia
Imagen: “The position for viewing the medial meniscus in right knee” por Gupta Y, Mahara DP, Lamichhane AP. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Pliegue del menisco medial visto a través del portal anterolateral
Imagen: “Appearance of medial meniscus flounce” por Gupta Y, Mahara DP, Lamichhane AP. Licencia: CC BY 4.0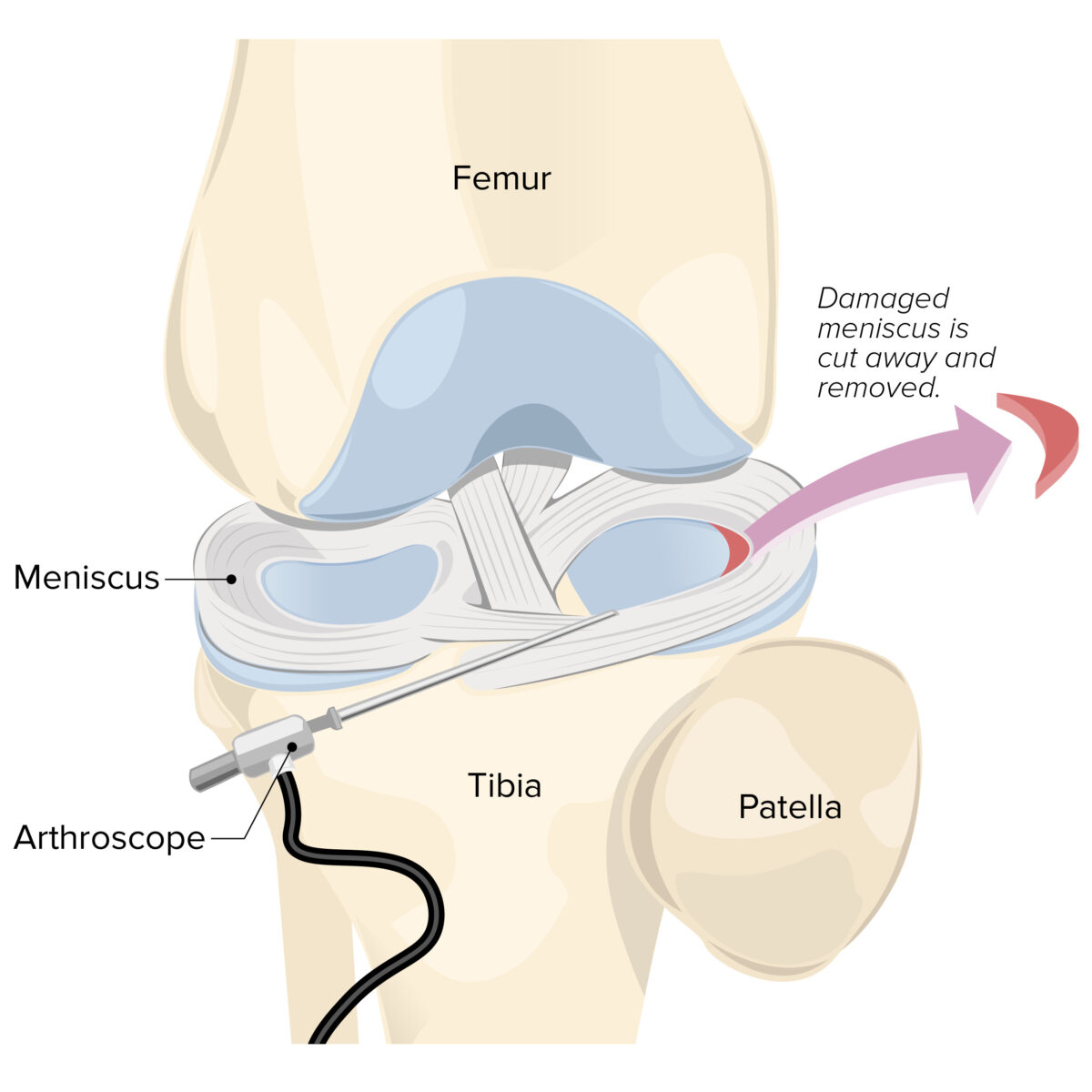
Artroscopia de rodilla con meniscectomía
Imagen por Lecturio.