La dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) seborreica es un trastorno cutáneo común, crónico y recidivante, que se presenta como placas eritematosas con escamas amarillas y grasientas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum zonas susceptibles (cuero cabelludo, cara y tronco). La dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) seborreica tiene una incidencia bimodal, presentándose en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum dos picos: primero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria bebés, y luego en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la adolescencia y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria primeros años de la edad adulta. Aunque se desconoce la etiología exacta, se han observado mecanismos patológicos que implican a las glándulas sebáceas y a Malassezia Malassezia Malassezia is a lipophilic yeast commonly found on the skin surfaces of many animals, including humans. In the presence of certain environments or triggers, this fungus can cause pathologic diseases ranging from superficial skin conditions (tinea versicolor and dermatitis) to invasive disease (e.g., Malassezia folliculitis, catheter-associated fungemia, meningitis, and urinary tract infections). Malassezia Fungi en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos tópicos se utilizan para la exacerbación aguda o el tratamiento de mantenimiento. Estas opciones tienen como objetivo inhibir la colonización de la piel (agentes antifúngicos), reducir la inflamación (esteroides, inhibidores de la calcineurina) y aflojar las escamas y costras (agentes queratolíticos). La dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) seborreica grave y refractaria puede justificar el uso de medicamentos antifúngicos sistémicos.
Last updated: Apr 20, 2022
La dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) seborreica es un trastorno cutáneo crónico común que se caracteriza por la aparición de manchas eritematosas con escamas grasientas y amarillentas que aparecen con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum zonas con glándulas sebáceas prominentes (cuero cabelludo, cara, parte superior del tronco y zona anogenital).
No está claro, pero puede verse afectado por lo siguiente:
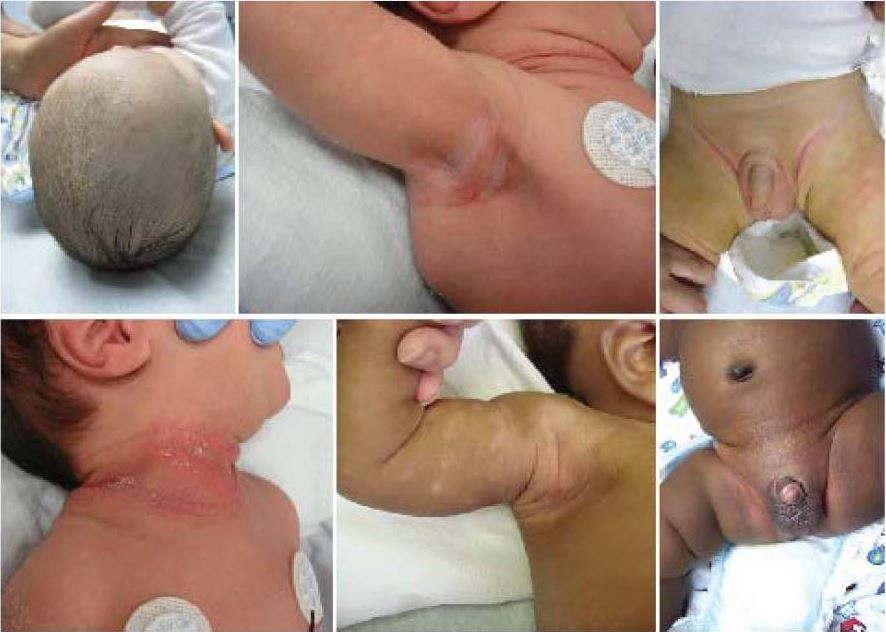
Las imágenes muestran los hallazgos típicos de la dermatitis seborreica en los recién nacidos. Observe la afectación común de las zonas intertriginosas y del cuero cabelludo.
Imagen: “Seborrheic dermatitis.” por Siegfried EC, Hebert AA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0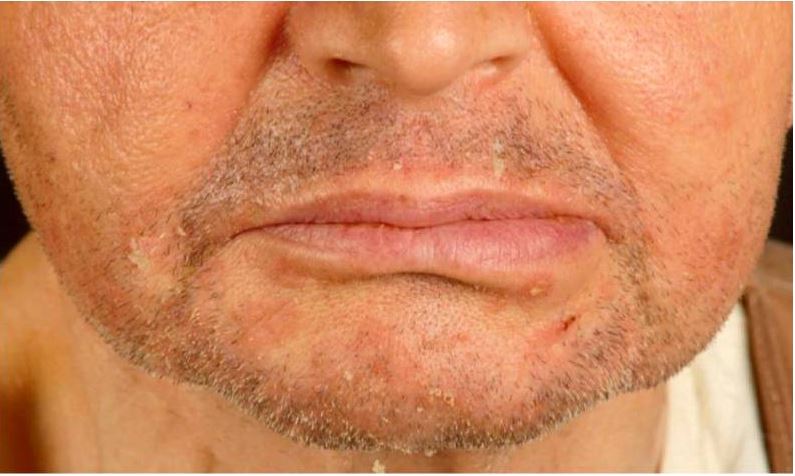
Dermatitis seborreica en un receptor de trasplante renal.
Observe las pápulas eritemato-escamosas en el mentón y los pliegues nasolabiales.
Los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales de la dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) seborreica incluyen las siguientes afecciones:
| Sitio | Diagnóstico diferencial |
|---|---|
| Cuero cabelludo | Psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis, caspa, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) atópica, tinea capitis Tinea capitis Ringworm of the scalp and associated hair mainly caused by species of Microsporum; Trichophyton; and Epidermophyton, which may occasionally involve the eyebrows and eyelashes. Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections |
| Cara | Psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis, impétigo, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) de contacto |
| Canal auditivo | Psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) de contacto |
| Párpados | Dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) atópica, infestación por Demodex folliculorum Demodex Folliculorum Infectious Folliculitis |
| Pecho y tronco | Pitiriasis rosada, tiña versicolor |
| Zonas intertriginosas | Psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis, candidiasis Candidiasis Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis |
| Todos los LOS Neisseria sitios, descartar | Sífilis secundaria, pénfigo, escabiosis |