La enfermedad de Gaucher es un trastorno autosómico recesivo que afecta el almacenamiento lisosómico, causado por una deficiencia de la actividad enzimática de la glucocerebrosidasa; que da lugar a la acumulación de glucocerebrósido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células y ciertos órganos. La enfermedad se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 tipos con presentación clínica variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables. El tipo 1 es no neuropático, mientras que los LOS Neisseria tipos 2 y 3 son neuropáticos. Las manifestaciones pueden incluir hematomas, letargo, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, afectación esquelética y hepatoesplenomegalia. Los LOS Neisseria tipos neuropáticos pueden presentarse con deterioro cognitivo, ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia, anomalías de la mirada, y convulsiones. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha clínica y se confirma mediante la medición de la actividad de la glucocerebrosidasa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria leucocitos de sangre periférica. El análisis genético también puede utilizarse para confirmar el diagnóstico. El tratamiento es de soporte y se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el control de los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la mejora de la calidad de vida. La terapia de reemplazo enzimático, la terapia de reducción de sustrato y el trasplante de médula ósea son opciones de tratamiento para algunos pacientes.
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
La enfermedad de Gaucher es el resultado de una deficiencia de la hidrolasa lisosómica beta-glucosidasa (glucocerebrosidasa).
La enfermedad de Gaucher se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 tipos:
Una deficiencia de glucocerebrosidasa da lugar a la acumulación de glucocerebrósido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células del sistema reticuloendotelial, lo que provoca:
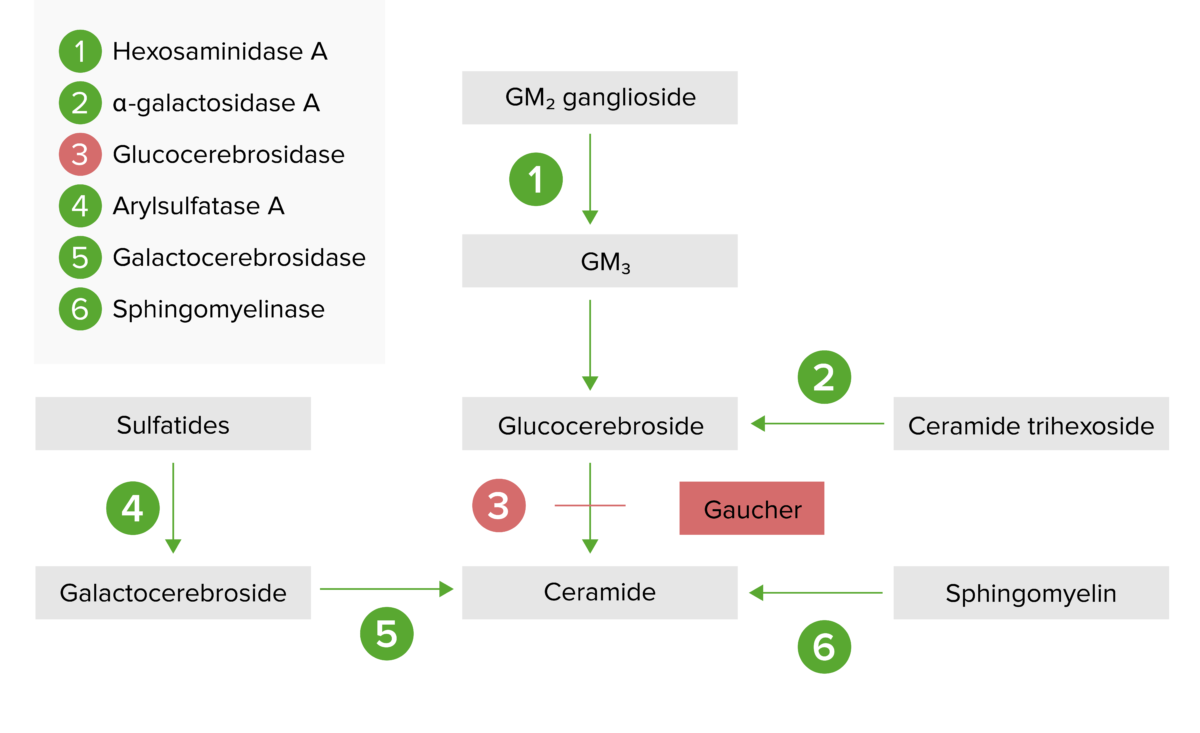
La vía de almacenamiento lisosómico:
La deficiencia de glucocerebrosidasa es el resultado de la deficiencia de la glucocerebrosidasa (paso 3), lo que conduce a una acumulación de glucocerebrósido.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La enfermedad de Gaucher es una lipidosis multisistémica con una presentación clínica variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables.
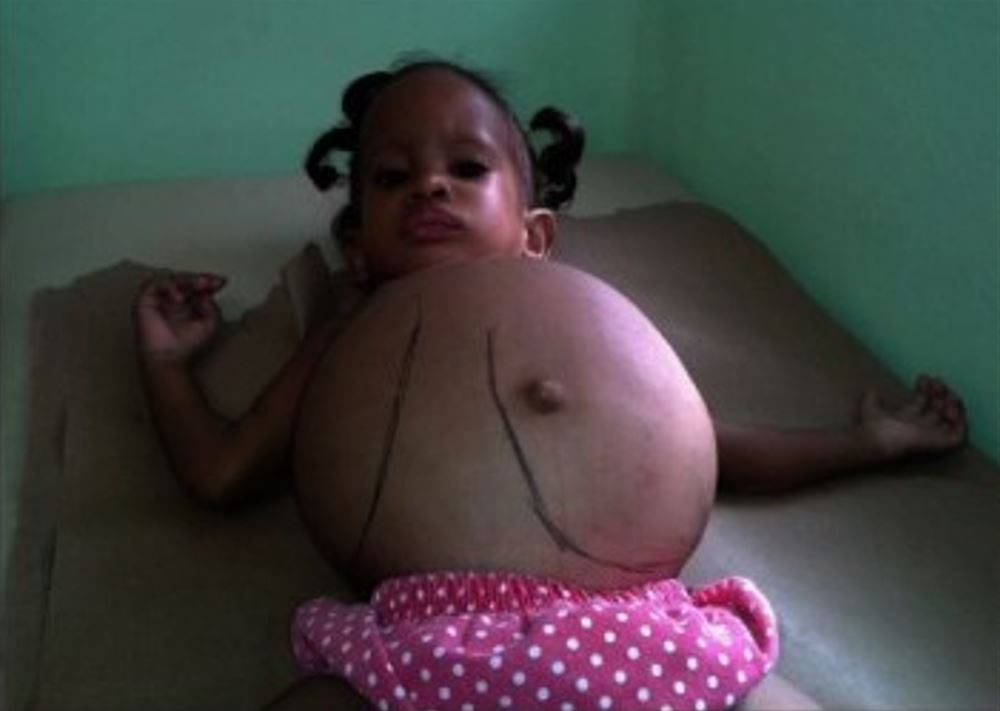
Una niña con hepatoesplenomegalia masiva debido a deficiencia de glucocerebrosidasa
Imagen: “Dominican child with Gaucher disease” por Estrada-Veras JI, Cabrera-Peña GA, Pérez-Estrella de Ferrán C. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortada por Lecturio.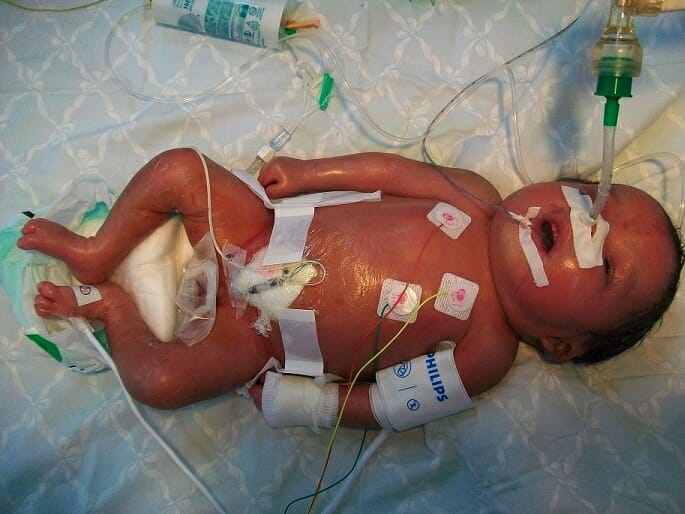
Presentación neonatal de la enfermedad de Gaucher, subtipo 2: hidropesía, descamación y piel brillante
Imagen: “Neonatal presentations of Gaucher disease” por Neonatology Department, Charles Nicolle Hospital, Tunis-El Manar University, Tunis, Tunisia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0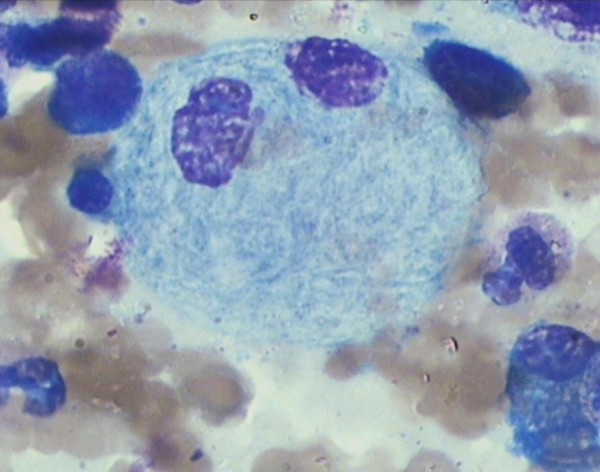
Frotis de médula ósea que muestra una célula de Gaucher en un paciente con deficiencia de glucocerebrosidasa tipo 3:
Observe que el citoplasma tiene un aspecto estriado y arrugado.
El tratamiento es de soporte y se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mejorar la calidad de vida. Algunos pacientes con enfermedad de Gaucher tienen síntomas leves y no requieren tratamiento.