La deficiencia del componente 3 del complemento (C3) es la ausencia, reducción o disfunción del factor C3 del complemento y sus fragmentos, C3a y C3b. Los LOS Neisseria factores del complemento son componentes clave del sistema inmunológico innato. Los LOS Neisseria niveles reducidos de C3b aumentan la probabilidad de desarrollar infecciones por organismos encapsulados (e.g., Pneumococcus, Haemophilus Haemophilus Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth (factor V [NAD] and factor X [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The pathogenic species are H. influenzae and H. ducreyi. Haemophilus influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza, Neisseria meningitidis Neisseria meningitidis A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria. It is a commensal and pathogen only of humans, and can be carried asymptomatically in the nasopharynx. When found in cerebrospinal fluid it is the causative agent of cerebrospinal meningitis. It is also found in venereal discharges and blood. There are at least 13 serogroups based on antigenic differences in the capsular polysaccharides; the ones causing most meningitis infections being a, b, c, y, and w-135. Each serogroup can be further classified by serotype, serosubtype, and immunotype. Neisseria), especialmente infecciones respiratorias, debido a la reducción de la opsonización. Los LOS Neisseria individuos con deficiencias de C3 también son más susceptibles de sufrir reacciones de hipersensibilidad de tipo III, ya que una menor eliminación de los LOS Neisseria complejos antígeno-anticuerpo C3b de la circulación provoca un mayor riesgo de reacciones de hipersensibilidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La deficiencia del componente 3 del complemento (C3) forma parte de la categoría más amplia de deficiencias del complemento:
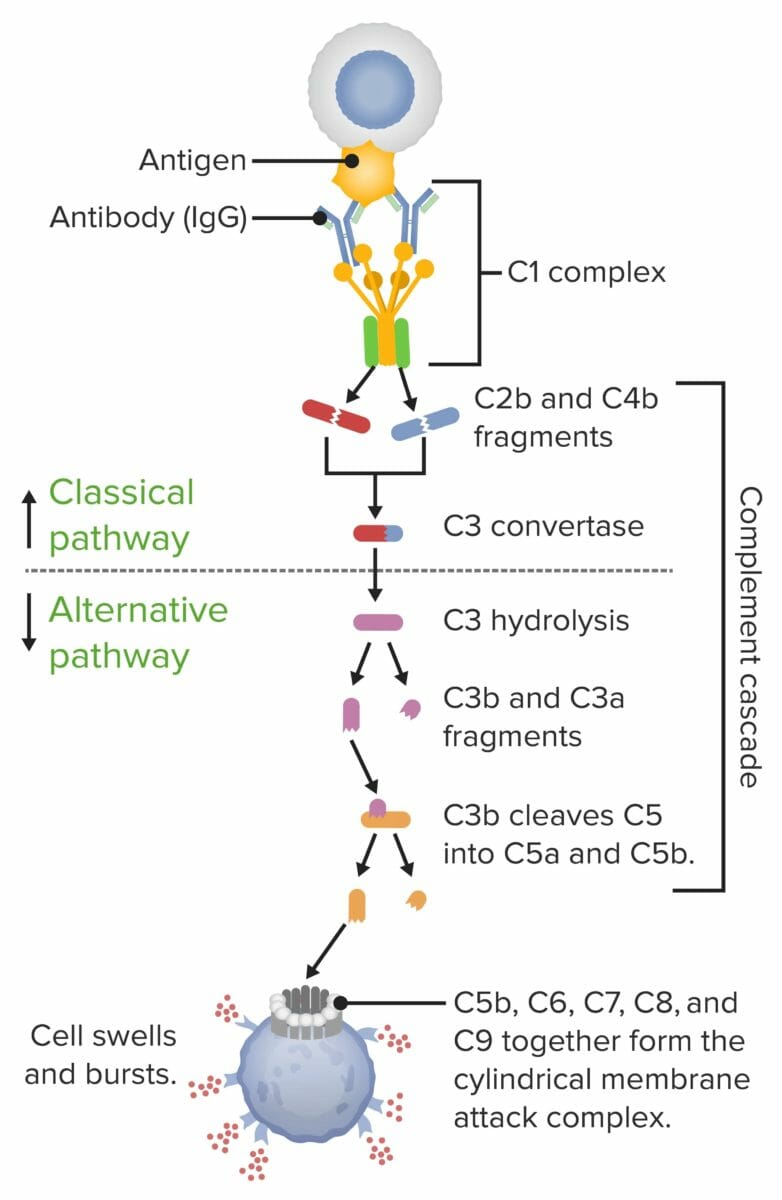
Formación del complejo de ataque a la membrana:
Cuando la 1ra proteína de la serie del complemento se activa (normalmente por un anticuerpo que se ha fijado a un antígeno), pone en marcha un efecto dominó. Cada componente sigue su turno en una cadena precisa de pasos conocida como la cascada del complemento. El producto final es un cilindro del complejo de ataque a la membrana que se inserta en la pared de la célula (y se perfora). Con los fluidos y las moléculas que entran y salen, la célula se hincha y estalla.
Pruebas clínicas dirigidas por el patrón de infección:
El tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con deficiencia de C3 se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la prevención de enfermedad.