Cystoisospora Cystoisospora Cystoisospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cystoisosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis y Cyclospora Cyclospora Cyclospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cyclosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis son géneros de la subclase de protozoos Coccidia Coccidia A subclass of protozoans commonly parasitic in the epithelial cells of the intestinal tract but also found in the liver and other organs. Its organisms are found in both vertebrates and higher invertebrates and comprise two orders: eimeriida and eucoccidiida. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis. Estos parásitos unicelulares e intracelulares obligatorios causan infecciones intestinales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria seres humanos. El ser humano es el único huésped de estas especies y ambas se transmiten por vía fecal-oral. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas de la cistoisosporiasis y la ciclosporiasis son diarrea acuosa, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal y fiebre. La cistoisosporiasis severa puede ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos, particularmente aquellos con VIH/SIDA y pueden conducir a la malabsorción, pérdida de peso y deshidratación. Ambas enfermedades son autolimitadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocompetentes, aunque la ciclosporiasis tiene una duración mayor. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la identificación de ooquistes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las muestras de heces. Puede utilizarse un tratamiento antimicrobiano, como el trimetoprim-sulfametoxazol (especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Ambos organismos causan enfermedades intestinales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria humanos.
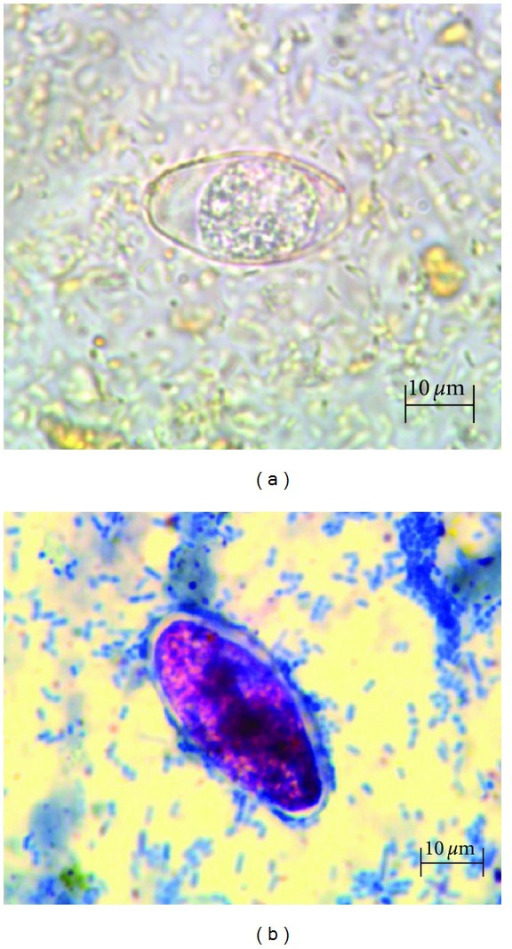
Imágenes microscópicas de Cystoisospora:
(a): Cystoisospora belli en un montaje en solución salina
(b): Cystoisospora belli en una tinción ácido-alcohol resistente modificada
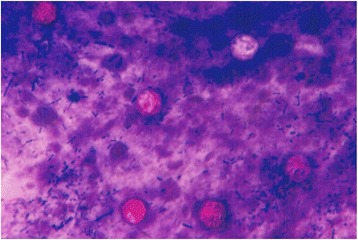
Ooquistes de Cyclospora cayetanensis en un frotis fecal con tinción ácido-alcohol resistente
Imagen: “Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts” por Kaminsky RG et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Cystoisospora Cystoisospora Cystoisospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cystoisosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis:
Cyclospora Cyclospora Cyclospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cyclosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis:
Ambas especies se encuentran solamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria seres humanos.
Cystoisospora Cystoisospora Cystoisospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cystoisosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis (enfermedad grave):
Cyclospora Cyclospora Cyclospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cyclosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis:
Ambas especies se transmiten por vía fecal-oral (ingestión de agua y alimentos contaminados).
Cystoisospora Cystoisospora Cystoisospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cystoisosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis y Cyclospora Cyclospora Cyclospora is a genus within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans. They are single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites that cause intestinal infections in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal-oral route. The symptoms of cyclosporiasis are watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Cystoisospora/Cystoisosporiasis and Cyclospora/Cyclosporiasis tienen un ciclo de vida similar:
Ciclo de vida de Cystoisospora belli. La ingestión de ovocitos maduros permite al parásito invadir las células epiteliales del intestino delgado. Allí, continúa su ciclo de vida y se reproduce. Los ovocitos inmaduros se excretan en las heces y maduran en el medio ambiente, lo que permite que el ciclo continúe.
Imagen por Lecturio.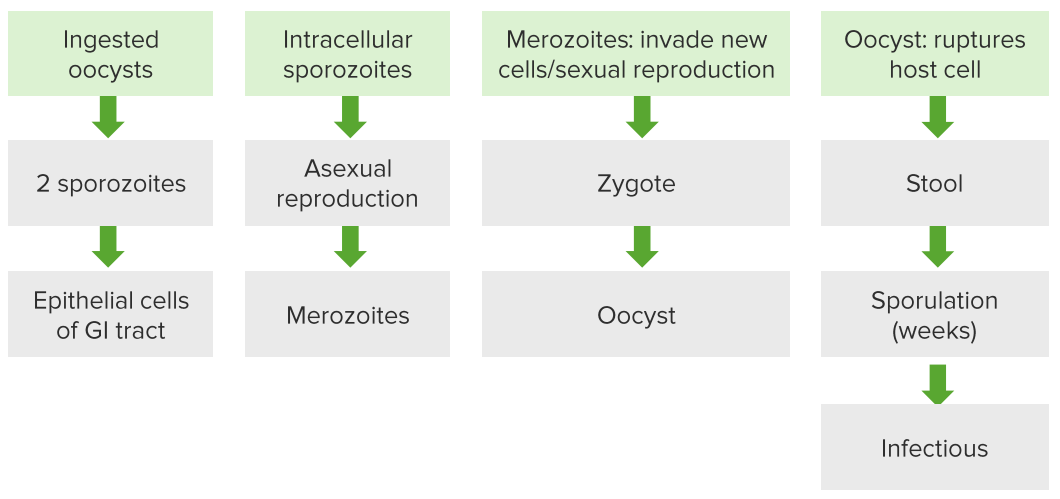
Un diagrama del ciclo de vida de Cyclospora cayetanensis
Imagen por Lecturio.La cistoisosporiasis tiene un periodo de incubación de 7–14 días. La presentación de la enfermedad puede variar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del estado inmunológico del individuo.
La ciclosporiasis tiene un periodo de incubación de aproximadamente 7 días.
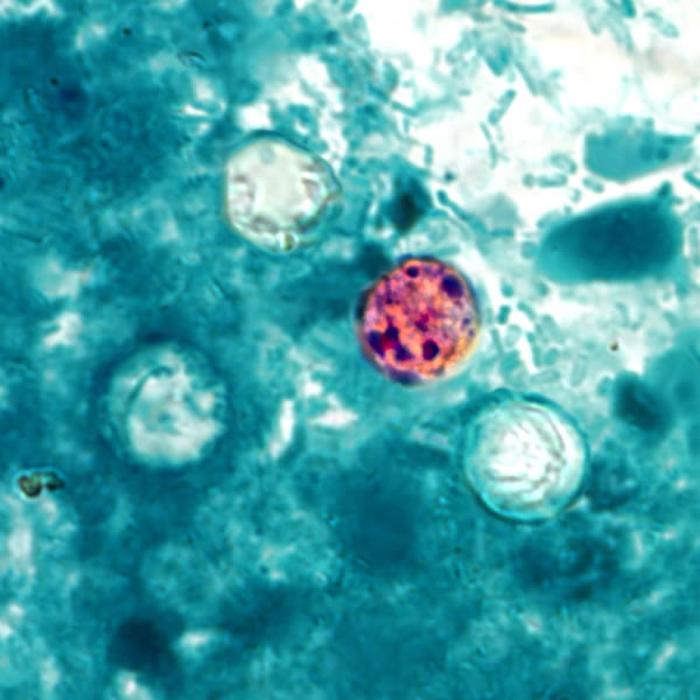
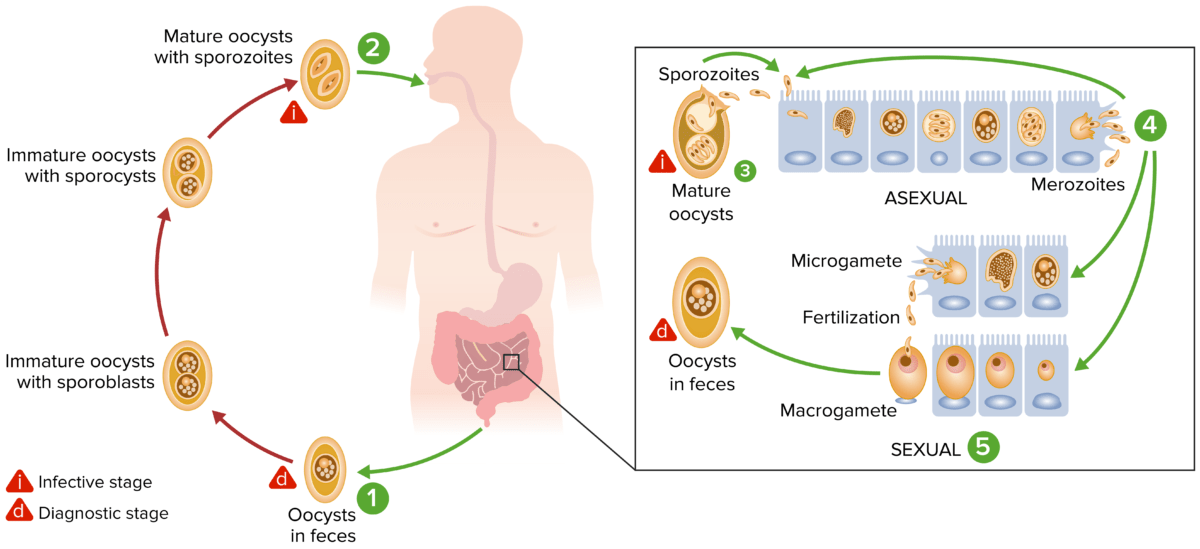
Microfotografía de ooquistes de Cyclospora cayetanensis en una muestra de heces encontrada mediante la tinción ácido-alcohol resistente modificada
Imagen: “Cyclospora cayetanensis” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria antimicrobianos utilizados para el tratamiento de la ciclosporiasis incluyen: