El cuerpo humano adulto está compuesto por un 60% de agua y se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum compartimentos de líquido extracelular e intracelular. El líquido extracelular está presente fuera de las células y constituye ⅓ del agua corporal total. El líquido intracelular está presente dentro de las células y constituye ⅔ del agua corporal total. Los LOS Neisseria líquidos intracelulares y extracelulares están separados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum compartimentos por membranas semipermeables, y el transporte de líquidos e iones se mantiene mediante canales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana celular. Cada compartimento contiene diferentes concentraciones de iones y moléculas osmolares. La carga relativa y la osmolaridad se mantienen rigurosamente por el transporte de agua y sustancias entre compartimentos. La hipernatremia, hiponatremia y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema son afecciones clínicas que surgen de alteraciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mantenimiento de la osmolaridad de los LOS Neisseria compartimentos de líquidos corporales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El agua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo humano adulto constituye aproximadamente el 60% del peso corporal total. El líquido se distribuye en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios órganos, sistemas de órganos y tejidos. La suma del agua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estos tejidos se conoce como agua corporal total.
El agua corporal total se distribuye principalmente entre 2 compartimentos, a saber, los LOS Neisseria compartimentos de líquido extracelular y líquido intracelular.

Compartimentos de líquidos corporales
Imagen por Lecturio.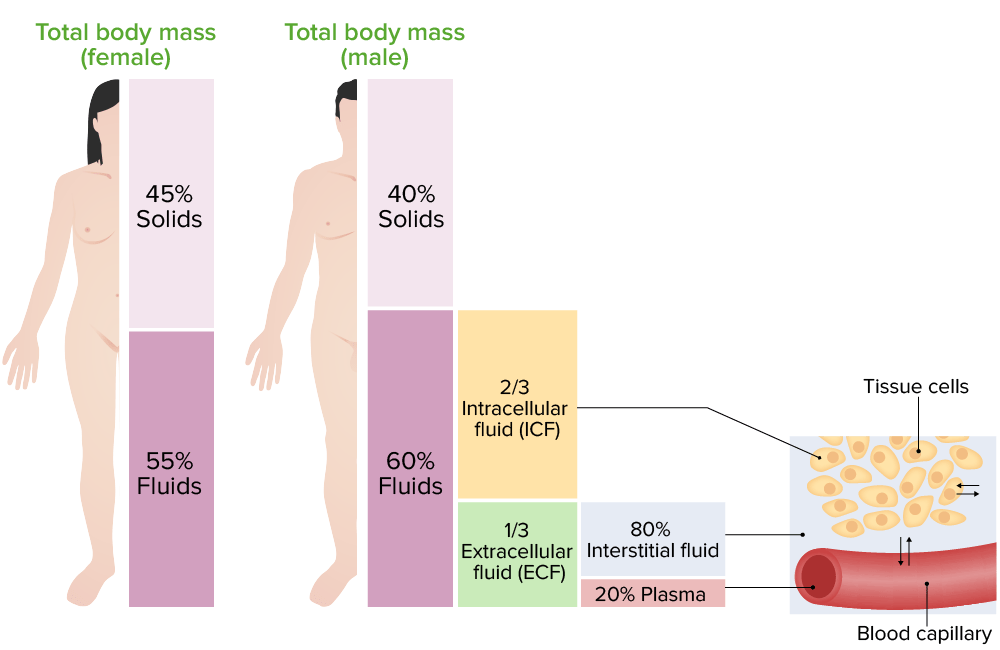
Distribución de los líquidos corporales:
A la izquierda hay una imagen que muestra el porcentaje de distribución de los líquidos corporales en hombres y mujeres, en diferentes compartimentos. A la derecha hay una imagen que representa el intercambio de agua entre los compartimentos de líquidos corporales.
Los LOS Neisseria volúmenes de los LOS Neisseria compartimentos se pueden medir determinando el volumen de distribución de una sustancia indicadora. Se agrega una cantidad conocida de un indicador a un compartimento, y la concentración del indicador en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ese compartimento se mide después de dejar suficiente tiempo para una distribución uniforme en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el compartimento. El volumen del compartimento se calcula de la siguiente manera:
Volumen = cantidad del indicador / concentración del indicador
| Volumen | Indicadores |
|---|---|
| Agua corporal total | 3H2O, 2H2O, antipirina |
| Líquido extracelular | 22Na, 125I-iotalamato, tiosulfato, inulina |
| Líquido intracelular | Calculado como: (agua corporal total — volumen de líquido extracelular) |
| Volumen de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products | 125I-albúmina, tinte azul de Evans (T-1824) |
| Volumen de sangre | Eritrocitos marcados con 51Cr, o calculados como: (volumen de sangre = volumen de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products / (1 − hematocrito)) |
| Líquido intersticial | Calculado como: (volumen de líquido extracelular – volumen de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products) |
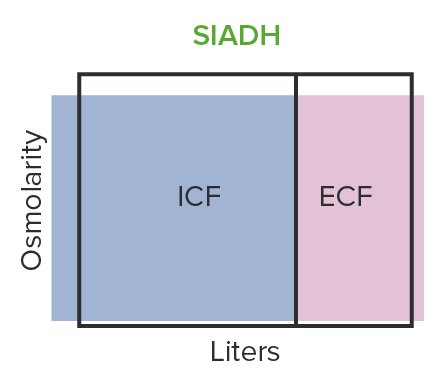
El SIADH provoca una expansión hipo-osmótica del volumen:
El cuerpo retiene demasiada agua y produce un exceso de hormona antidiurética.
ICF: líquido intracelular
ECF: líquido extracelular
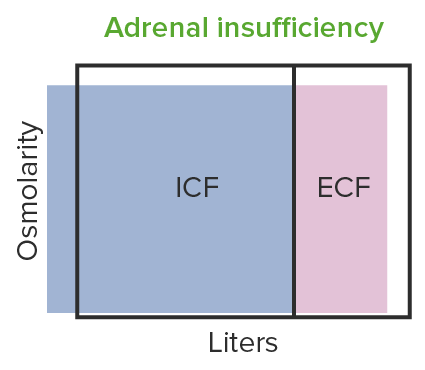
Contracción hipo-osmótica del volumen observada en la insuficiencia suprarrenal:
La baja de aldosterona conduce a la disminución de la absorción tubular de sodio, lo que resulta en la contracción del volumen hipo-osmótico.
ICF: líquido intracelular
ECF: líquido extracelular
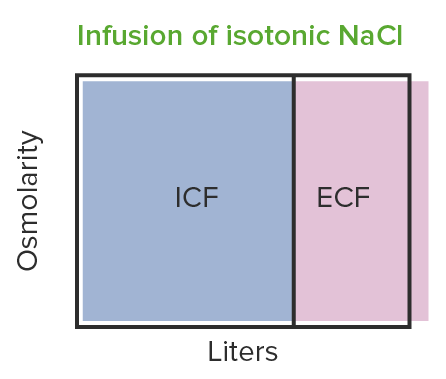
La infusión de NaCl isotónico produce una expansión iso-osmótica del volumen: se observan cambios en el líquido extracelular (i.e. aumento del volumen del líquido extracelular), pero la osmolaridad sigue siendo la misma.
ICF: líquido intracelular
ECF: líquido extracelular
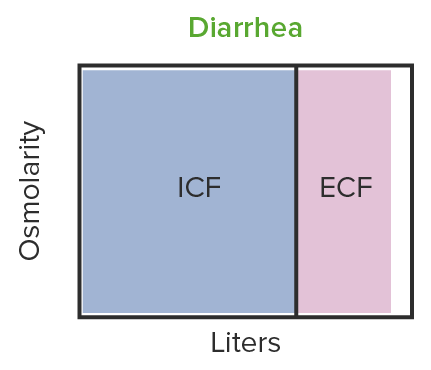
En la diarrea se observa una contracción iso-osmótica del volumen:
El líquido en la diarrea tiene la misma osmolaridad que el líquido extracelular. El volumen del líquido extracelular disminuye pero no la osmolaridad.
ICF: líquido intracelular
ECF: líquido extracelular
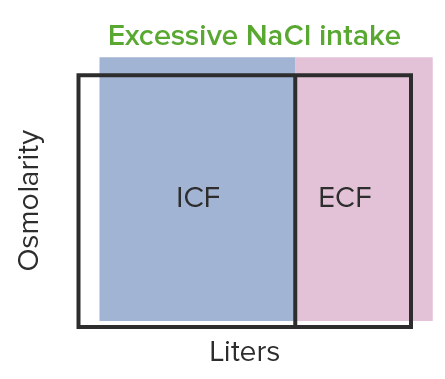
La expansión hiper-osmótica del volumen se observa en el aumento de la ingesta de NaCl:
Esto se debe a un aumento del nivel de sodio que provoca la retención de líquidos.
ICF: líquido intracelular
ECF: líquido extracelular
| Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products | Líquido intersticial | Líquido intracelular | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mOsm/L) | (mOsm/L) | (mOsm/L) | |
| Na+ | 142 | 139 | 14 |
| K+ | 4,2 | 4,0 | 140 |
| Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ | 1,3 | 1,2 | 0 |
| Mg2+ | 0,8 | 0,7 | 20 |
| Cloruro (Cl–) | 106 | 108 | 4 |
| HCO3– | 24 | 28,3 | 10 |
| HPO42–, H2PO4– | 2 | 2 | 11 |
| SO42– | 0,5 | 0,5 | 1 |
| Fosfocreatina | 45 | ||
| Carnosina | 14 | ||
| Aminoácidos | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Creatinina | 0,2 | 0,2 | 9 |
| Lactato | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,5 |
| Adenosin trifosfato | 5 | ||
| Monofosfato de hexosa | 3,7 | ||
| Glucosa | 5,6 | 5,6 | |
| Proteínas | 1,2 | 0,2 | 4 |
| Urea Urea A compound formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end product of protein catabolism and constitutes about one half of the total urinary solids. Urea Cycle | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Otros | 4,8 | 3,9 | 10 |
| mOsm/L totales | 299,8 | 300,8 | 301,2 |
| Actividad osmolar corregida | 282,0 | 281,0 | 281,0 |