La colestasis en neonatos y lactantes pequeños es una hiperbilirrubinemia conjugada en los 1ros 3 meses de vida debido a una excreción de bilis alterada. Las malformaciones de las vías biliares que involucran la vesícula biliar y el conducto biliar se agrupan en colangiopatías obliterantes quísticas y no quísticas, la más común de las cuales es la atresia biliar. Las causas menos comunes incluyen el síndrome genético de Alagille, causas infecciosas y trastornos metabólicos. La presentación clínica es con ictericia obstructiva. El ultrasonido y la colangiopancreatografía con resonancia magnética son herramientas de diagnóstico útiles y, a veces, se realiza un diagnóstico prenatal con ultrasonido. Las causas quísticas frecuentemente requieren cirugía para corregir el defecto y permitir el crecimiento normal del niño. El trasplante de hígado puede ser necesario en casos de atresia biliar con hipertensión portal.
Last updated: Feb 16, 2026
La colestasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum recién nacidos y lactantes pequeños es una hiperbilirrubinemia conjugada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria 1ros 3 meses de vida debido a una excreción de bilis alterada.
Las malformaciones de las vías biliares que involucran la vesícula biliar y el conducto biliar se agrupan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum colangiopatías obliterantes quísticas y no quísticas, la más común de las cuales es la atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) biliar. Las causas menos comunes incluyen el síndrome genético de Alagille, causas infecciosas y trastornos metabólicos.
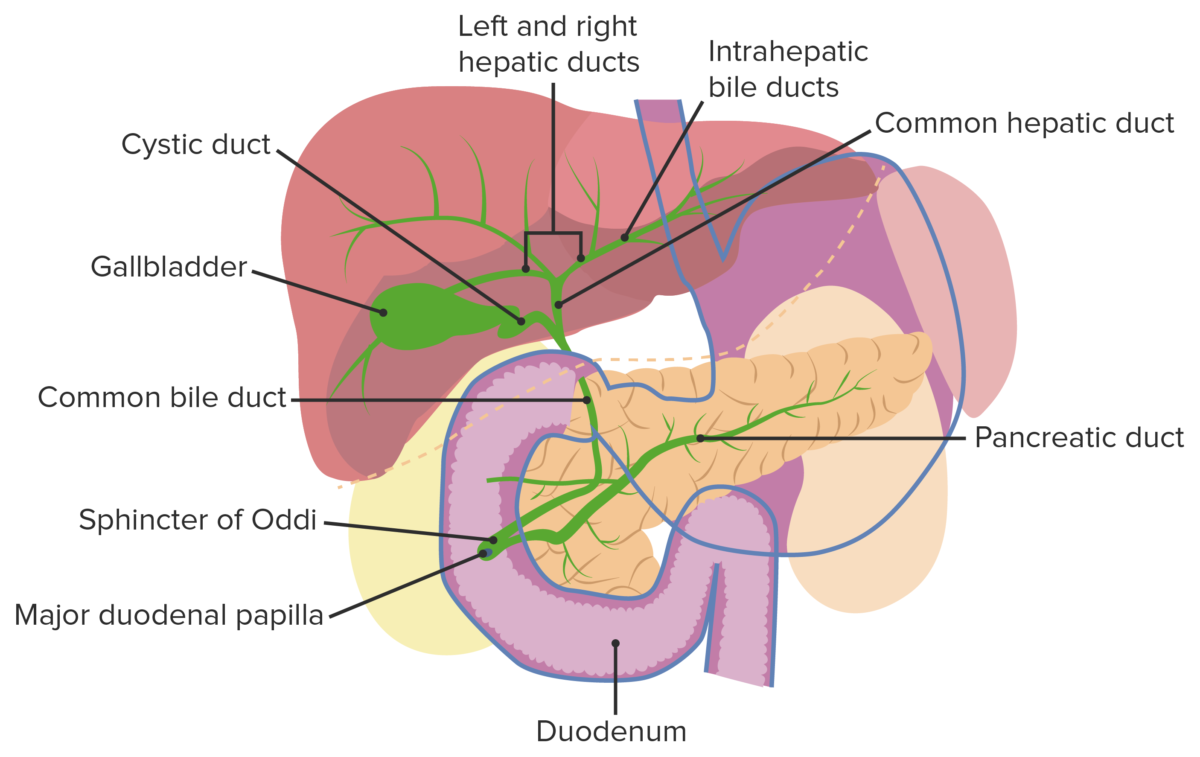
Anatomía normal del tracto biliar
Imagen por Lecturio.La atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) biliar es una obliteración idiopática, progresiva y fibrótica del árbol biliar extrahepático que se presenta con obstrucción biliar dentro de los LOS Neisseria 1ros 3 meses de vida.
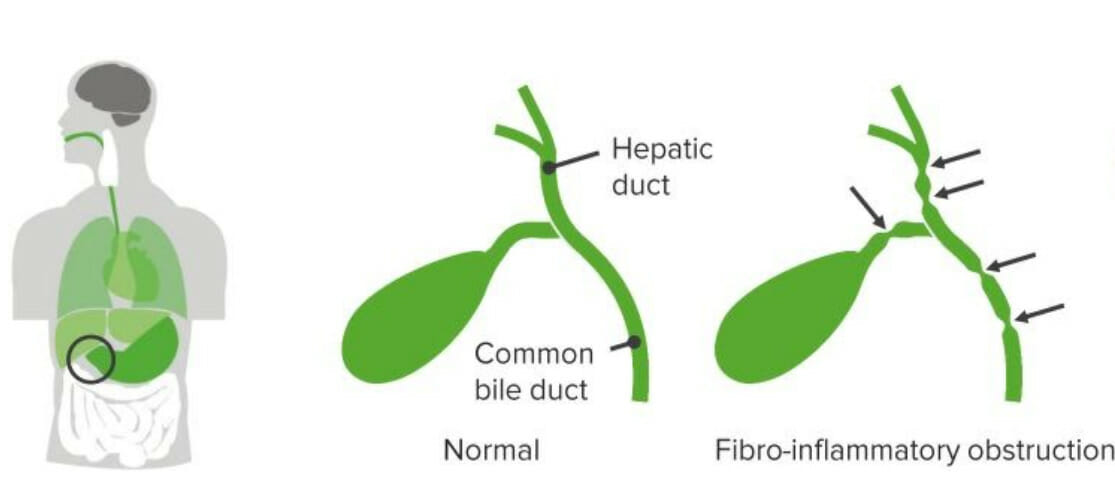
Atresia biliar
Imagen por Lecturio.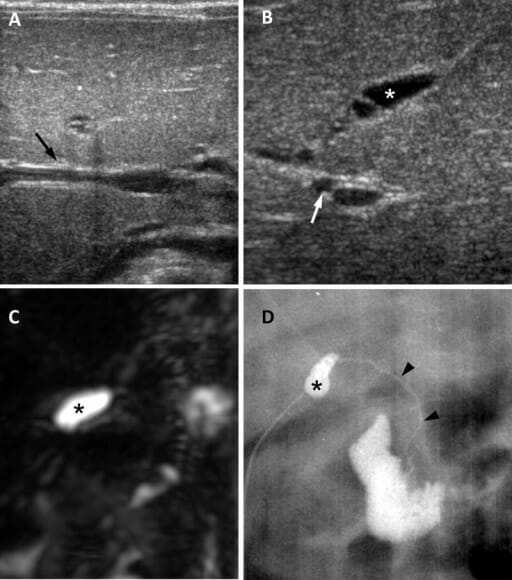
Atresia de vías biliares en una niña de 65 días:
A: El ultrasonido en el plano transversal muestra un signo de cordón triangular negativo (flecha).B: Imagen por ultrasonido en plano subcostal oblicuo que muestra vesícula biliar atrésica de 0,8 cm (asterisco) y arteria hepática dilatada de 1,5 mm (flecha).
C: Imagen de colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética tridimensional que muestra ausencia de un árbol biliar extrahepático visible y una vesícula biliar pequeña (asterisco).
D: La colangiografía quirúrgica muestra una vesícula biliar pequeña (asterisco) y un conducto biliar común permeable pero extremadamente hipoplásico (puntas de flecha).
Imagen: “Biliary atresia in a 65-day-old girl” por Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0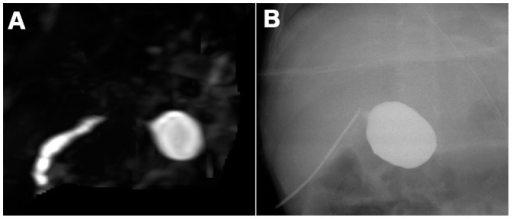
A: Atresia biliar en una lactante de 90 días. La colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética tridimensional no muestra los conductos biliares extrahepáticos a excepción del conducto cístico biliar común.
B: Colangiografía intraoperatoria en el mismo lactante.
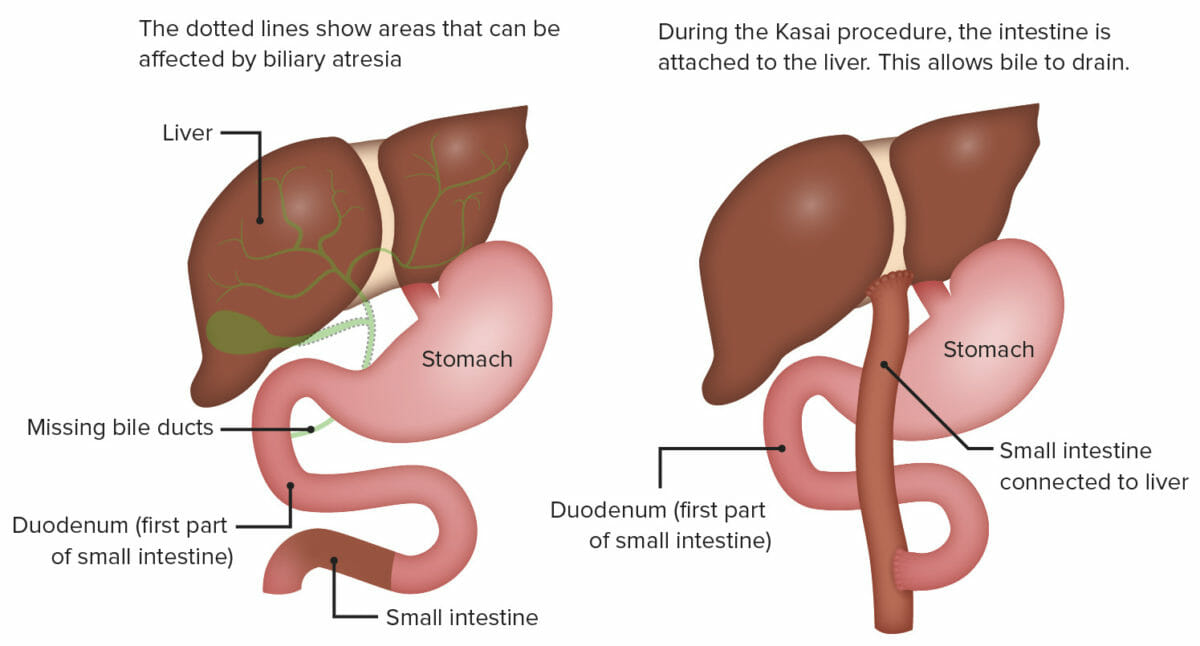
Portoenterostomía (procedimiento de Kasai):
Esta cirugía consiste en exponer la porta hepática mediante la escisión radical de todo el tejido del conducto biliar hasta la cápsula hepática y unir un asa de yeyuno en Y de Roux a la cápsula hepática expuesta por encima de la bifurcación de la vena porta.
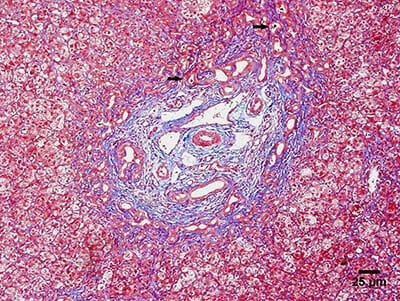
Microfotografía que muestra los principales hallazgos histológicos de la atresia biliar:
Biopsia hepática que muestra proliferación ductular y tapones biliares (flechas).
El síndrome de Alagille es un trastorno genético caracterizado por una escasez de conductos biliares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado, lo que lleva a la colestasis. Este síndrome también afecta a otros órganos.
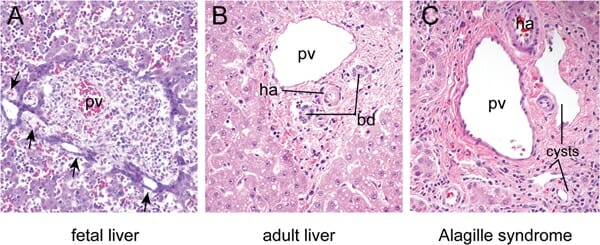
A: Hígado fetal a las 16 semanas de desarrollo que muestra dilataciones focales (flechas) en los precursores de células epiteliales biliares que rodean la vena porta (pv, por sus siglas en inglés).
B: Hígado maduro que muestra los conductos biliares (bd, por sus siglas en inglés) y la arteria hepática (ha, por sus siglas en inglés) incluidos en el mesénquima periportal en una disposición característica conocida como “tríada portal”. Hepatocitos dispuestos en cuerdas rodean la tríada portal.
C: La región de la tríada portal de un individuo con síndrome de Alagille muestra quistes ductales en lugar de conductos biliares normales debido a defectos en la remodelación de la placa ductal.
Los LOS Neisseria quistes de colédoco son anomalías congénitas de los LOS Neisseria conductos biliares que causan agrandamiento anormal y obstrucción de los LOS Neisseria conductos biliares intrahepáticos y/o extrahepáticos.
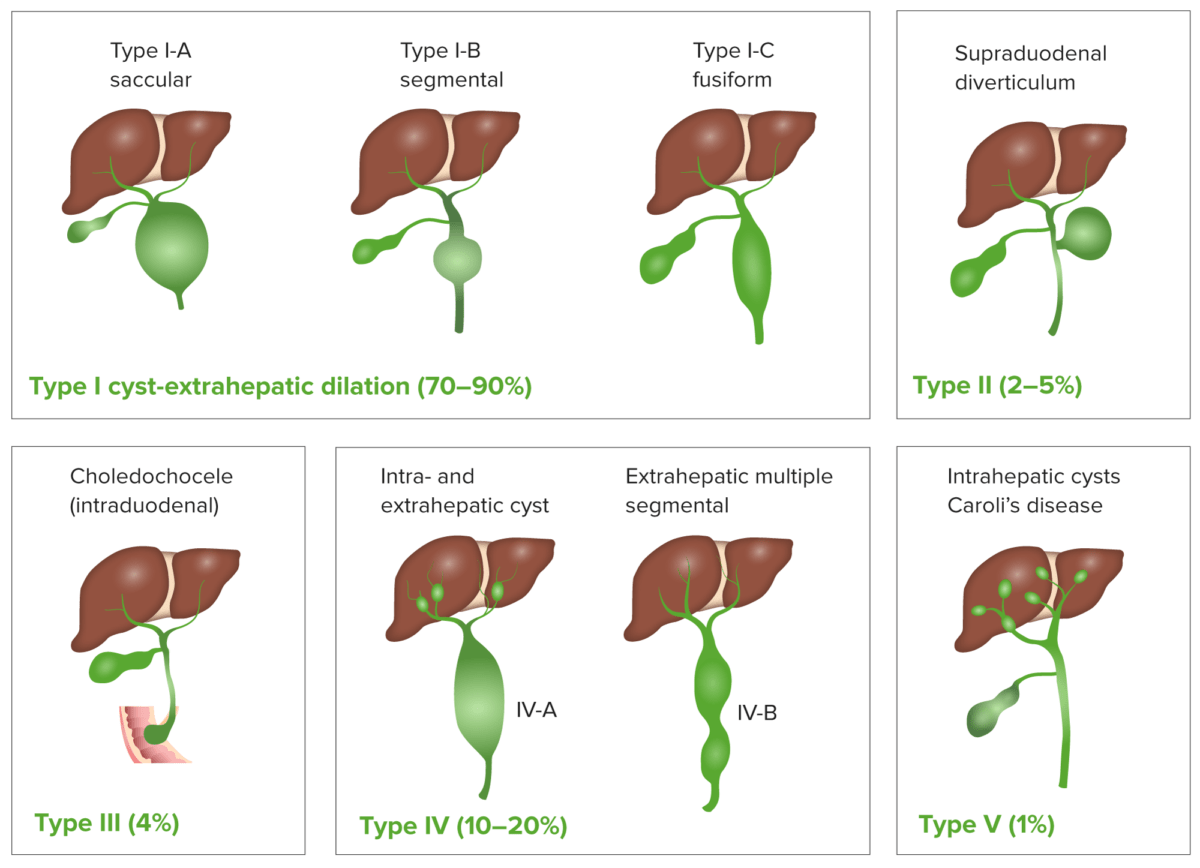
Clasificación de los quistes de colédoco
Imagen por Lecturio.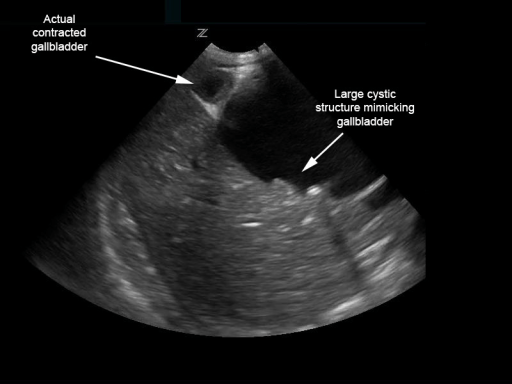
Quiste de colédoco biliar que simula una vesícula biliar distendida con múltiples cálculos:
Sin embargo, la vesícula biliar contraída está adyacente.
Imagen: “Biliary choledochal cyst” por University of Massachusetts, Department of Emergency Medicine, Boston. Licencia: CC BY 4.0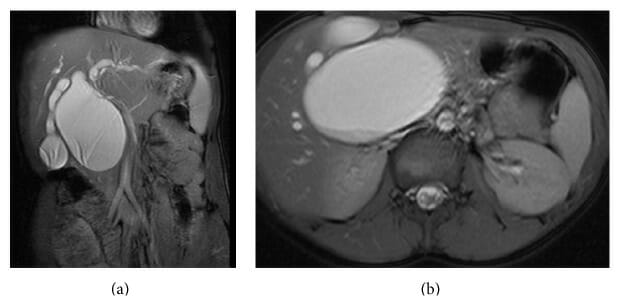
(a): Colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética que muestra un quiste de colédoco sacular tipo I-A.
(b): Colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética (sección transversal) que muestra un gran quiste de colédoco sacular tipo I-A.
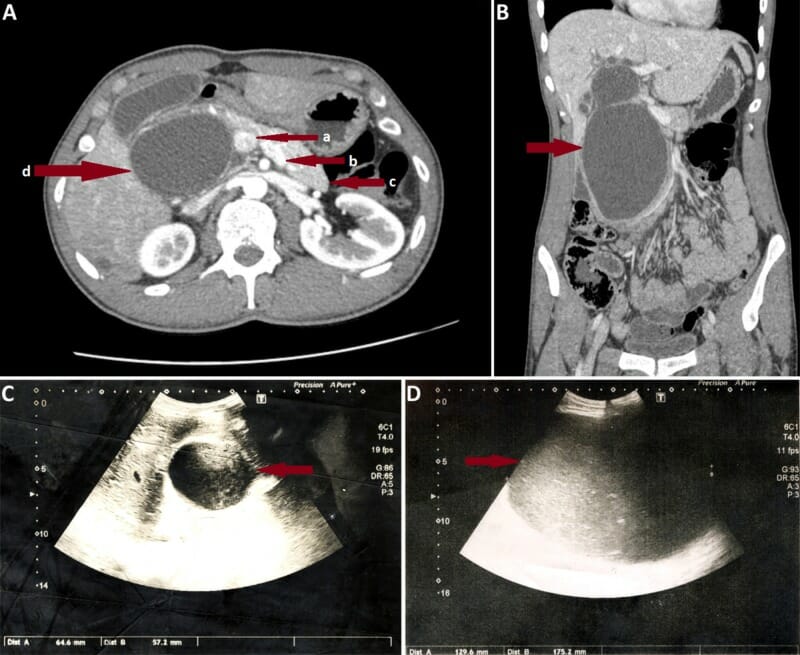
A: Corte coronal de TC abdominal en un individuo con un quiste de colédoco tipo I grande. Las flechas rojas muestran la vena porta (a), vena esplénica (b), cuerpo y cola del páncreas (c), y un quiste de colédoco gigante (d), que oblitera la cabeza pancreática.
B: TC axial del mismo individuo.
C: Imagen por ultrasonido en el mismo individuo el día del ingreso. Obsérvese el rápido aumento del tamaño del quiste observado el 7mo día de ingreso (D).
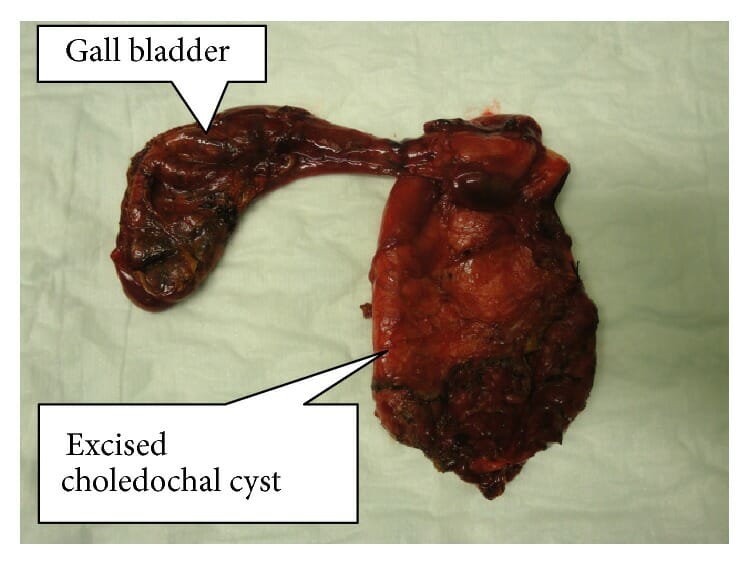
Muestra resecada de un quiste de colédoco completamente extirpado con la vesícula biliar
Imagen: “Resected specimen of completely excised choledochal cyst with gall bladder” por Norman Oneil Machado et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0