La cefalea tensional es el más común de las cefaleas primarias y uno de los LOS Neisseria trastornos más comunes que se presentan para evaluación médica a nivel mundial. Las cefaleas tensionales generalmente se describen como bilaterales, no-pulsátiles y de gravedad leve a moderada. No hay aura Aura Reversible neurological phenomena that often precede or coincide with headache onset. Migraine Headache u otras características asociadas. El diagnóstico es clínico, a menudo autodiagnosticado por el paciente o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el entorno de atención primaria. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum analgésicos abortivos, como AINE y aspirina para ataques aislados, y medidas preventivas, como cambios de comportamiento, biorretroalimentación y administración preventiva de medicamentos para ataques más crónicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una cefalea tensional se define por las siguientes características:
Tres cefaleas primarias:
Tres subtipos de cefalea tensional:
La fisiopatología de la cefalea tensional es multifactorial, pero los LOS Neisseria mecanismos precisos se desconocen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida. Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos del dolor Dolor Inflammation son dinámicos y varían de un individuo a otro.
Activación de los LOS Neisseria nociceptores miofasciales debido a la exposición a estímulos ambientales nocivos:
Sensibilización de los LOS Neisseria nociceptores miofasciales:
Sensibilización de las vías del dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sistema nervioso central:
Se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia demostrado que los LOS Neisseria factores genéticos desempeñan un papel en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la patogenia de la cefalea tensional crónica.
La cefalea tensional puede presentarse con una amplia variación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum frecuencia e intensidad entre individuos, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mismo individuo a lo largo del tiempo y de un ataque a otro en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mismo individuo.
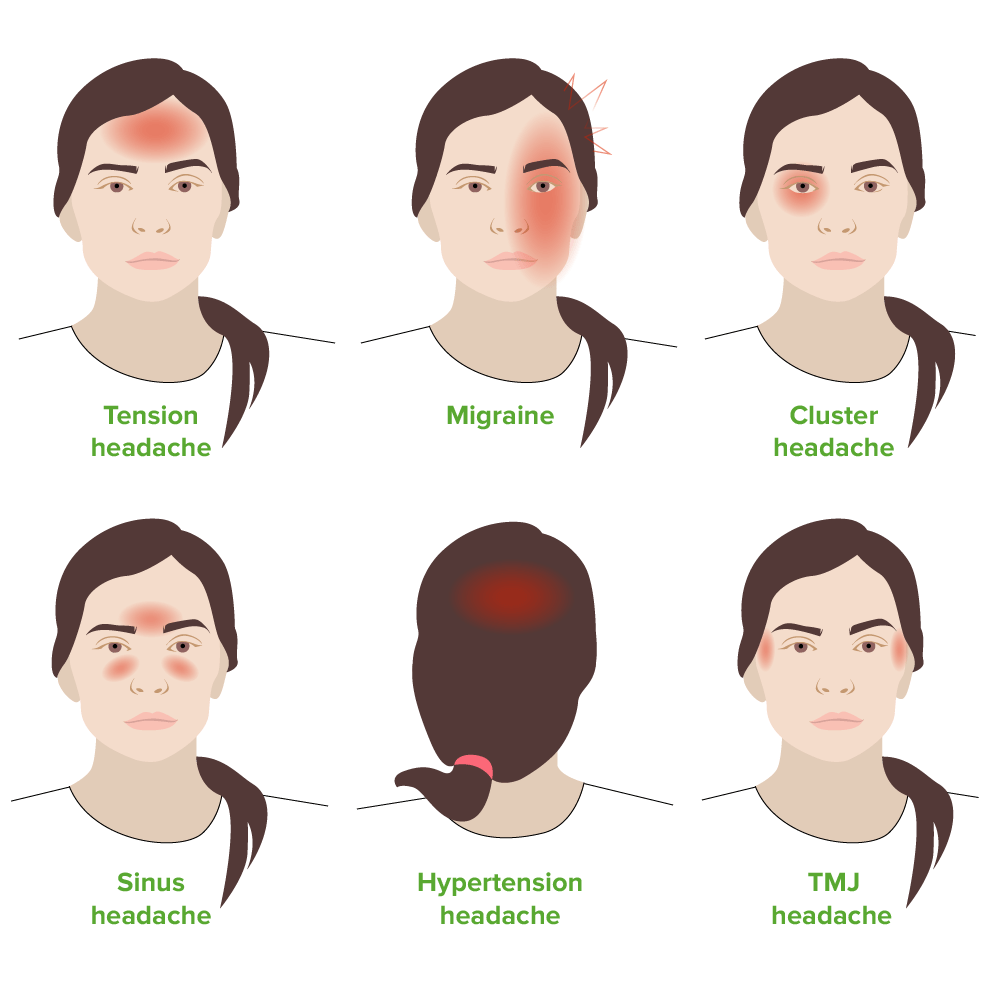
Ilustración que muestra las localizaciones del dolor para los diferentes tipos de cefalea
ATM: articulación temporomandibular
La evaluación de laboratorio está indicada solo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria siguientes casos:
Las pruebas de laboratorio deben ser específicas para la(s) causa(s) subyacente(s):
La imagenologia están indicadas solo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria siguientes casos:
Modalidades de imagenologia:
El tratamiento de la cefalea tensional suele ser autodirigido por los LOS Neisseria pacientes que usan analgésicos de venta libre sin buscar atención médica ni indicaciones. El médico de atención primaria debe ser capaz de diagnosticar y tratar la cefalea tensional sin necesidad de consultar a un especialista.