La apendicectomía es un procedimiento quirúrgico invasivo realizado con el objetivo de resecar y extraer el apéndice vermiforme a través de un abordaje abierto o laparoscópico. La indicación más común es la apendicitis aguda, por lo que las apendicectomías suelen realizarse de manera urgente. Es uno de los LOS Neisseria procedimientos abdominales de emergencia más frecuentes. Puede asociarse a una serie de complicaciones postoperatorias; sin embargo, la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes evolucionan muy bien y se recuperan rápidamente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La apendicectomía se refiere a la extirpación quirúrgica del apéndice vermiforme.
Es importante revisar el desarrollo de los LOS Neisseria órganos abdominales para entender la ubicación del apéndice dentro de la cavidad abdominal y sus posibles variantes.
Es importante revisar la anatomía del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy para localizar y reconocer más fácilmente el ciego y el apéndice dentro de la cavidad abdominal durante la cirugía.
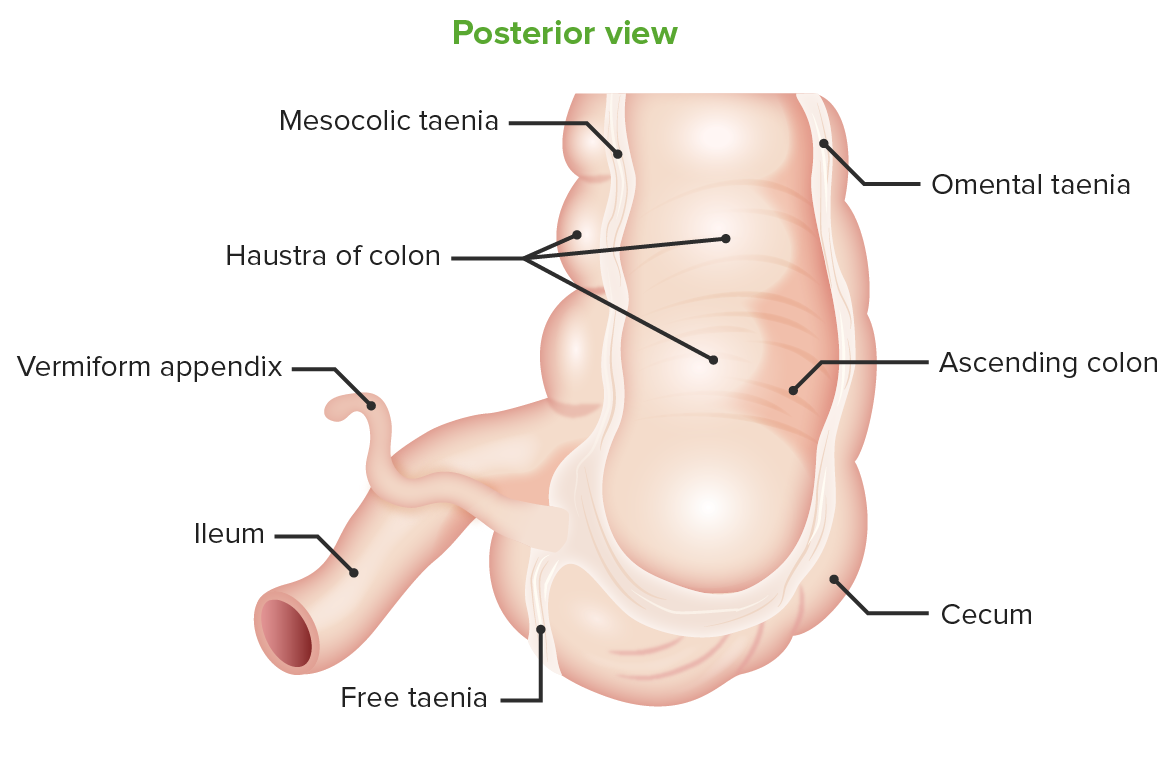
Vista posterior del ciego:
Ubicación del apéndice vermiforme en la confluencia de las tenias
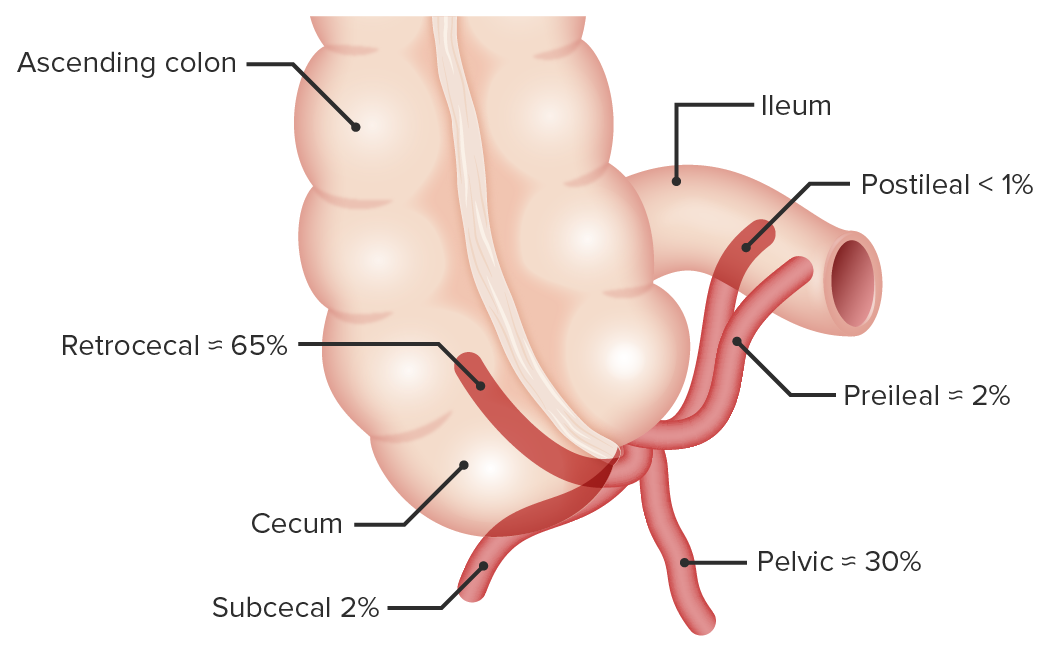
Variantes de localización del apéndice vermiforme
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0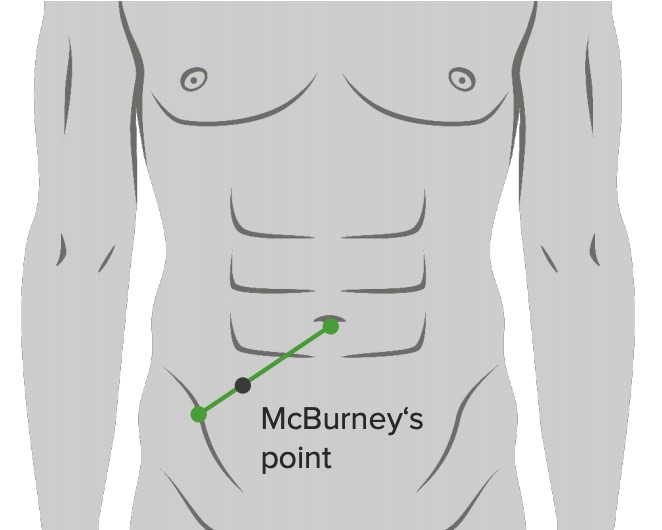
Localización del punto de McBurney: 2/3 desde el ombligo en una línea recta que va desde el ombligo hasta la espina ilíaca anterosuperior
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Se consideran aceptables tanto el abordaje abierto como el laparoscópico. La elección depende de la experiencia del cirujano y la preferencia del paciente. Las apendicectomías laparoscópicas se asocian a estancias hospitalarias ligeramente más cortas y a mejores puntuaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la escala subjetiva de dolor Dolor Inflammation.
Apendicectomía abierta:
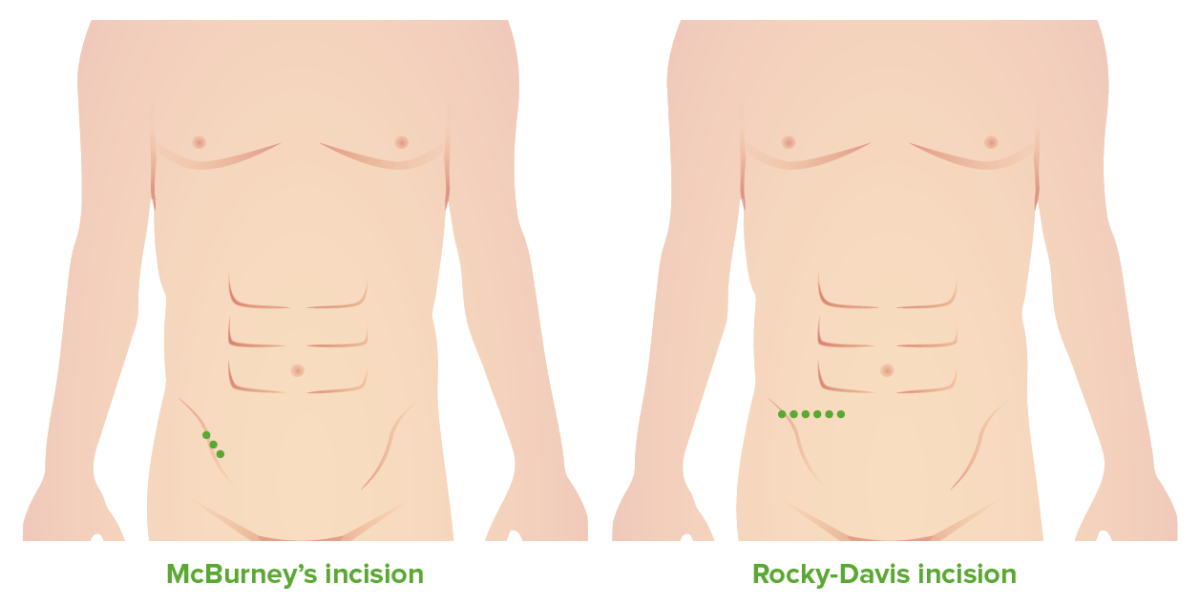
Incisiones de McBurney y Rocky-Davis
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Apendicectomía laparoscópica:
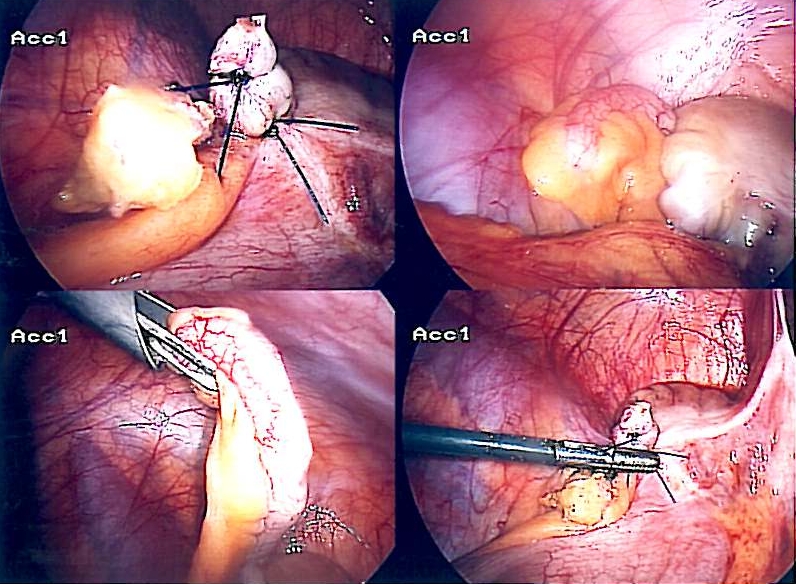
Apendicectomía laparoscópica
Imagen: “Appendix-Entfernung” por Life-of-hannes.de. License: Dominio PúblicoLavado peritoneal:
Laparotomía exploratoria:
Mujeres embarazadas: