Los LOS Neisseria amebicidas son medicamentos tóxicos para amebas como Entamoeba histolytica Entamoeba Histolytica A species of parasitic protozoa causing entamoebiasis and amebic dysentery (dysentery, amebic). Characteristics include a single nucleus containing a small central karyosome and peripheral chromatin that is finely and regularly beaded. Amebicides (el organismo causante de la amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis). Los LOS Neisseria parásitos ingresan al AL Amyloidosis tracto gastrointestinal donde los LOS Neisseria trofozoítos pueden penetrar la pared intestinal y causar una infección invasiva. Los LOS Neisseria amebicidas se clasifican según el lugar donde el medicamento es más eficaz: el lumen o los LOS Neisseria tejidos intestinales. Los LOS Neisseria amebicidas del lumen intestinal incluyen yodoquinol y paromomicina. Los LOS Neisseria amebicidas tisulares incluyen la clase de medicamentos nitroimidazol (e.g., metronidazol, tinidazol). El tratamiento de la enfermedad sintomática generalmente requiere una combinación de ambas clases.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
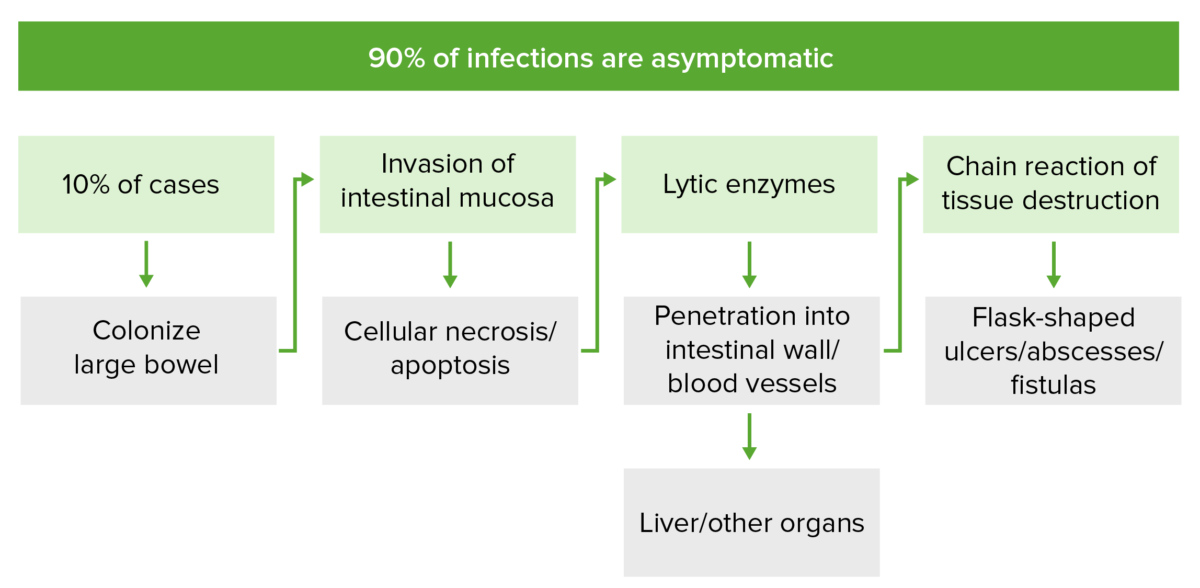
Patogénesis de la infección invasiva por Entamoeba histolytica:
En el 10% de los casos, E. histolytica coloniza la mucosa del intestino grueso e invade mediante la secreción de proteinasas y enzimas líticas. Esto provoca necrosis celular y lisis de las membranas, respectivamente. Esta cadena de eventos induce la apoptosis de las células de la mucosa y rompe las uniones estrechas entre las células, lo que permite la formación de úlceras en forma de botella, abscesos y fístulas. La invasión puede alcanzar el sistema venoso portal, a través del cual E. histolytica puede diseminarse a otros órganos.
Se prescribe una combinación de amebicidas tisulares y luminales para tratar la amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis.
Amebicidas luminales:
Amebicidas tisulares:
El yodoquinol se utilizaba para tratar la amebiasis Amebiasis Amebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Transmission is through the fecal-oral route or by consumption of contaminated food and water. Most patients infected with E. histolytica are asymptomatic, but about 10% may develop dysentery. Entamoeba spp./Amebiasis intestinal. Ya no está disponible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria Estados Unidos a partir de 2025 debido a la aplicación de medidas de la FDA contra productos no aprobados.
El yodoquinol está contraindicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con alergia o intolerancia al AL Amyloidosis yodo.
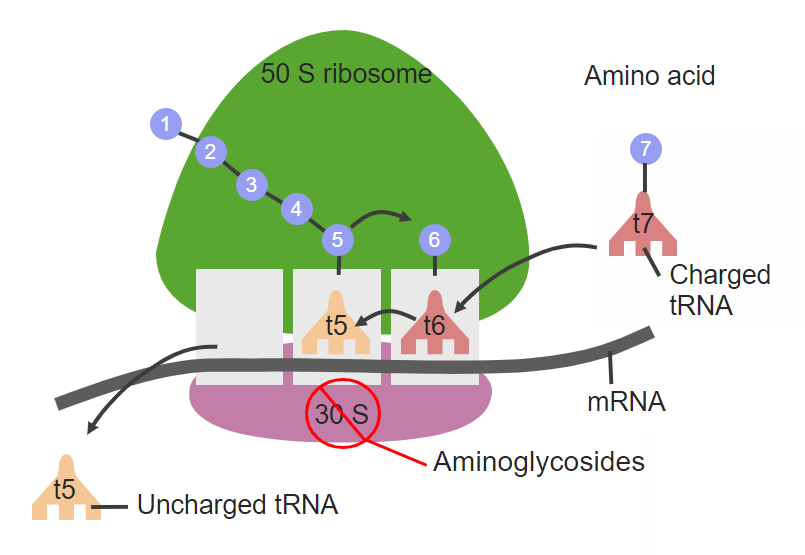
El sitio de acción de los aminoglucósidos, que se dirigen a la subunidad ribosomal 30S
tRNA: ARN de transferencia (por sus siglas en inglés)
mRNA: ARN mensajero (por sus siglas en inglés)
Se debe tener precaución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con:
Además de las infecciones por bacterias anaeróbicas, los LOS Neisseria nitroimidazoles Nitroimidazoles Nitroimidazoles are prodrugs composed of an imidazole ring with an attached nitro group. Nitroimidazoles are reduced within susceptible microorganisms, leading to free radical formation and disruption of DNA integrity. Nitroimidazoles se pueden usar para: