La evaluación abdominal y cardíaca con ultrasonido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estado de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock ( ACES ACES Abdominal and cardiac evaluation with sonography in shock (ACES) and rapid ultrasound for shock and hypotension (RUSH) are point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examinations indicated in cases of nontraumatic, undifferentiated hypotension, or shock. ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y el ultrasonido rápido para shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock e hipotensión ( RUSH RUSH Abdominal and cardiac evaluation with sonography in shock (ACES) and rapid ultrasound for shock and hypotension (RUSH) are point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examinations indicated in cases of nontraumatic, undifferentiated hypotension, or shock. ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) son estudios de ultrasonido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el punto de atención ( POCUS POCUS Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) indicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de hipotensión indiferenciada o shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hipotensión, el diagnóstico oportuno y el tratamiento orientado a objetivos son esenciales para obtener resultados óptimos y conducir a una disminución de la mortalidad. Tanto el protocolo ACES ACES Abdominal and cardiac evaluation with sonography in shock (ACES) and rapid ultrasound for shock and hypotension (RUSH) are point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examinations indicated in cases of nontraumatic, undifferentiated hypotension, or shock. ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols como el RUSH RUSH Abdominal and cardiac evaluation with sonography in shock (ACES) and rapid ultrasound for shock and hypotension (RUSH) are point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examinations indicated in cases of nontraumatic, undifferentiated hypotension, or shock. ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols examinan las cavidades torácica y abdominal mediante ultrasonido para evaluar rápidamente las causas reversibles del shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock y aumentar las probabilidades de un diagnóstico preciso. Cada uno de estos protocolos combinan muchos de los LOS Neisseria mismos elementos centrales del ultrasonido, que difieren principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la secuencia de la evaluación.
Last updated: Jan 26, 2026

Conceptos de imagenología del ultrasonido
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0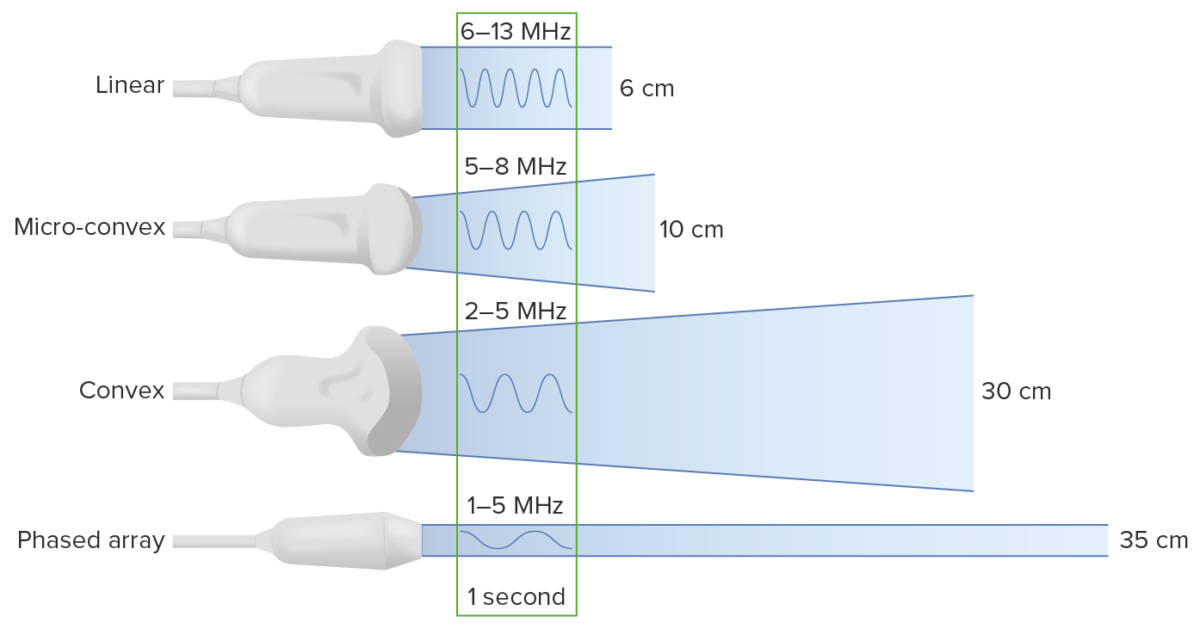
Tipos de transductores:
Se debe tener en cuenta que la disminución de la frecuencia aumenta la profundidad a la que viaja la onda de ultrasonido. Sin embargo, esto viene a costa de la resolución de la imagen.
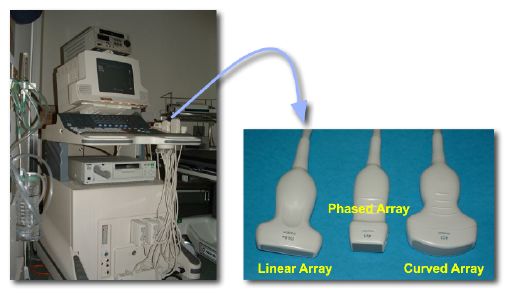
Imagen que muestra la máquina de ultrasonido y las diferentes sondas
Imagen : “Photos of a sonography system and typical transducers.” por Kieran Maher Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa evaluación abdominal y cardíaca con ultrasonido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estado de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock es un examen POCUS POCUS Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) utilizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de hipotensión indiferenciada realizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum urgencias.

Protocolo de evaluación abdominal y cardíaca con ultrasonido en estado de shock (ACES):
1: 1 o más ventanas cardíacas
2: Ventana de la vena cava inferior
3: Tamizaje de la aorta abdominal
4: Derecha y 5: Ventanas del flanco izquierdo para líquido pleural y peritoneal
6: Ventana pélvica para el tamaño de la vejiga y el líquido libre
| Tipo de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock | Estructuras cardíacas | VCI | Aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy | Líquido peritoneal/sangre | Líquido pleural/sangre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Séptico | VI hiperdinámico o hipodinámico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock tardía | VCI estrecha/colapsada | Normal | Sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock quirúrgica/ginecológica | Neumonía, empiema |
| Cardiogénico | VI hipodinámico/↓ FE | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Hipovolémico | VI hiperdinámico | VCI estrecha/colapsada | AAA AAA An aortic aneurysm is the abnormal dilation of a segment of the aorta. Abdominal aortic aneurysm is the most common aortic aneurysm, occurring frequently in the infrarenal area. Most aneurysms are asymptomatic, but can cause compression of surrounding structures or rupture, which is a life-threatening emergency. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms | Ruptura esplénica espontánea, víscera perforada, hemorragia ginecológica | Normal |
| Obstructivo (cardíaco) | Derrame pericárdico, taponamiento cardíaco | VCI variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Obstructivo (pulmonar) | VD dilatado, ↑ relación VI/VD | VCI dilatada | Normal | Normal | Normal |
El ultrasonido rápido para shock e hipotensión es un protocolo de examen POCUS que se enfoca en la evaluación del corazón y los vasos principales que se divide en 3 pasos: “bomba”, “depósito” y “tuberías”.

Colocación de la sonda para el examen rápido de ultrasonido para shock e hipotensión (RUSH)
Imagen por Lecturio.| Tipo de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock | Bomba | Depósito | Tubería |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiogénico | VI hipodinámico, ↓ FE, corazón dilatado | VCI dilatada, venas yugulares distendidas, cohetes pulmonares, líquido pleural, líquido peritoneal | Normal |
| Hipovolémico | VI hiperdinámico, tamaño pequeño de las cámaras | VCI estrecha, venas yugulares planas, líquido peritoneal, líquido pleural | Normal |
| Obstructivo | VI hiperdinámico, derrame pericárdico, taponamiento cardíaco, distensión del VD, trombo cardíaco | VCI dilatada, venas yugulares distendidas, ausencia de deslizamiento pulmonar (neumotórax) | TVP |
| Distributivo | VI hiperdinámico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock aguda, VI hipodinámico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock tardía | VCI normal/pequeña ( sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock aguda), líquido peritoneal ( sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock), líquido pleural ( sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock) | Normal |