A síndrome de Lynch, também chamada cancro colorretal hereditário sem polipose (HNPCC, pela sigla em inglês), é a síndrome de cancro de cólon hereditária mais comum e acarreta um risco significativamente aumentado de cancro do endométrio e outras malignidades. A síndrome de Lynch tem um padrão hereditário autossómico dominante que envolve variantes patogénicas num dos genes de reparação mismatch (MMR, pela sigla em inglês) ou molécula de adesão celular epitelial (EpCAM, pela sigla em inglês). O diagnóstico é feito por testes genéticos nos doentes índice e seus familiares. O tratamento consiste em rastreio precoce de indivíduos com genes MMR defeituosos, bem como colectomia total, caso seja descoberta neoplasia colorretal. A histerectomia profilática associada à salpingo-ooforectomia é recomendada para mulheres além da idade reprodutiva.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
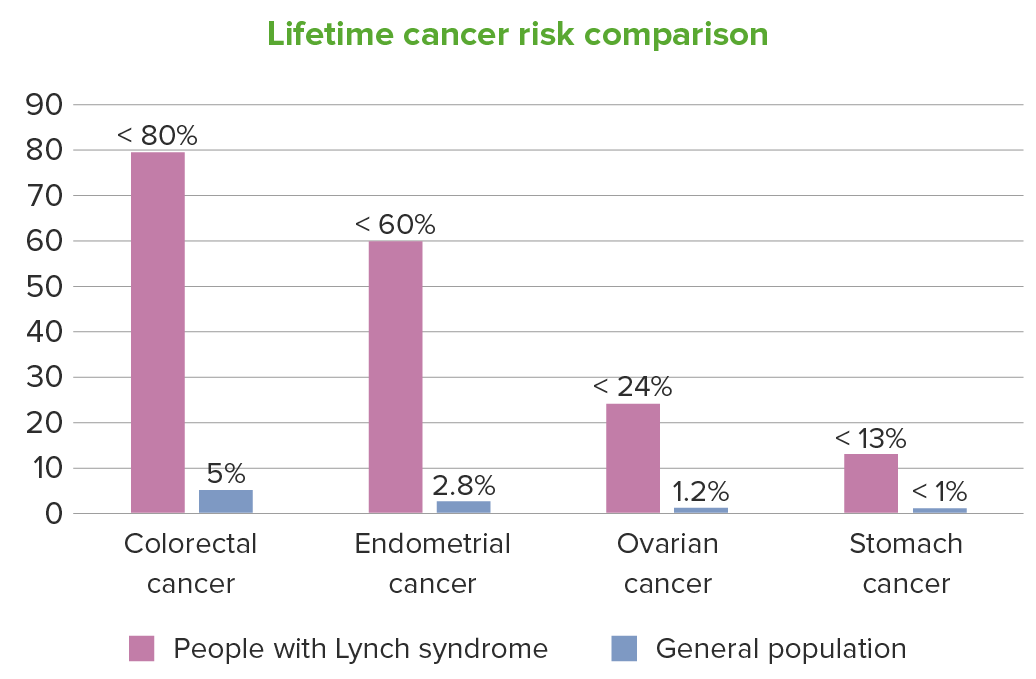
Para as pessoas com síndrome de Lynch, o risco de carcinoma ao longo da vida também é aumentado em menor grau para outras neoplasias, incluindo: renal, ureteres, bexiga, cérebro, intestino delgado, trato hepatobiliar, pâncreas, próstata e pele. Na figura, estão apresentados os intervalos dos riscos individuais.
Imagem por Lecturio.Os doentes com síndrome de Lynch herdam um ou mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome mutantes e os respetivos alelos/alelos normais; o 2.º alelo sofre mutação ou perde a função por silenciamento epigenético com tanta frequência que o padrão de transmissão é autossómico dominante.
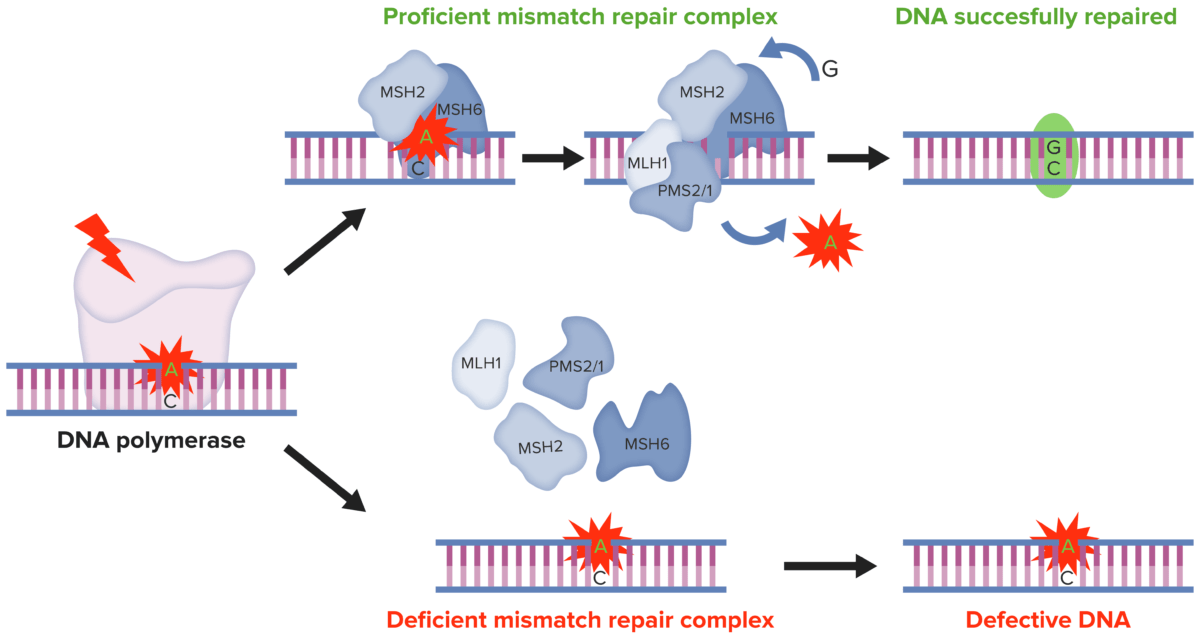
DNA MMR:
MMR do ADN:
Nas células normais, o MMR do ADN reconhece e repara as inconsistências genéticas geradas durante a replicação do mesmo. Pelo contrário, nas células tumorais com MSI, a presença de defeito no sistema MMR culmina em alterações nas sequências de ADN microssatélite, resultando na acumulação de mutações em diferentes codões genéticos.
MMR, pela sigla em inglês: reparação mismatch
MSI, pela sigla em inglês: instabilidade de microssatélites
Para o CCR:
Para o carcinoma do endométrio:
Quimioprevenção:
Imunoterapia: